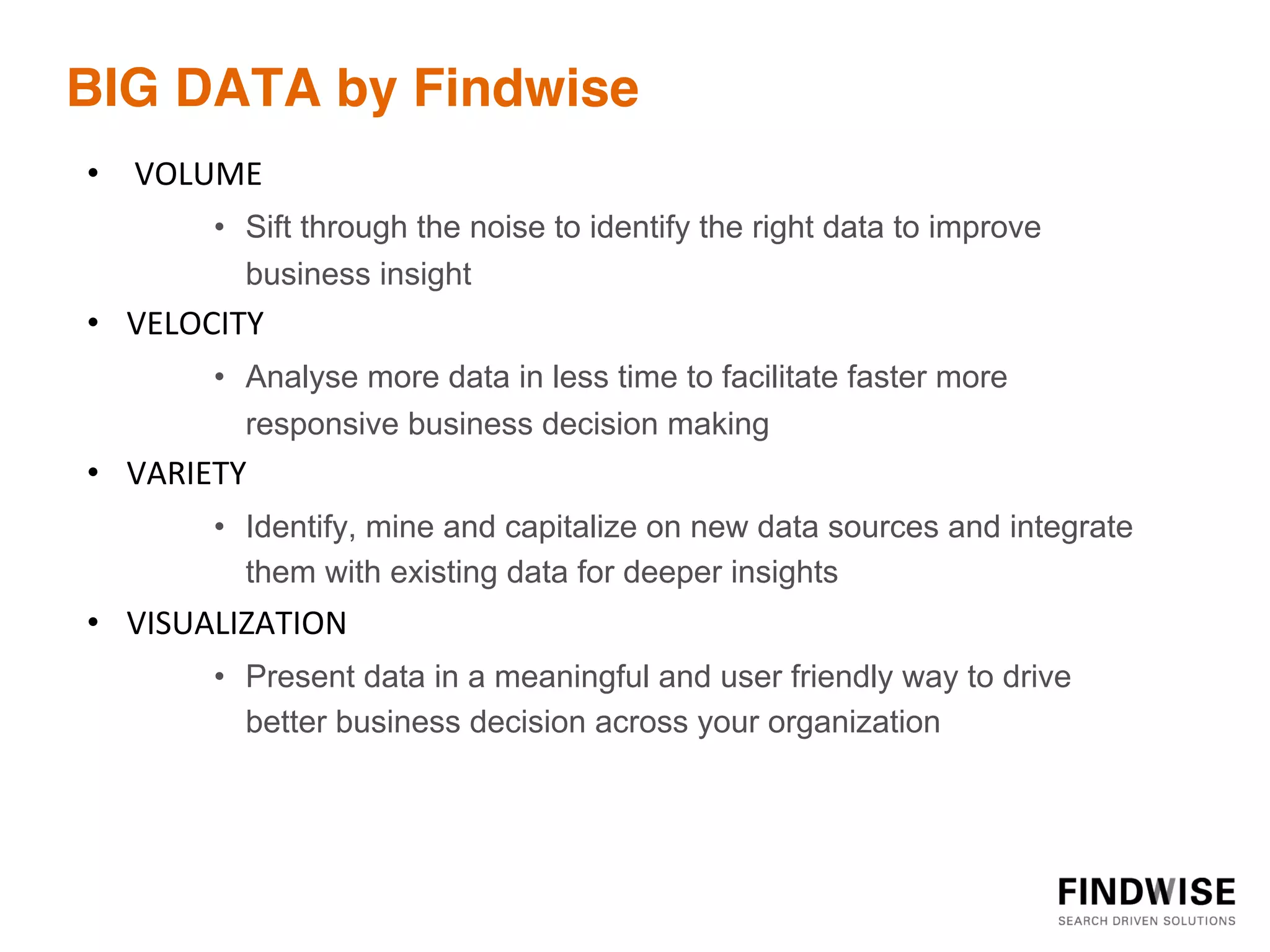
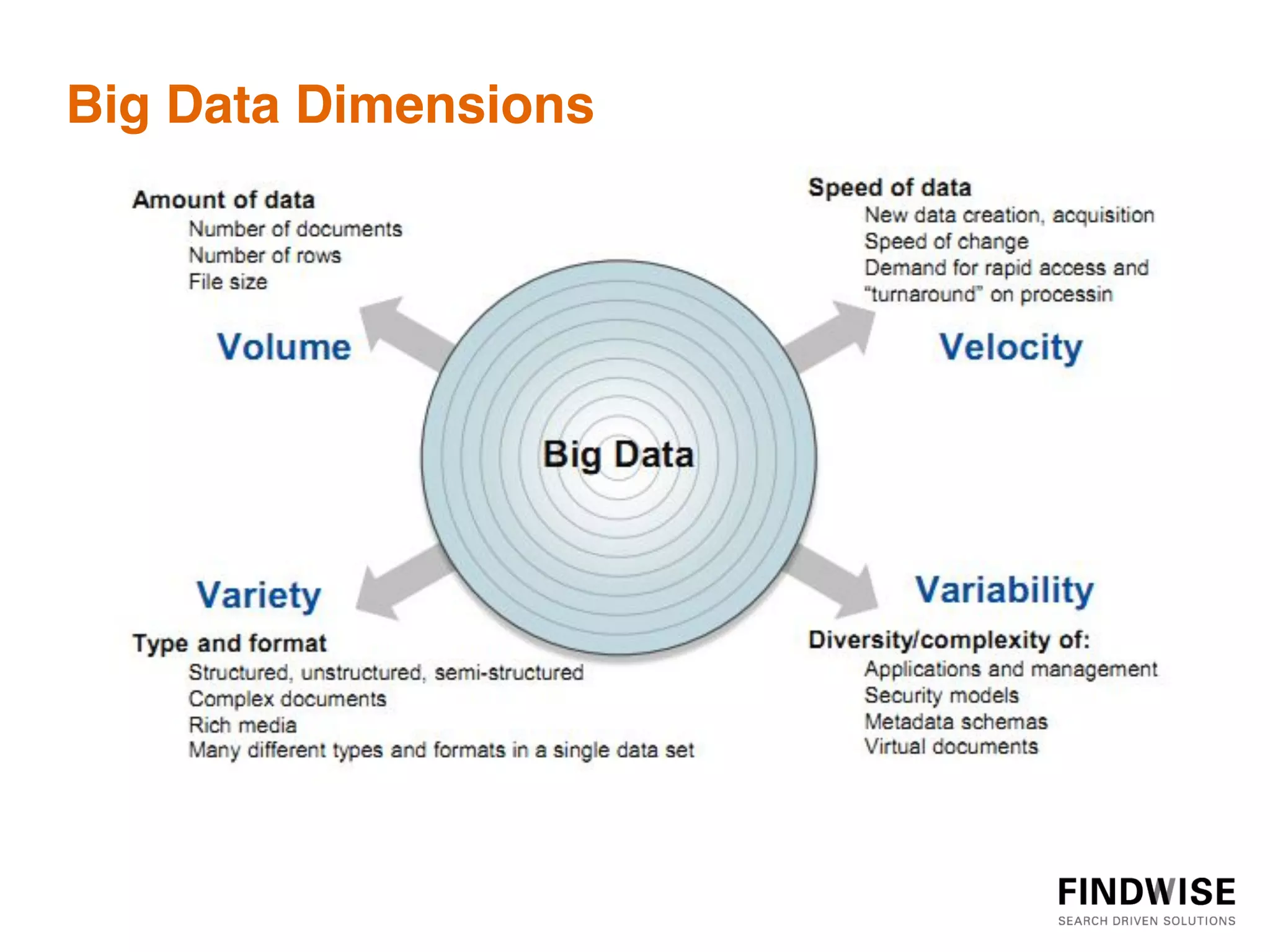
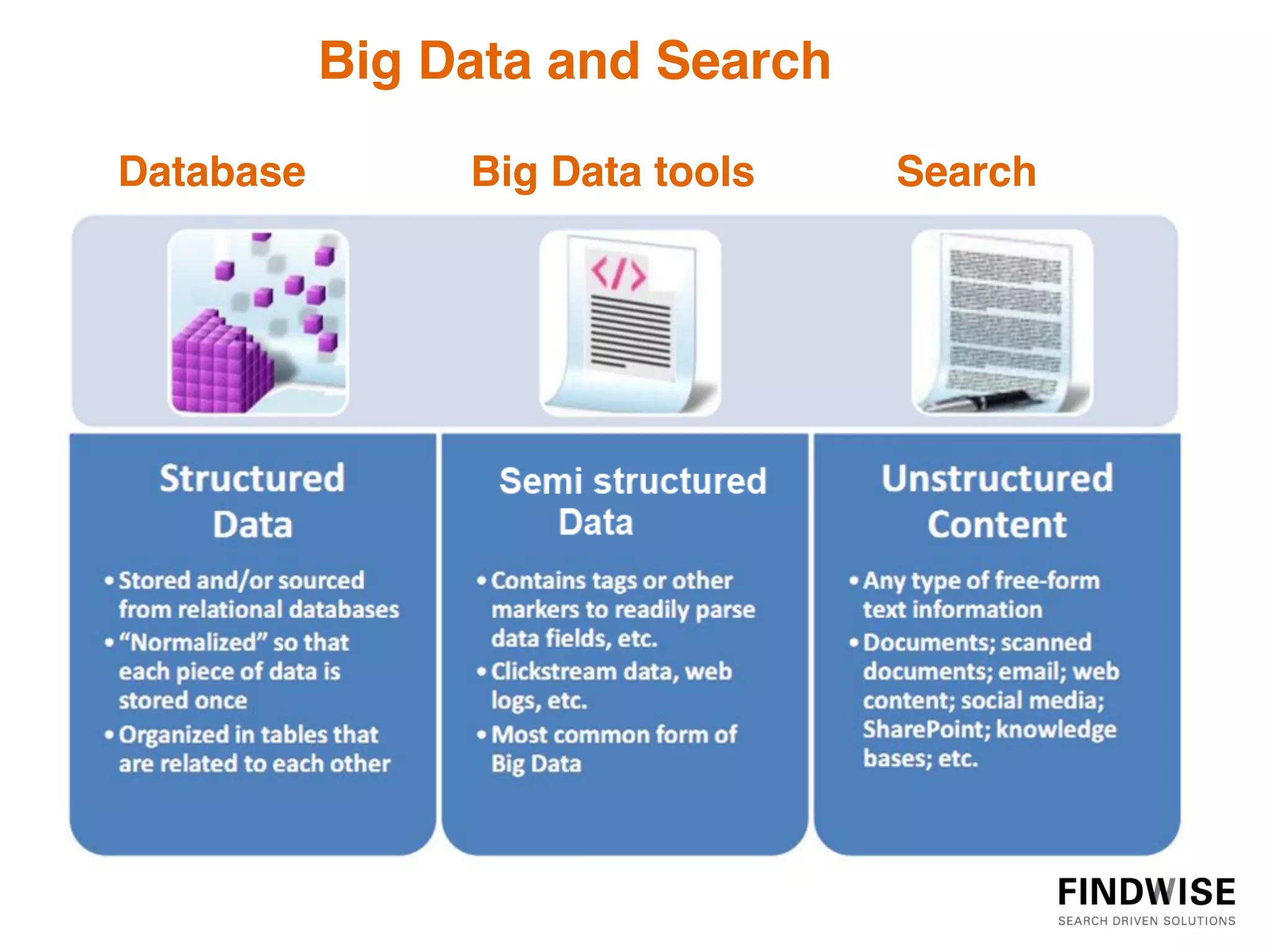
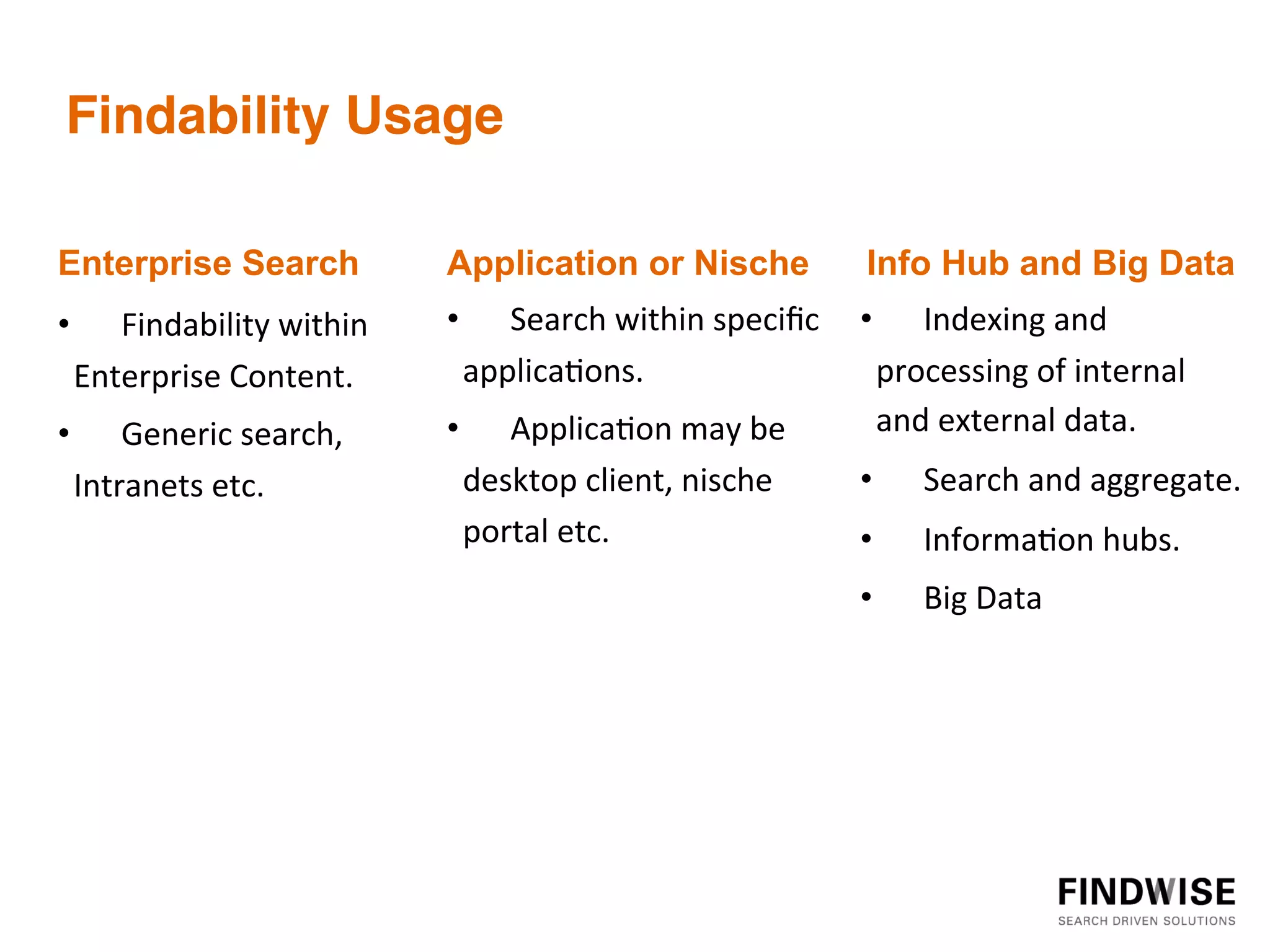
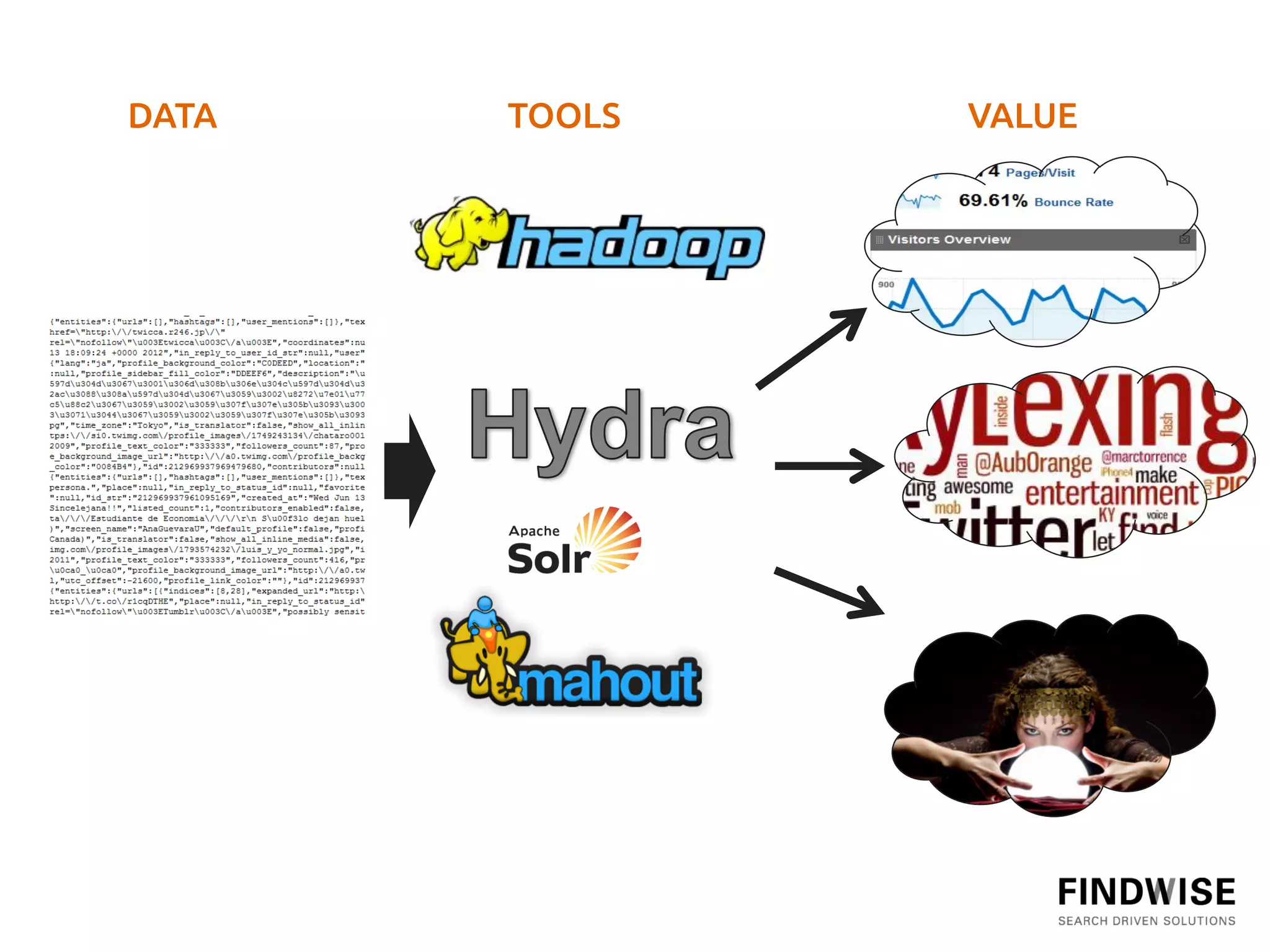
This document discusses big data, defining it as large volumes of diverse data that come in at high velocity, requiring new techniques and technologies to capture, store, distribute, manage and analyze the data to extract value and enable better decision making. It notes that 90% of data in the world has been created in just the past two years, and data is doubling every two years. Big data tools are needed to analyze both structured and unstructured data from a variety of internal and external sources to gain business insights. Examples provided discuss using big data in insurance to identify risk patterns and sales leads, and in banking to analyze customer transactions and enrich customer profiles.