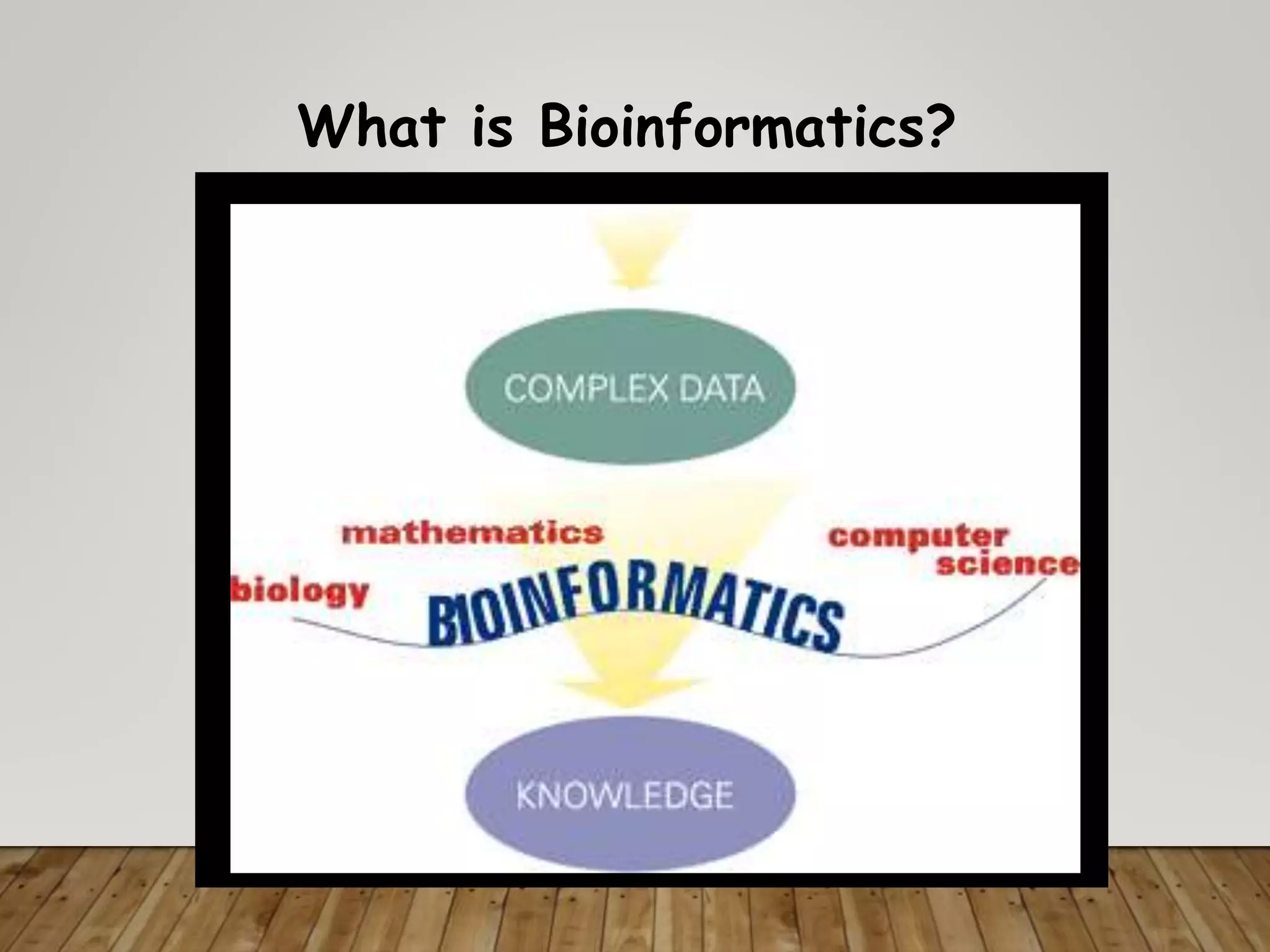
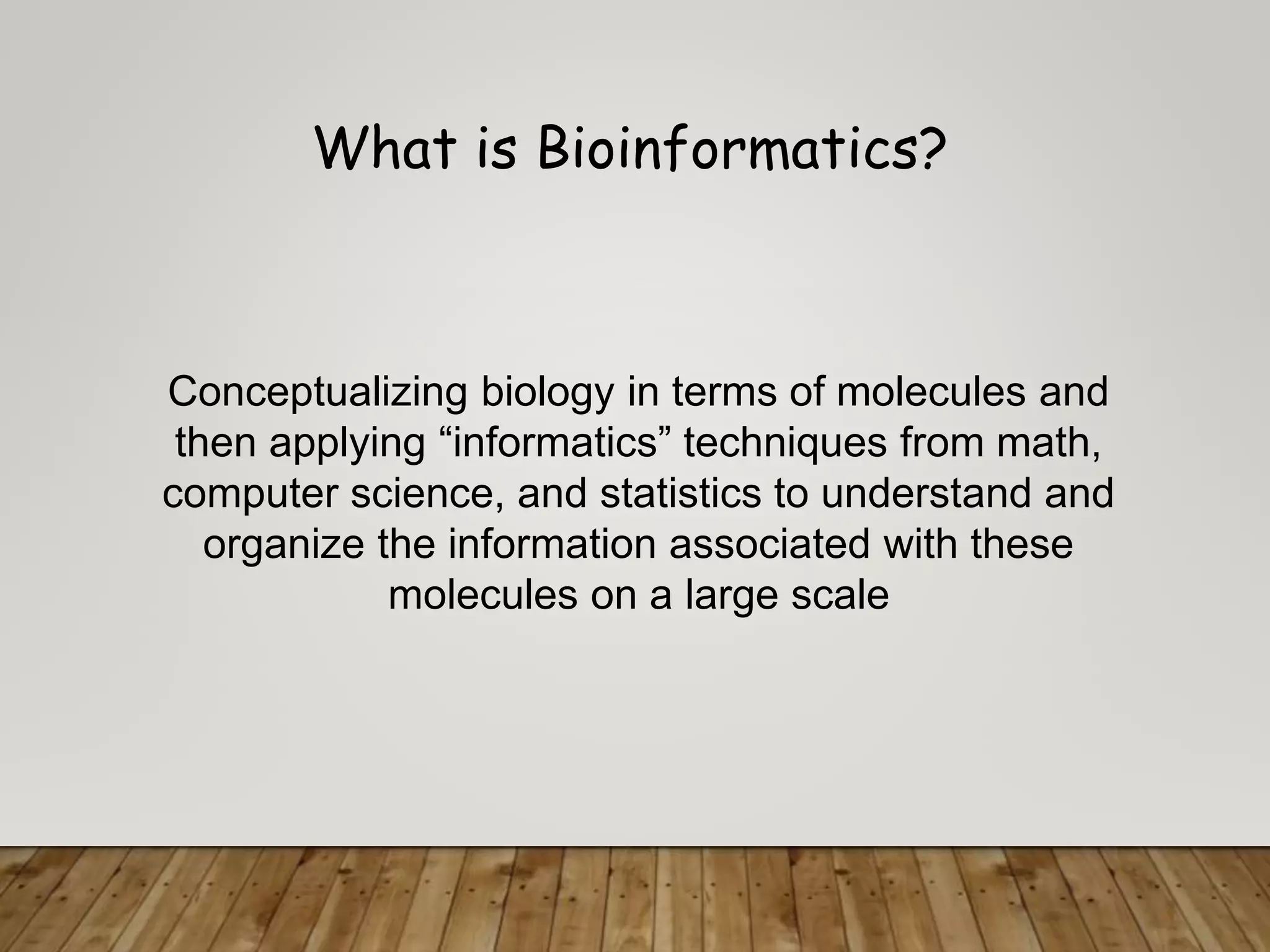
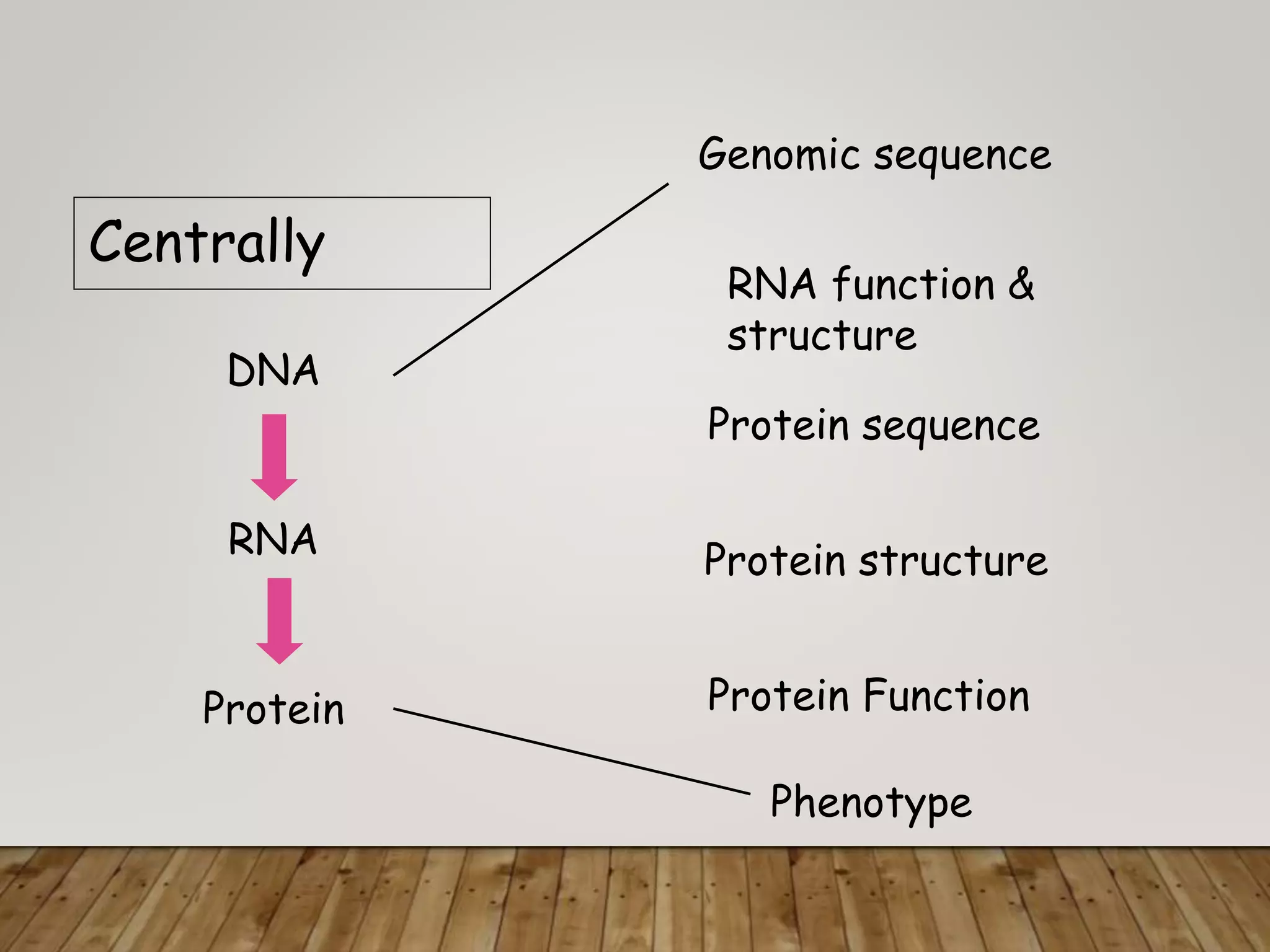
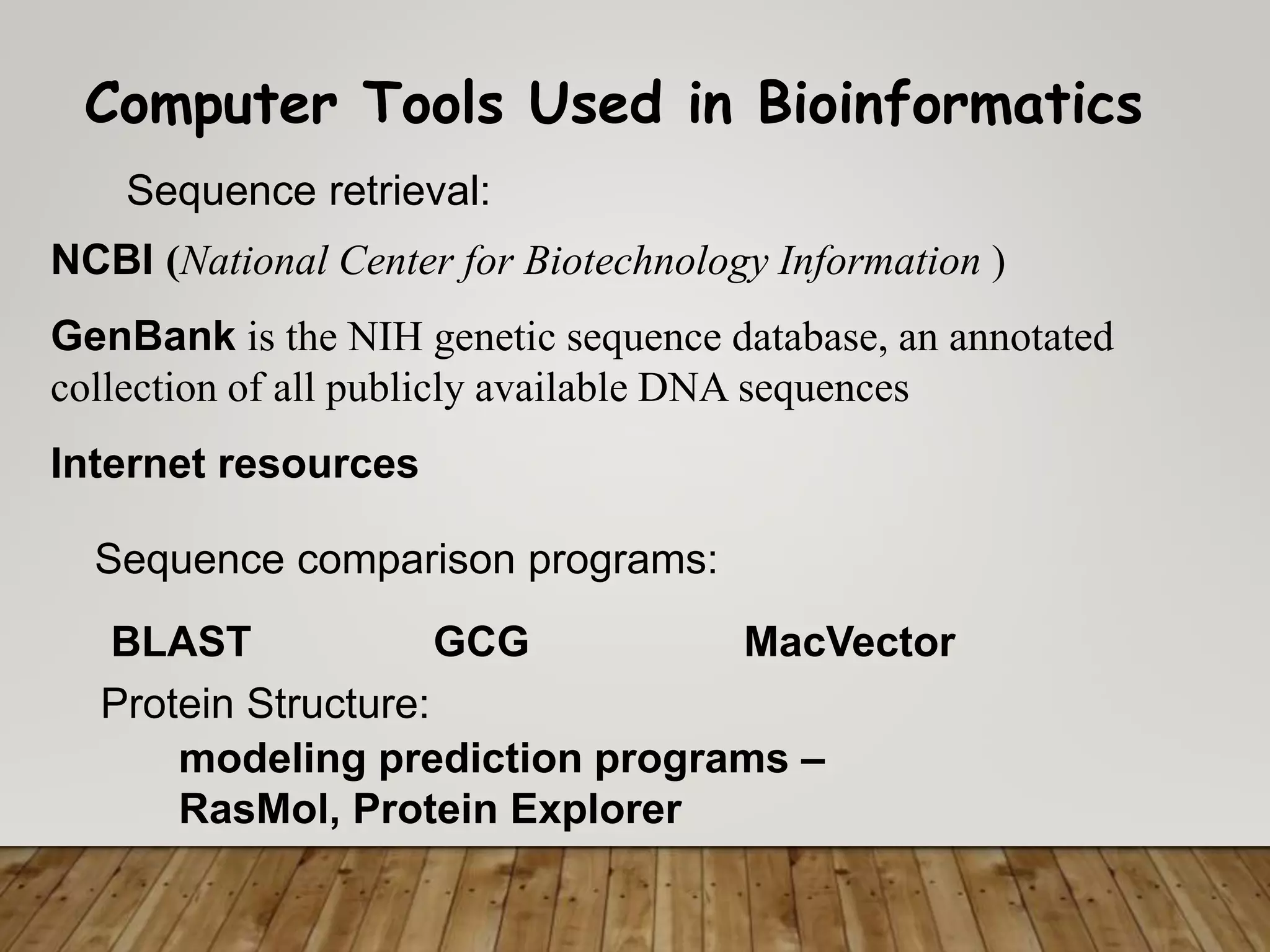
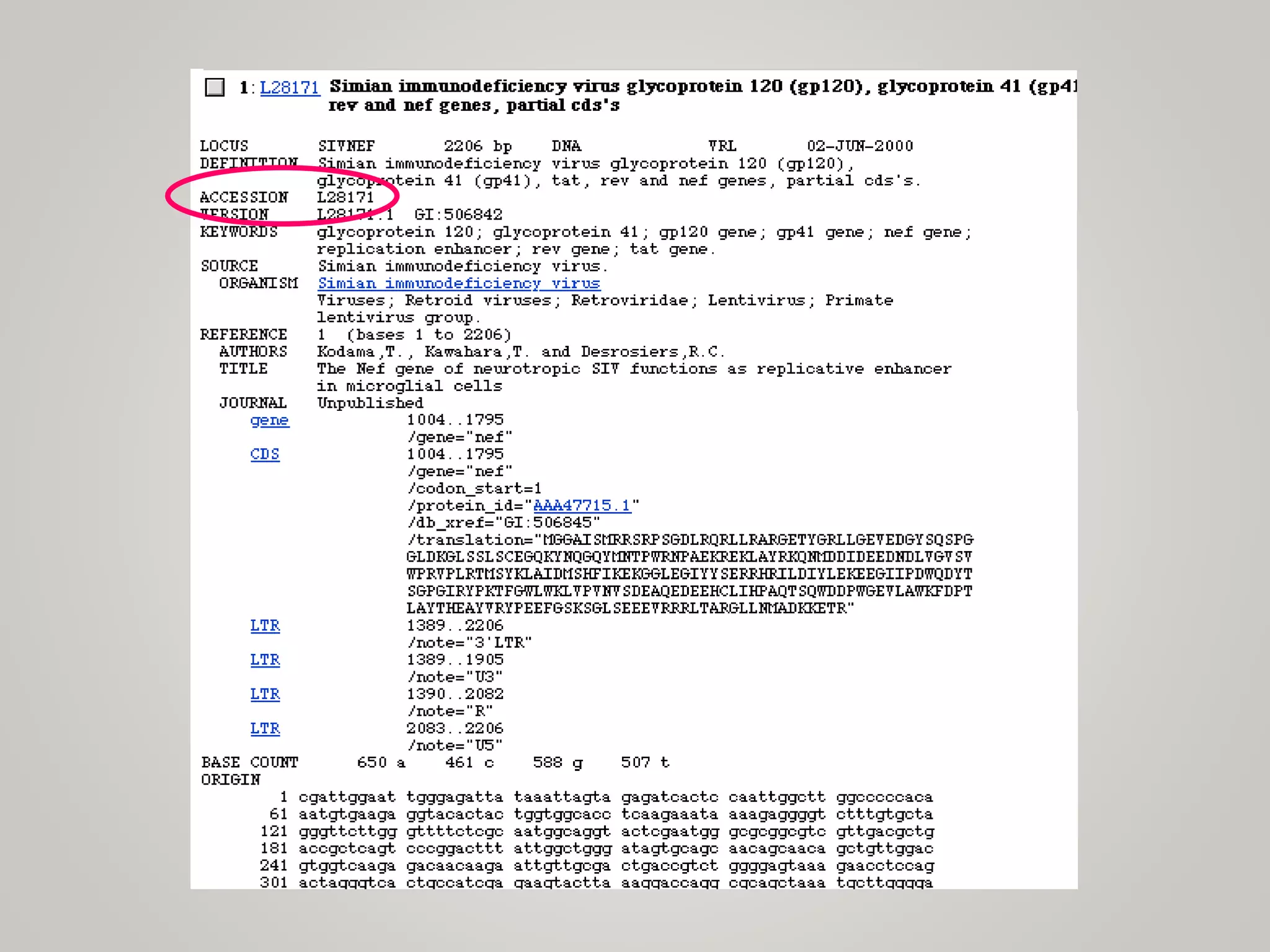
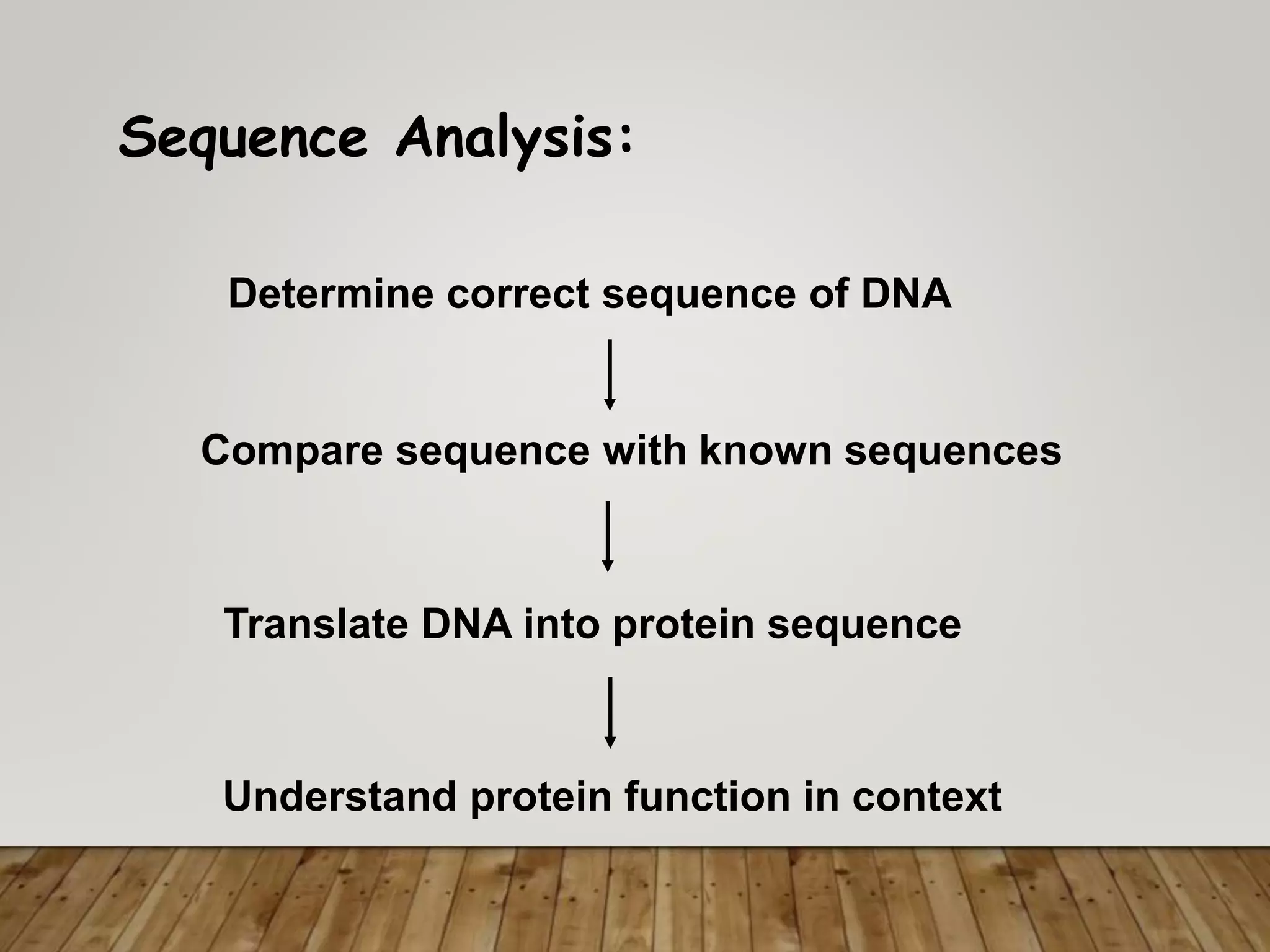
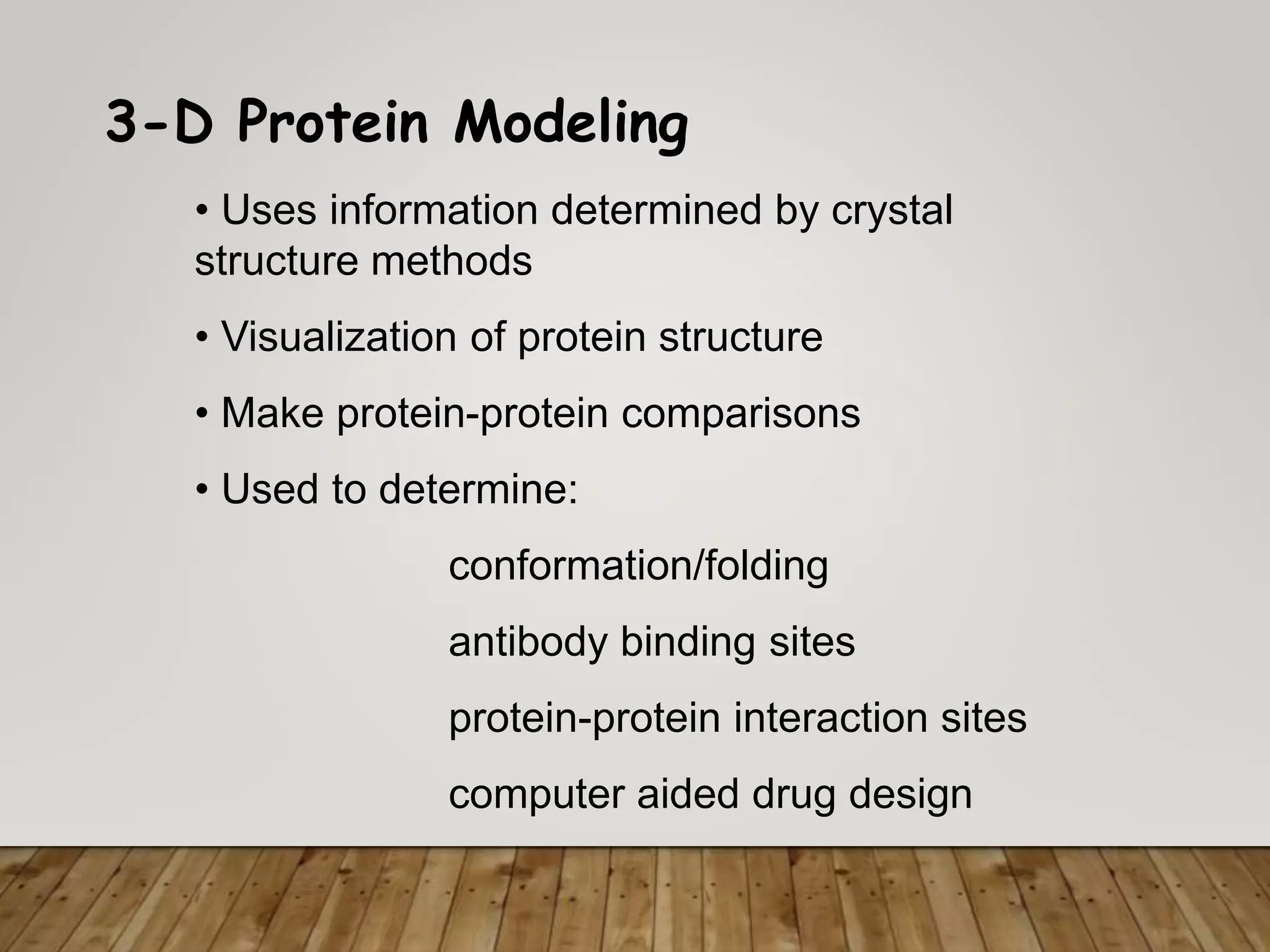
The document outlines the field of bioinformatics, which combines biology with informatics techniques to manage and analyze biological data at a large scale. It covers objectives, tools, and applications used in bioinformatics, such as sequence retrieval and protein structure analysis, as well as the importance of databases like GenBank. Additionally, it emphasizes data mining and 3-D protein modeling as critical aspects for understanding biological functions and processes.