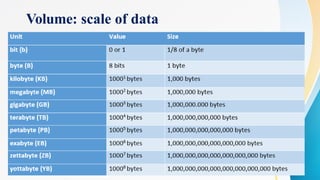
The document provides an overview of data mining, big data, and business intelligence, emphasizing the growing significance of large datasets and their analysis. It outlines various sources of big data, types of data, and key benefits of utilizing big data tools for cost and time savings, market understanding, and customer insights. Additionally, it covers data mining techniques, processes, and applications in fraud detection and business decision-making.