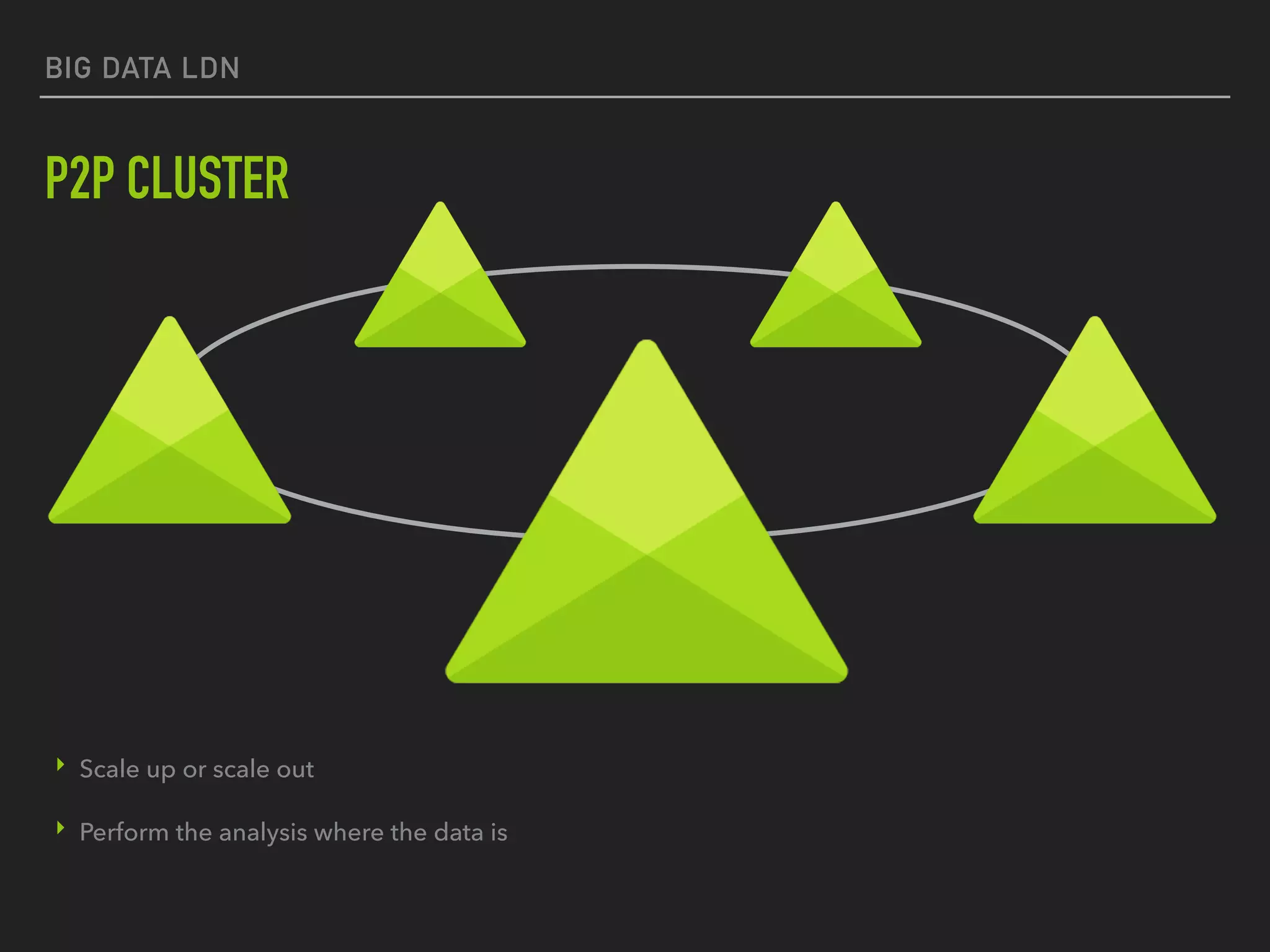
This document discusses using data streams and lakes for big data analytics in utilities. It begins by explaining how smart meter rollouts have increased meter reads from 80 million to 350 billion per year. Traditional data warehousing is challenged by the time criticality, resource demands, and scale of this unbounded data. The document then introduces data streams for real-time analytics and data lakes for flexible storage of huge amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. It describes Valo, an open lambda architecture that uses multiple repositories and stream processing to enable both real-time and historical analysis across disparate data sources.