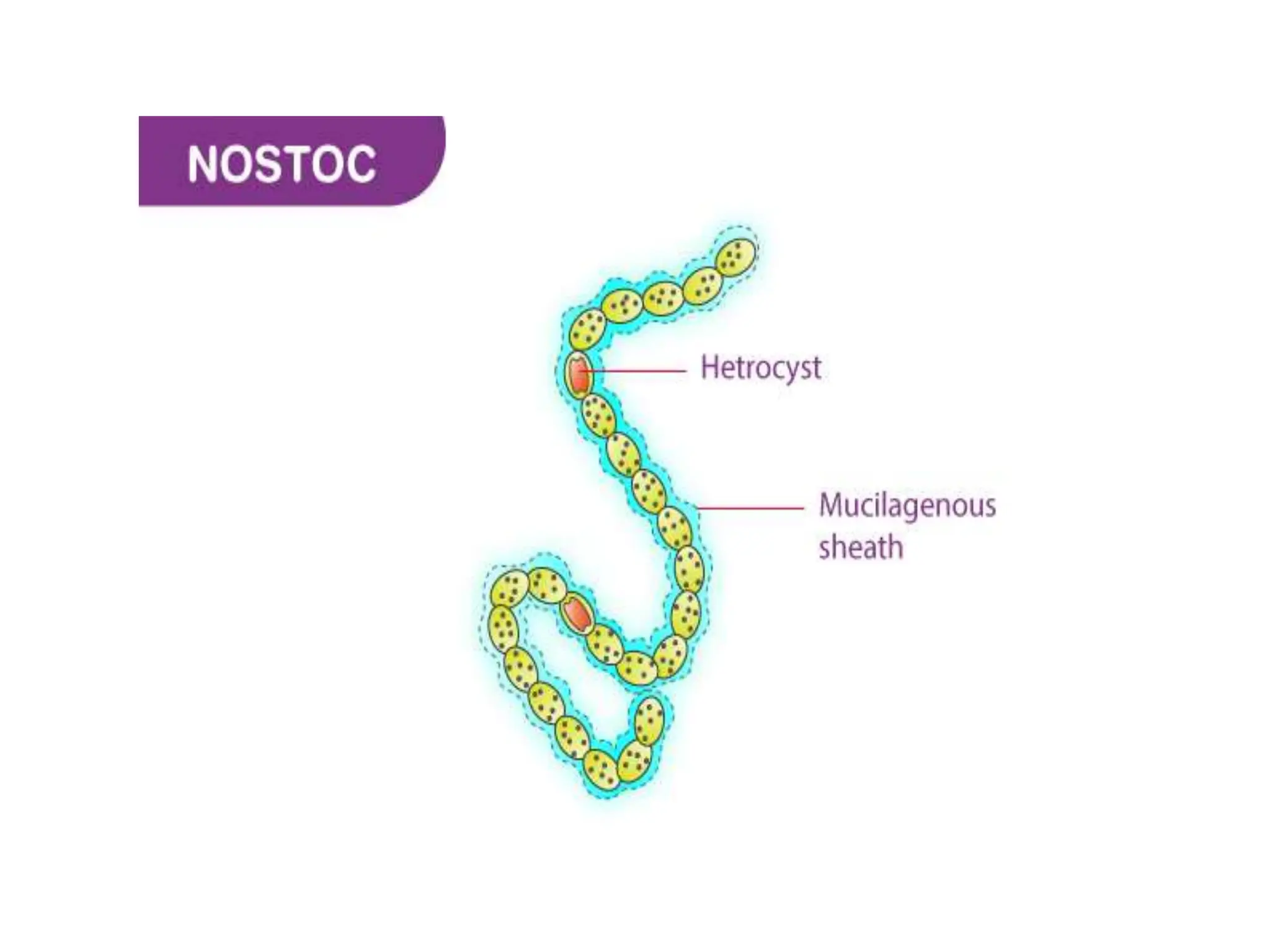
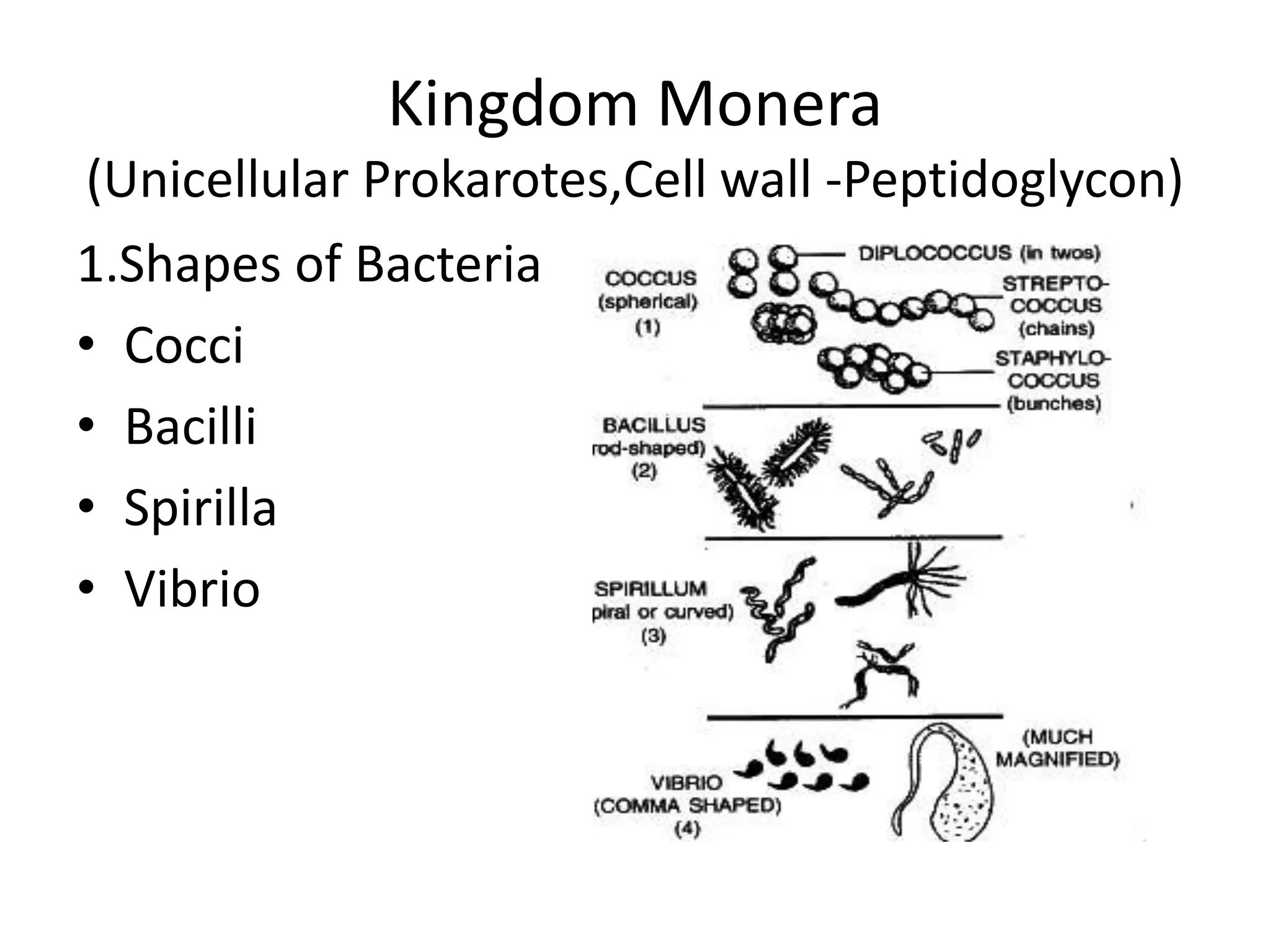
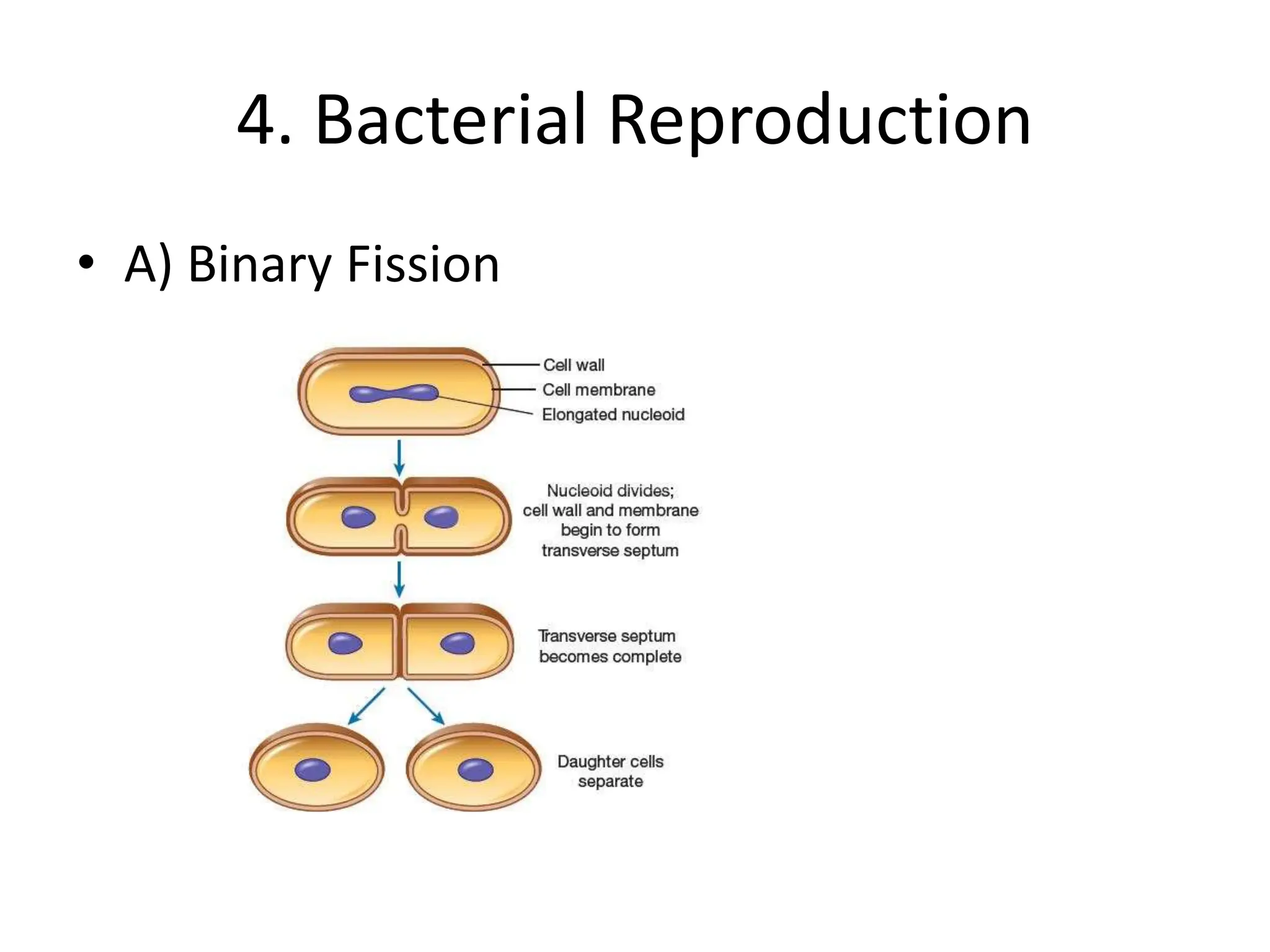
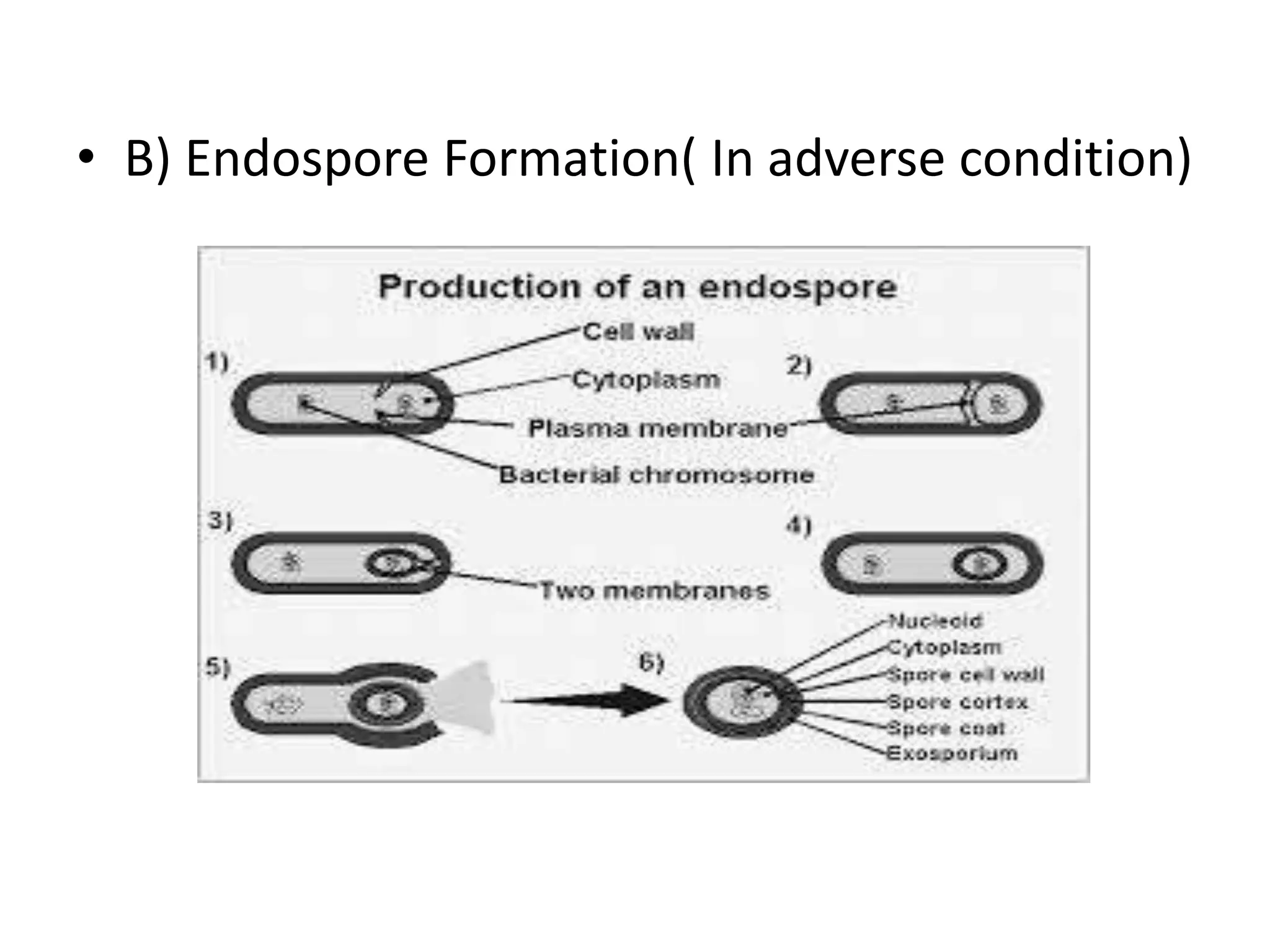
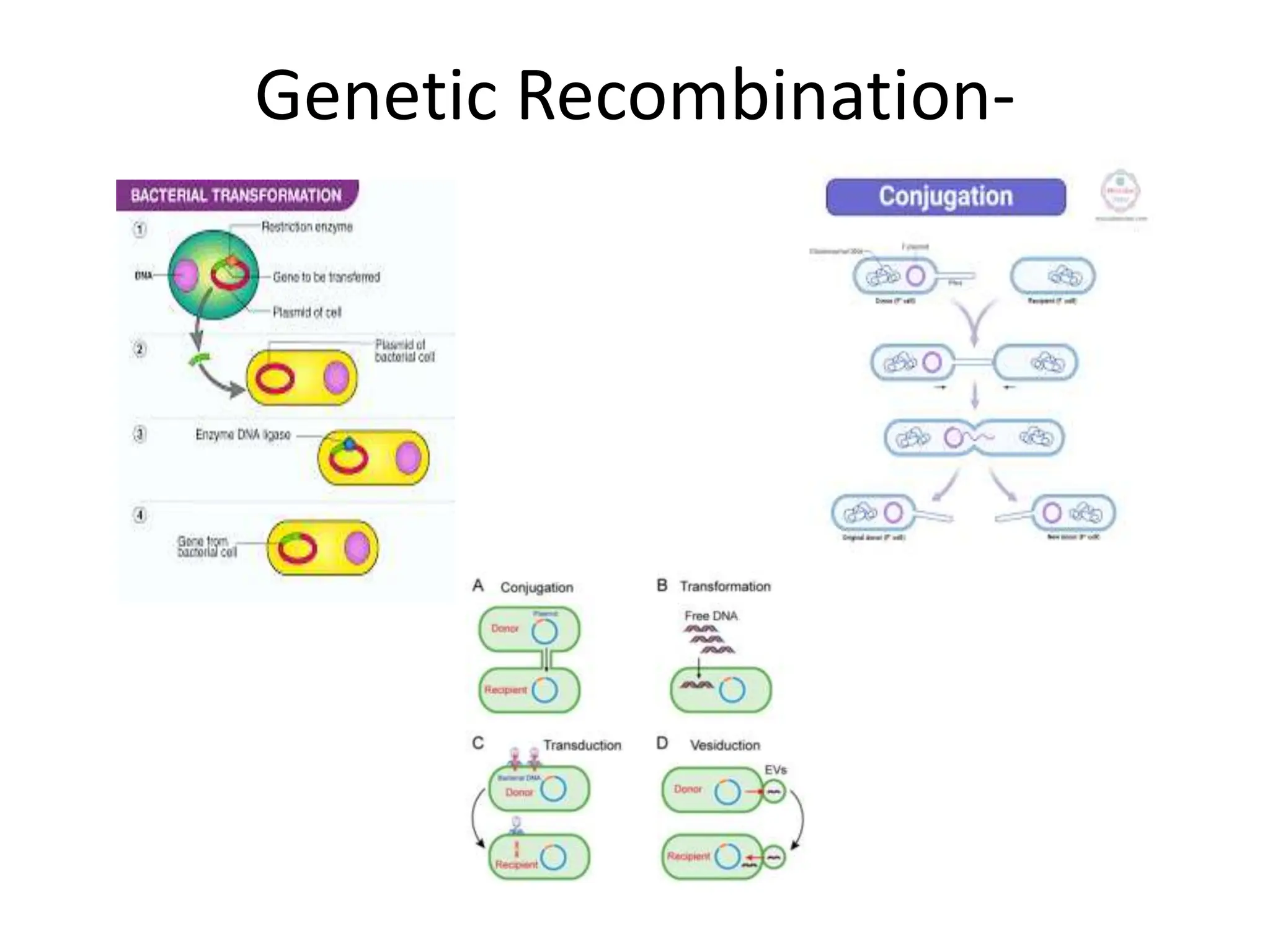
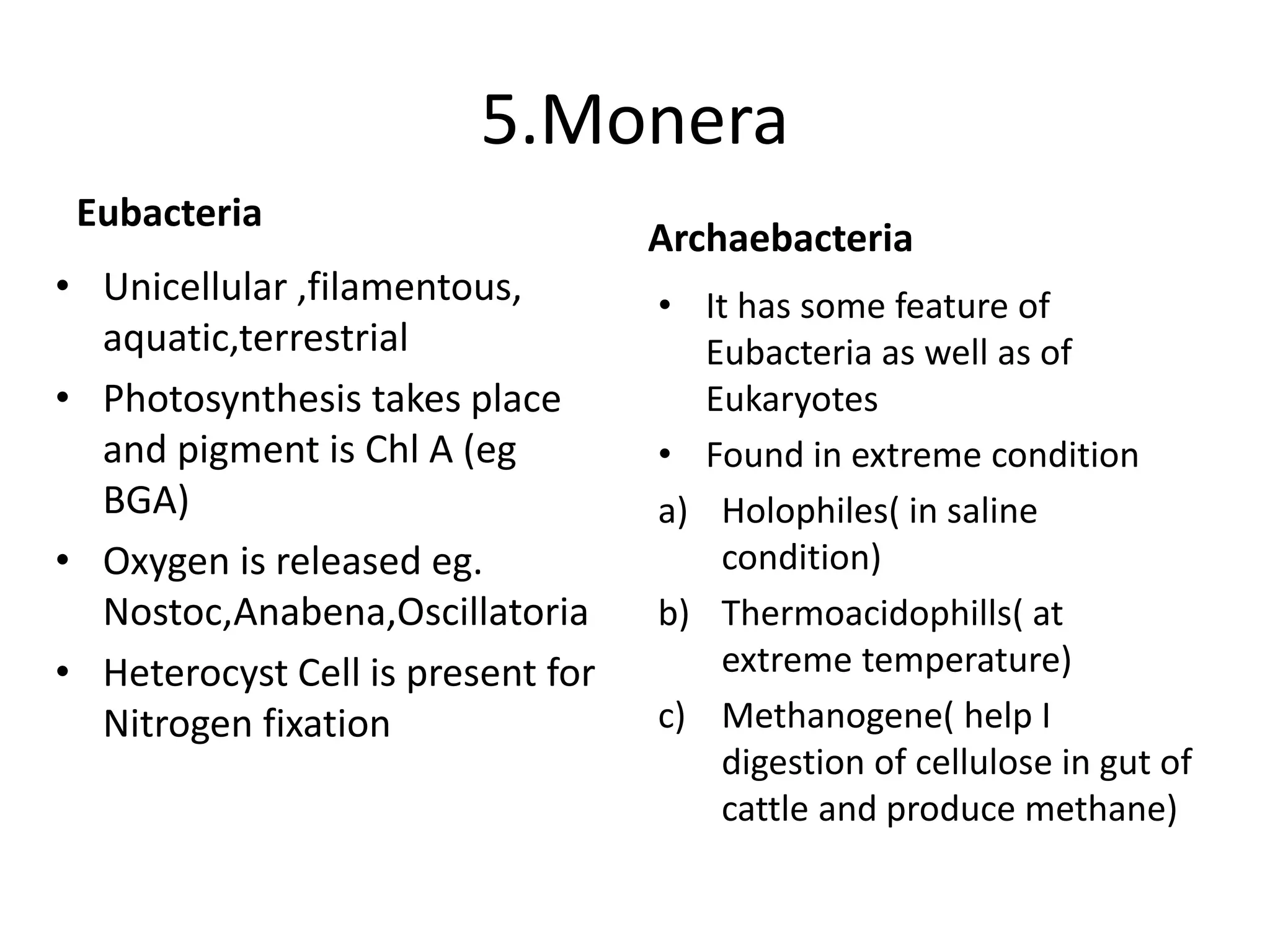
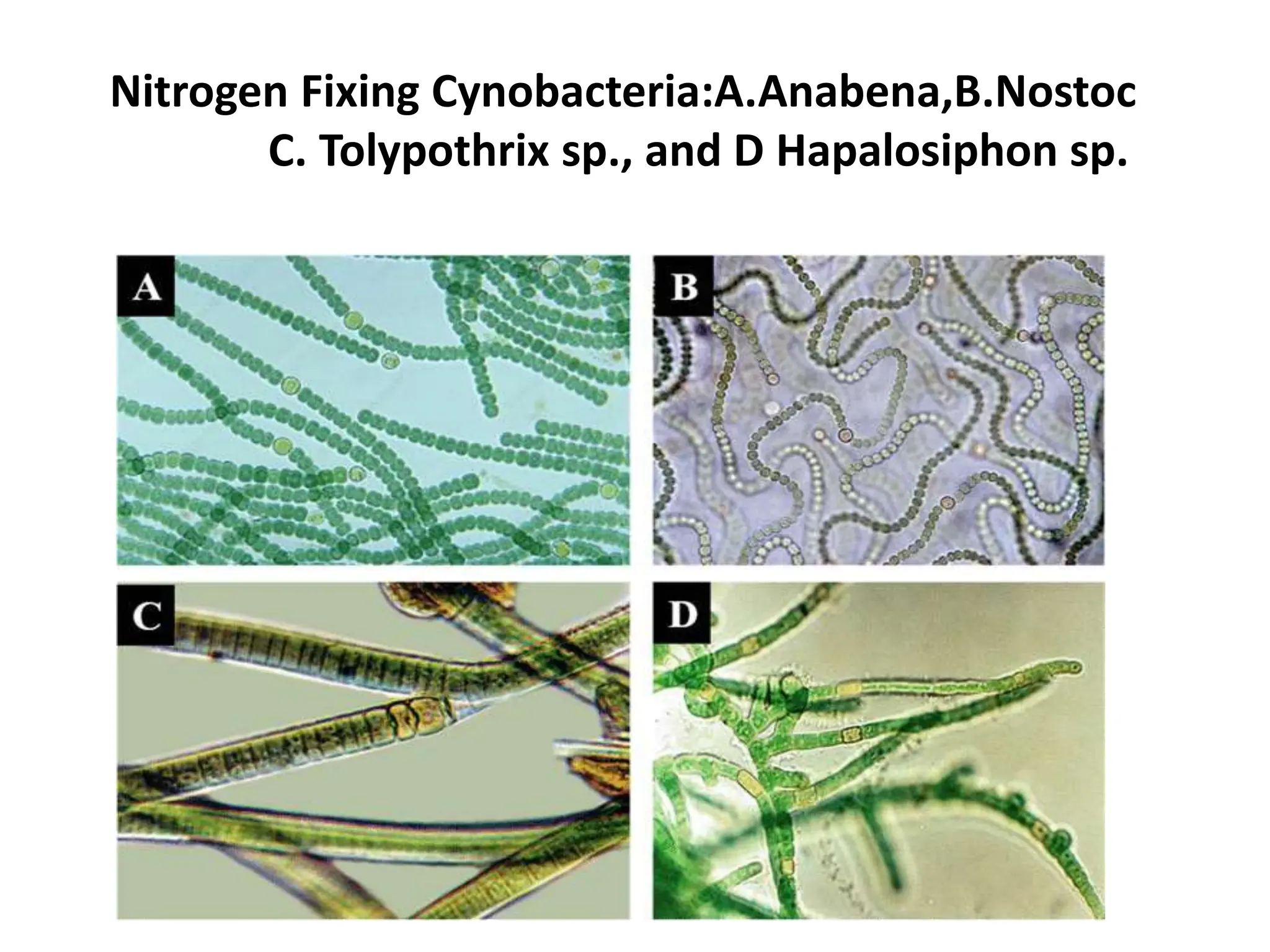
The document outlines the history and criteria of biological classification, starting from Aristotle's two-kingdom system to the six-kingdom classification by Carl Woese, which separated organisms into domains. It details the characteristics of various kingdoms, emphasizing the distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and provides insights into bacterial respiration, nutrition, and reproduction methods. Key features include a discussion on the nutritional modes of bacteria and their genetic recombination processes.