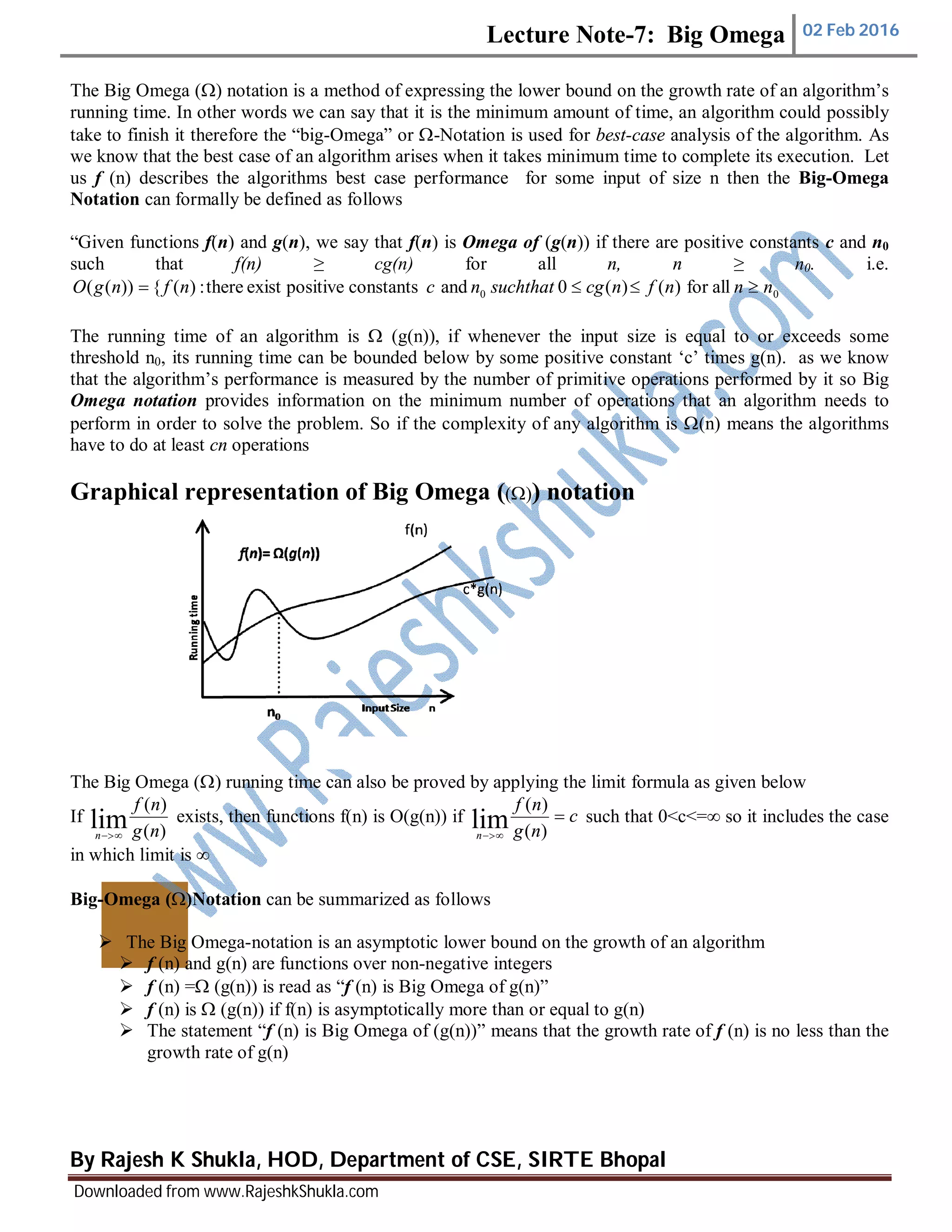
The document explains the big omega (Ω) notation, which represents the lower bound on the growth rate of an algorithm's running time, specifically for best-case analysis. It defines that f(n) is Ω(g(n)) if there are positive constants such that f(n) is greater than or equal to c * g(n) for sufficiently large n. Overall, big omega notation provides information on the minimum number of operations an algorithm must perform to solve a problem.