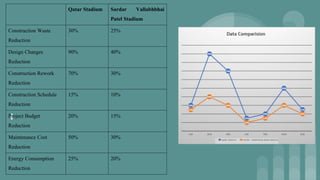
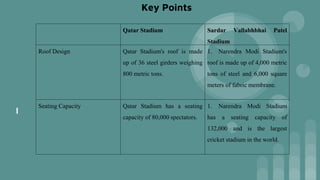
The presentation provides an overview of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and its application on two case studies - the Nagpur Metro Rail Project in India and a comparative study of the Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Stadium in India and the Qatar Stadium. It discusses how BIM was used for clash detection, structural modeling, and facility management on the Nagpur Metro project. For the stadiums, it compares how BIM helped with simulation, coordination, safety, and reducing costs and schedule on construction. It concludes that BIM adoption is growing and provides benefits like improved quality, efficiency, and sustainability for infrastructure projects in India and globally.