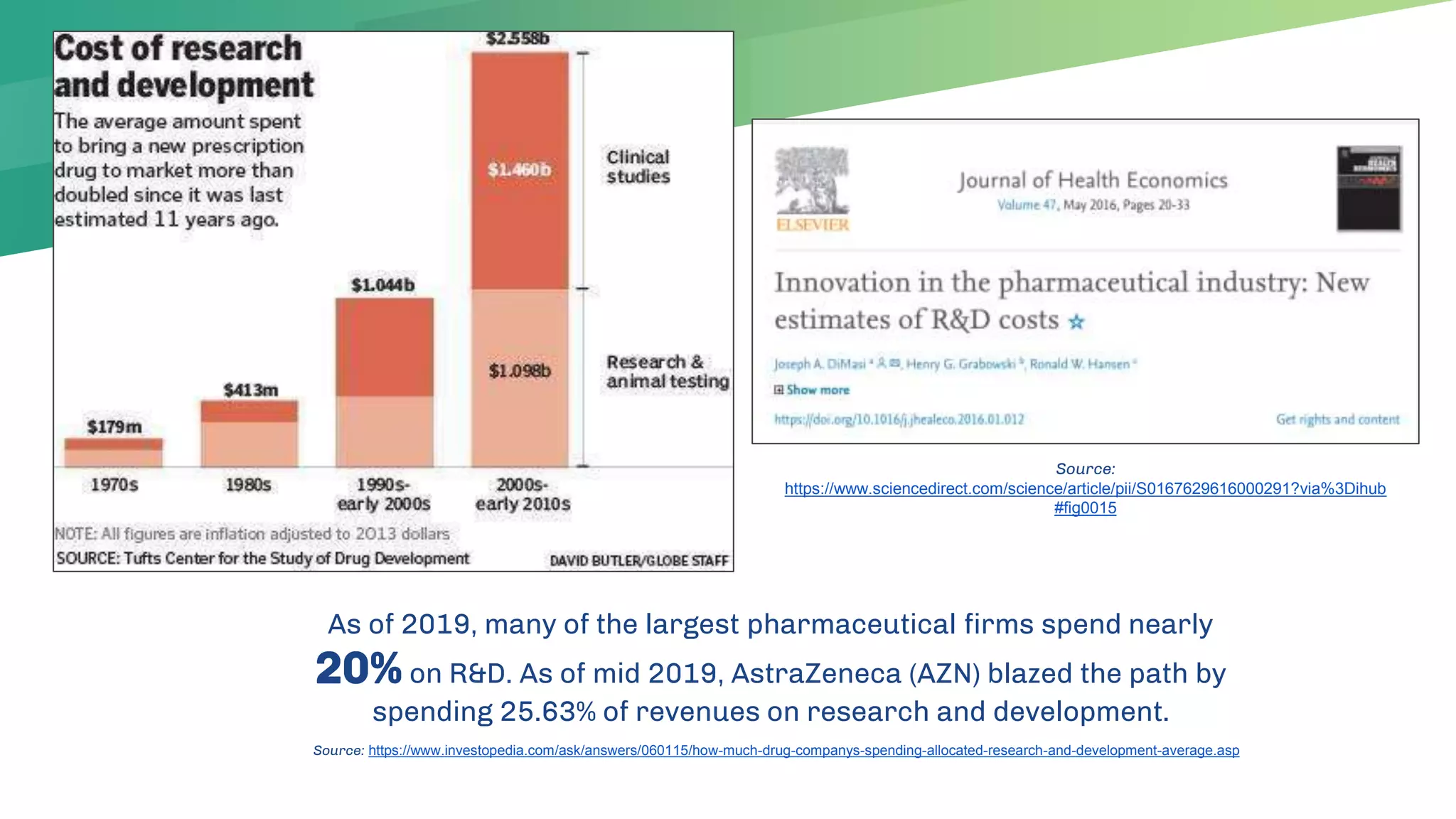
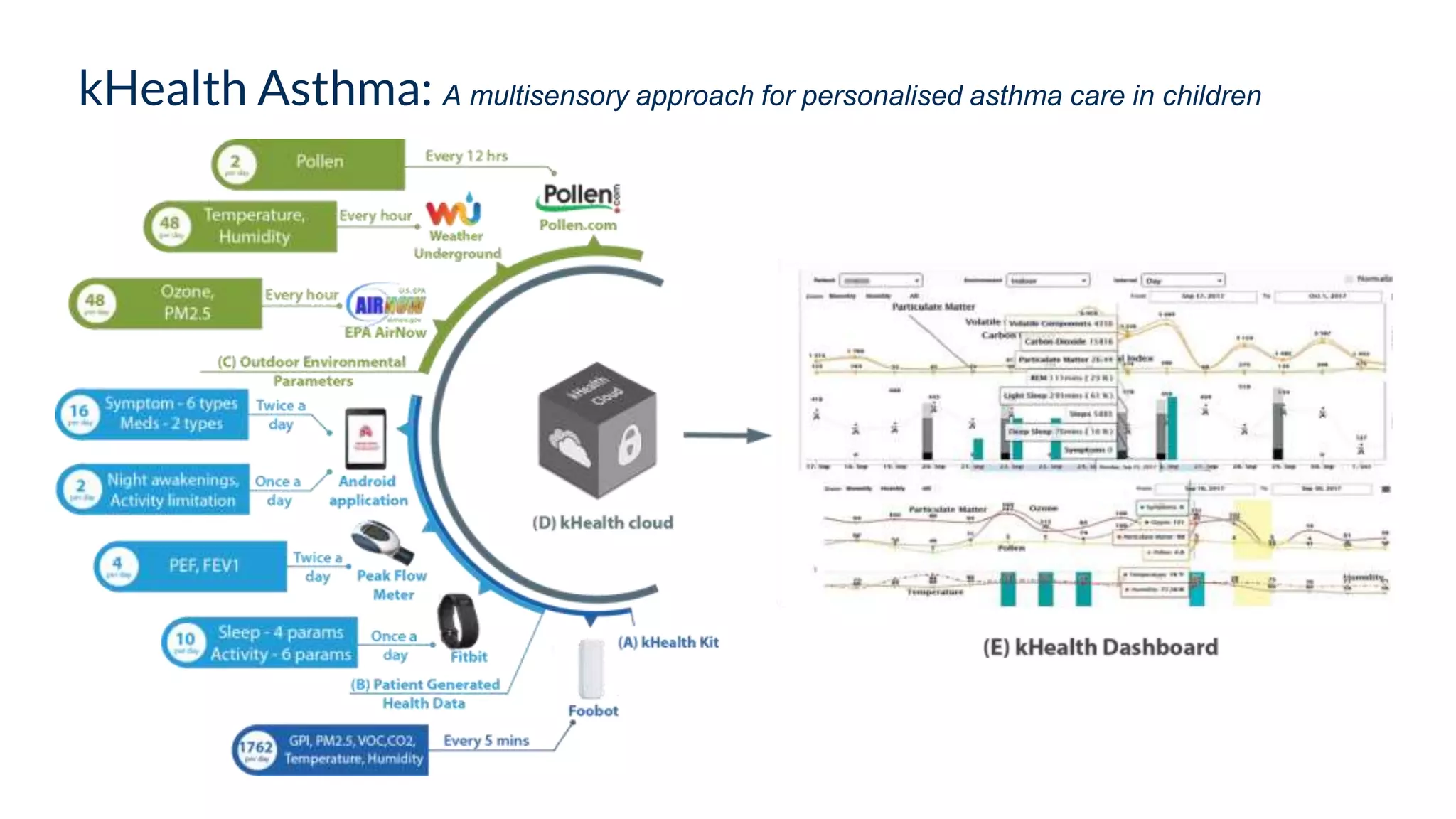
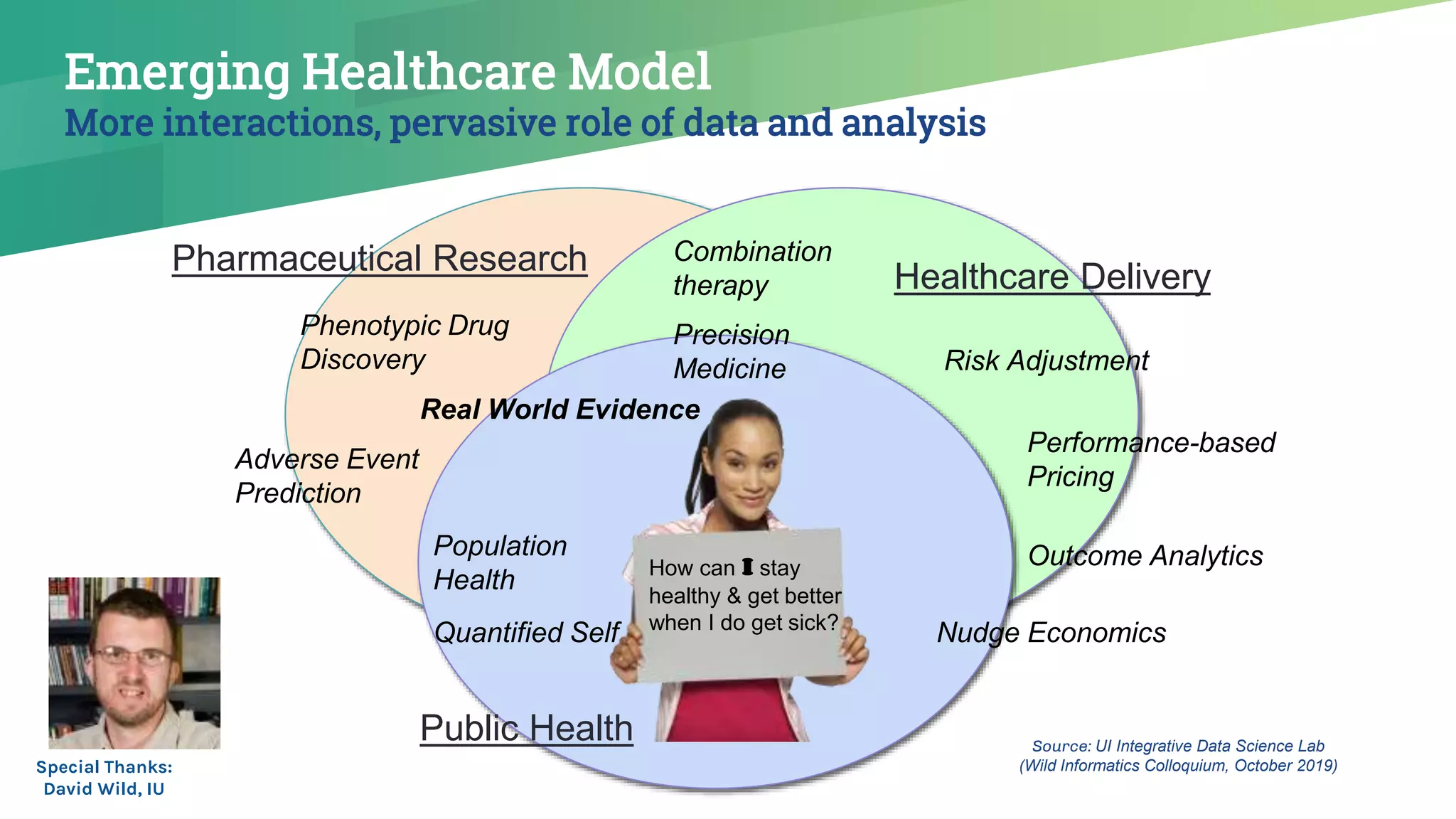
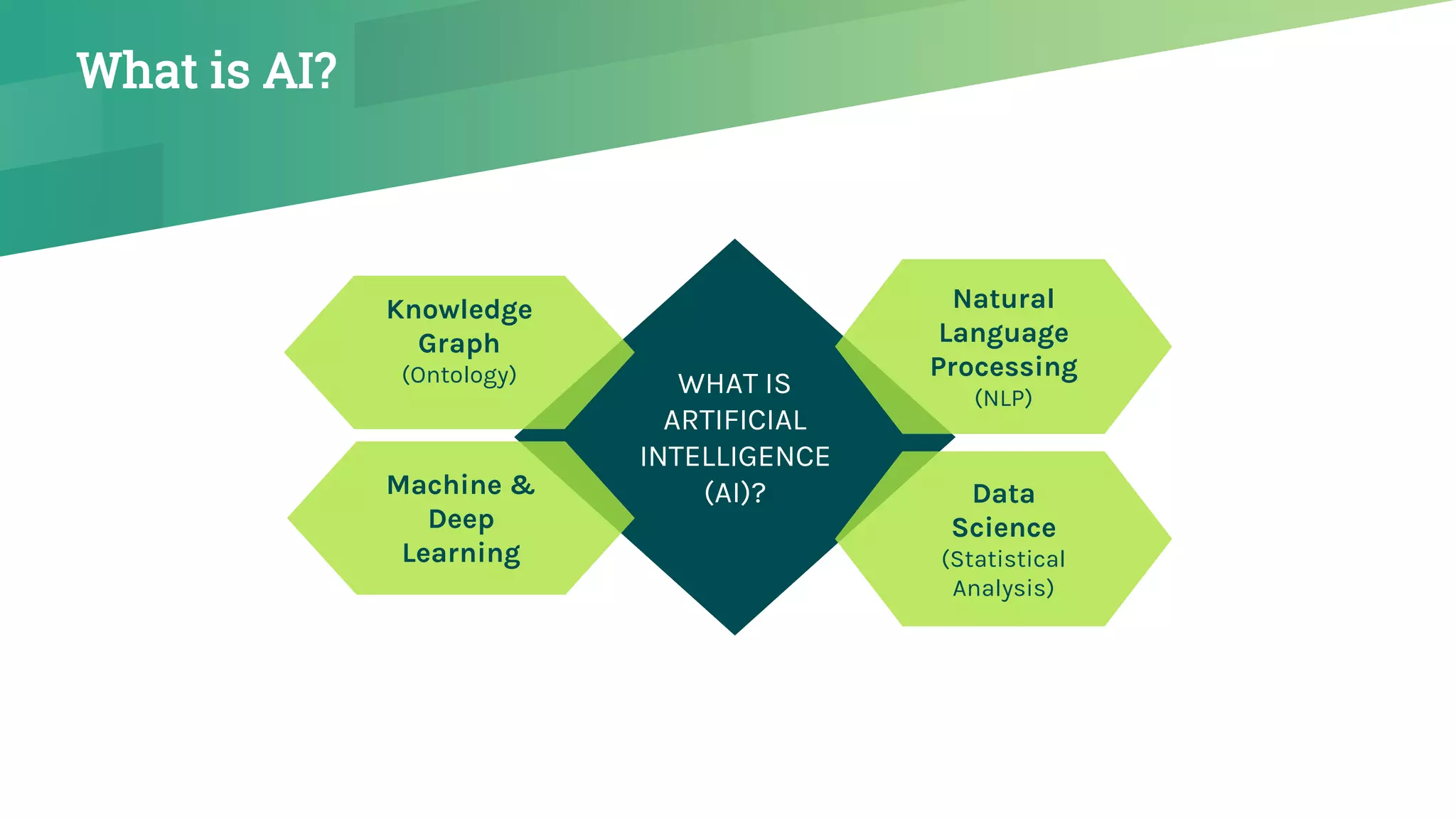
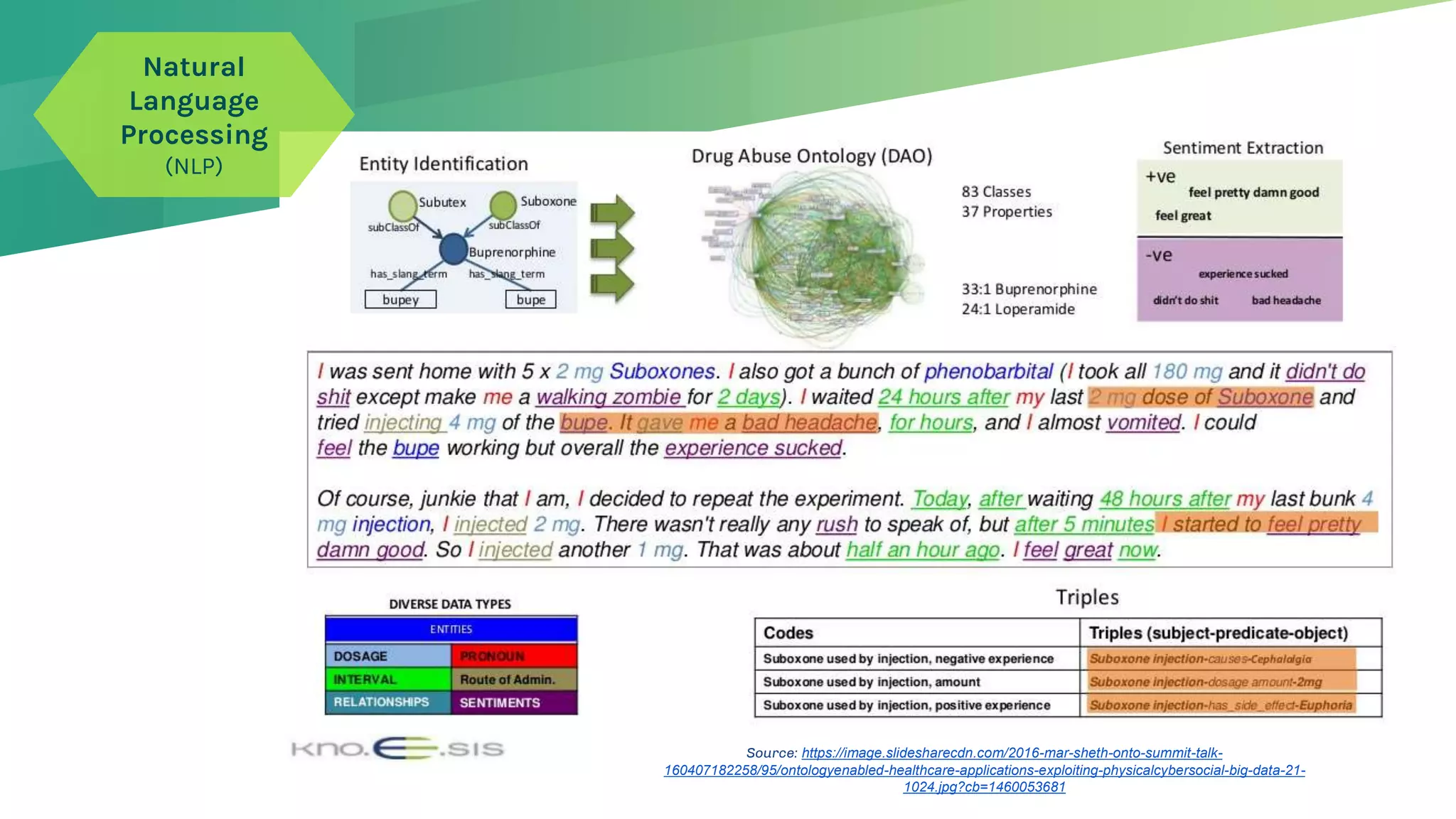
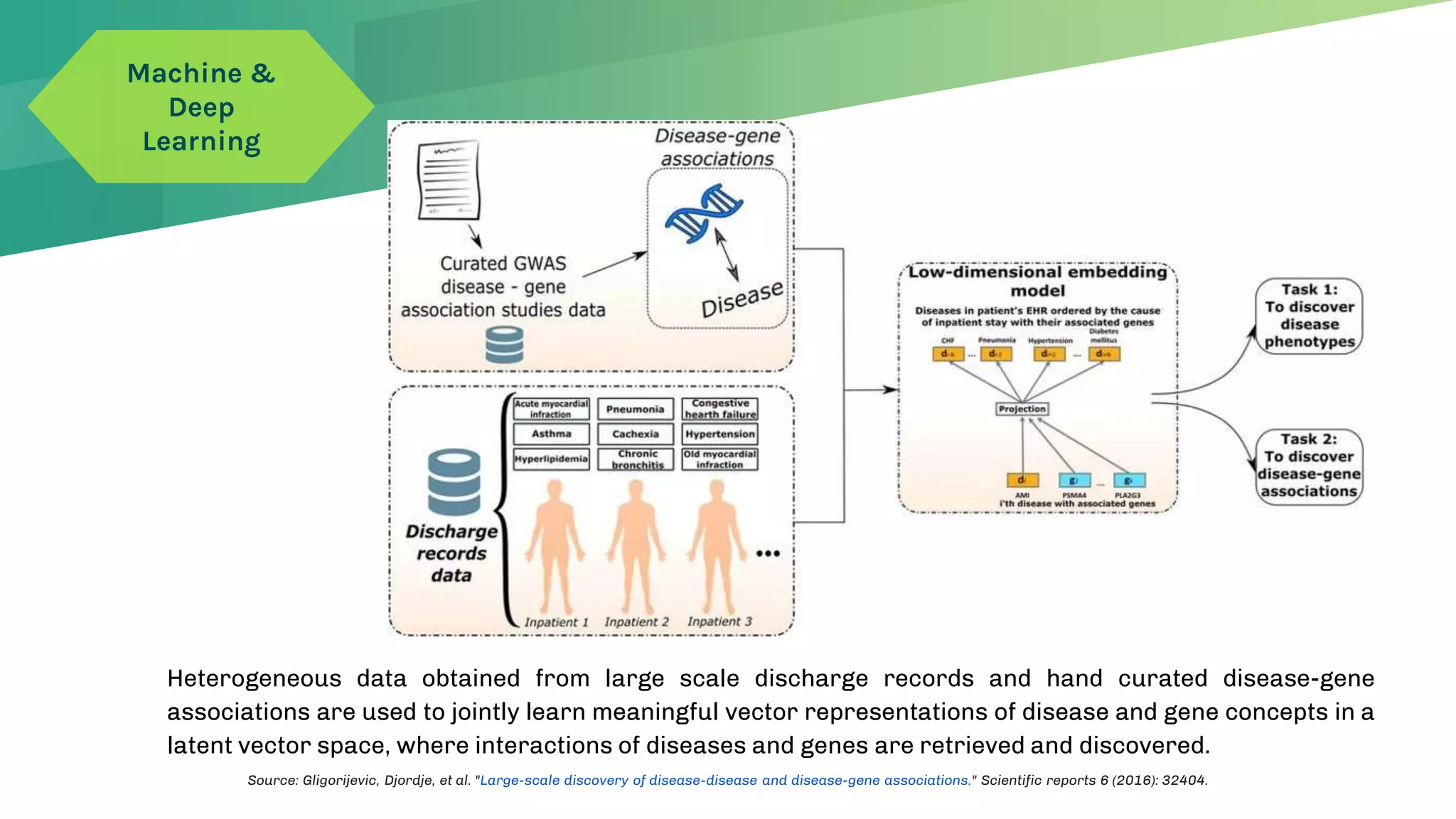
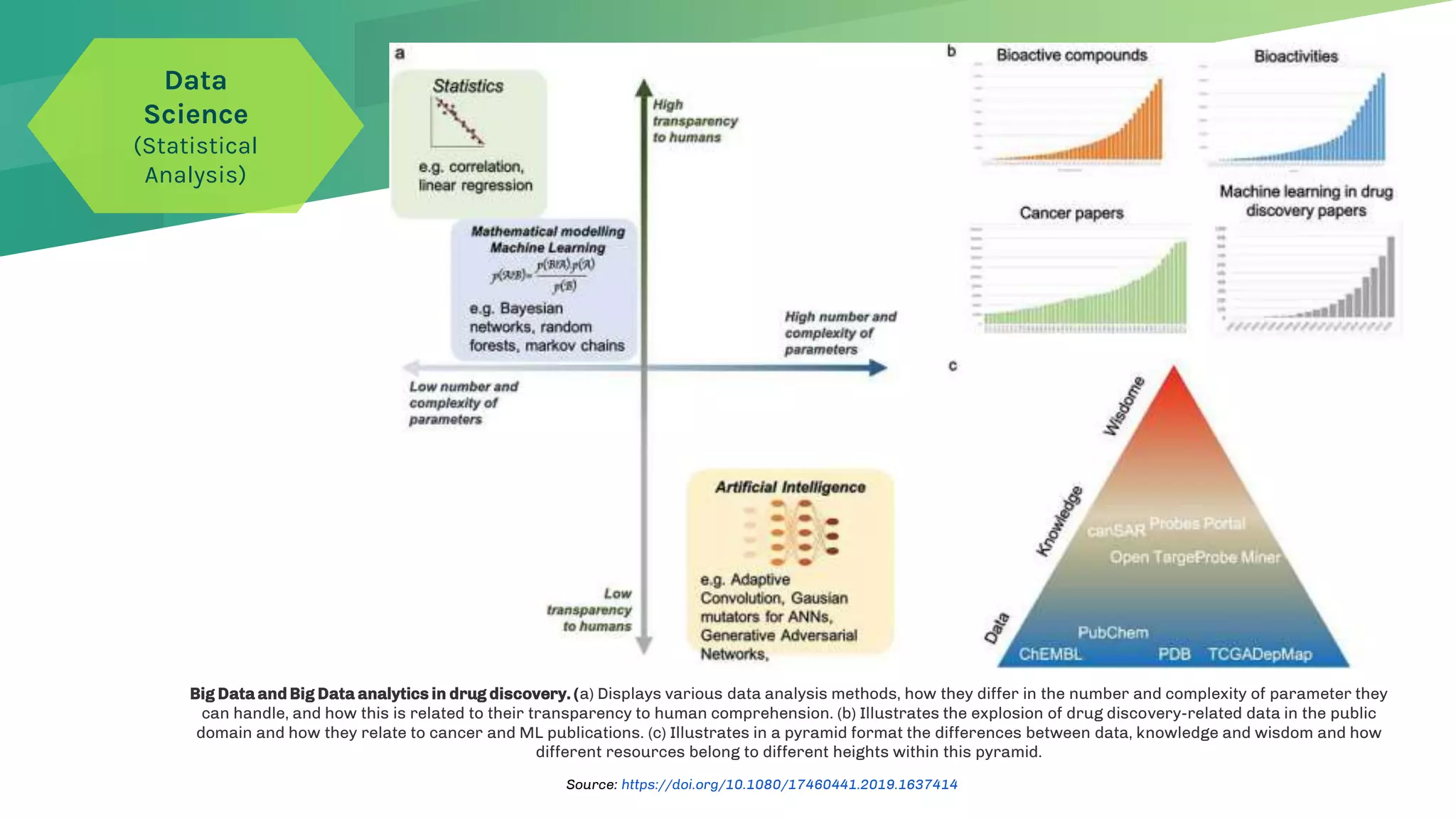
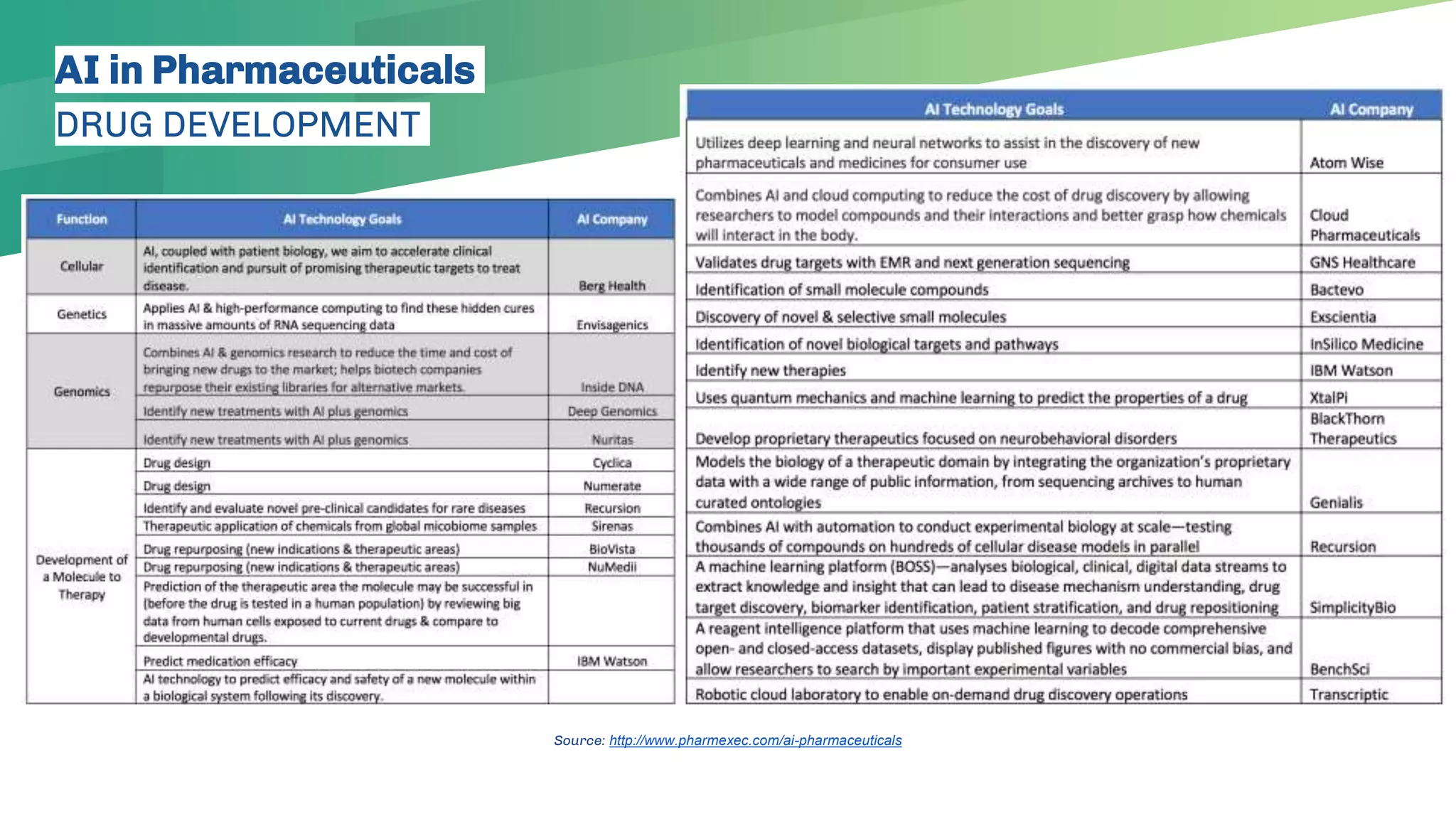
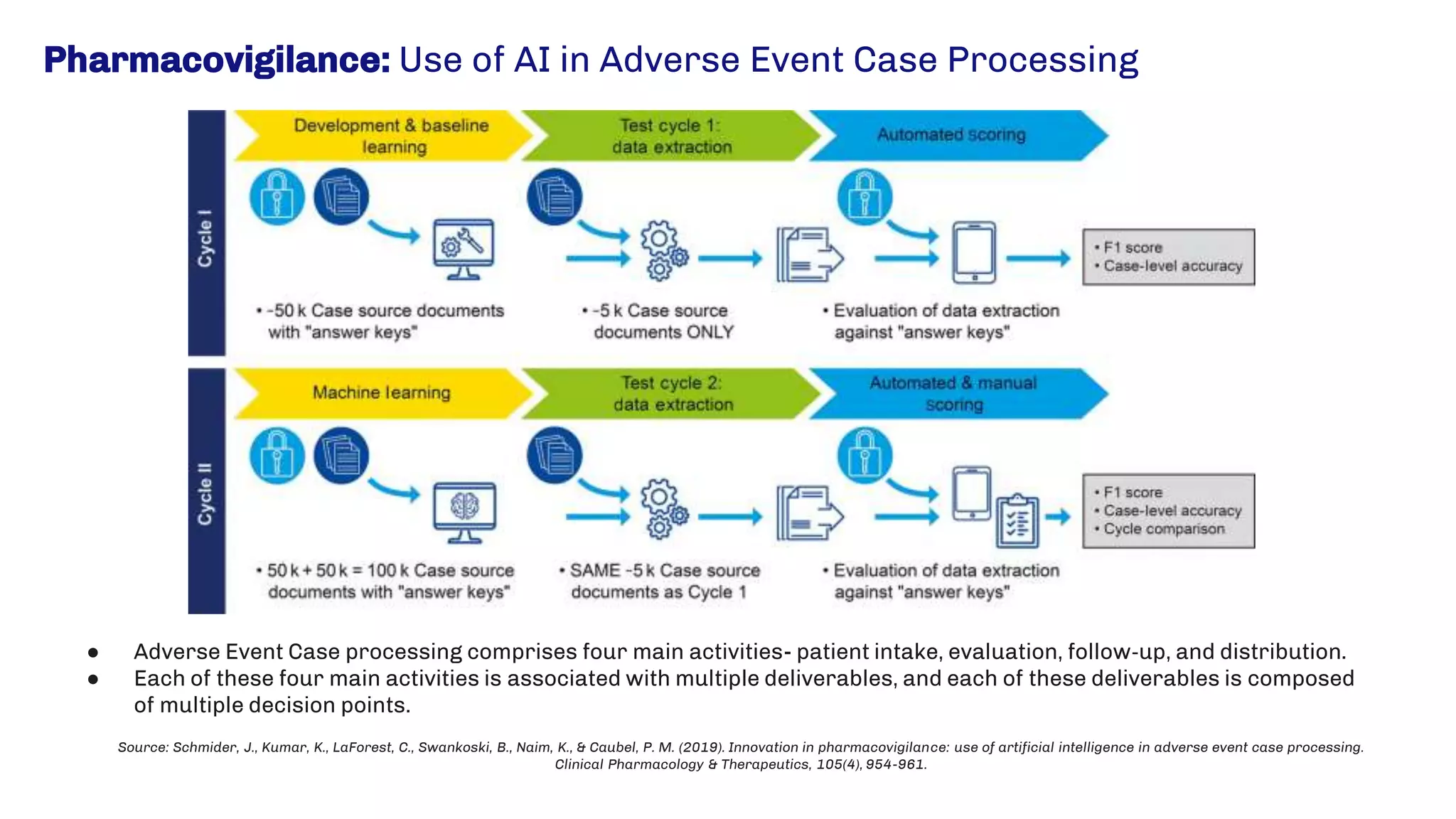
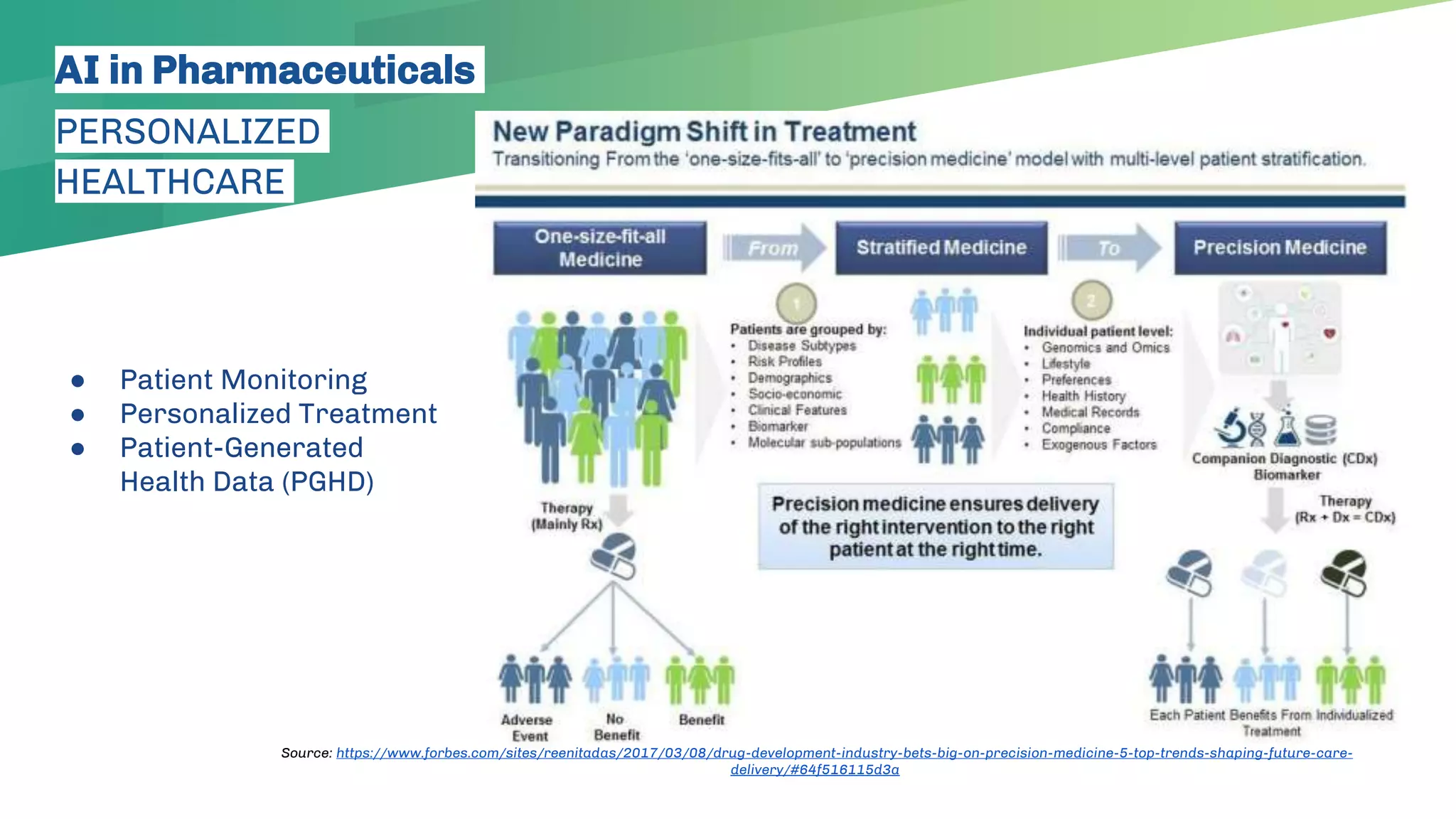
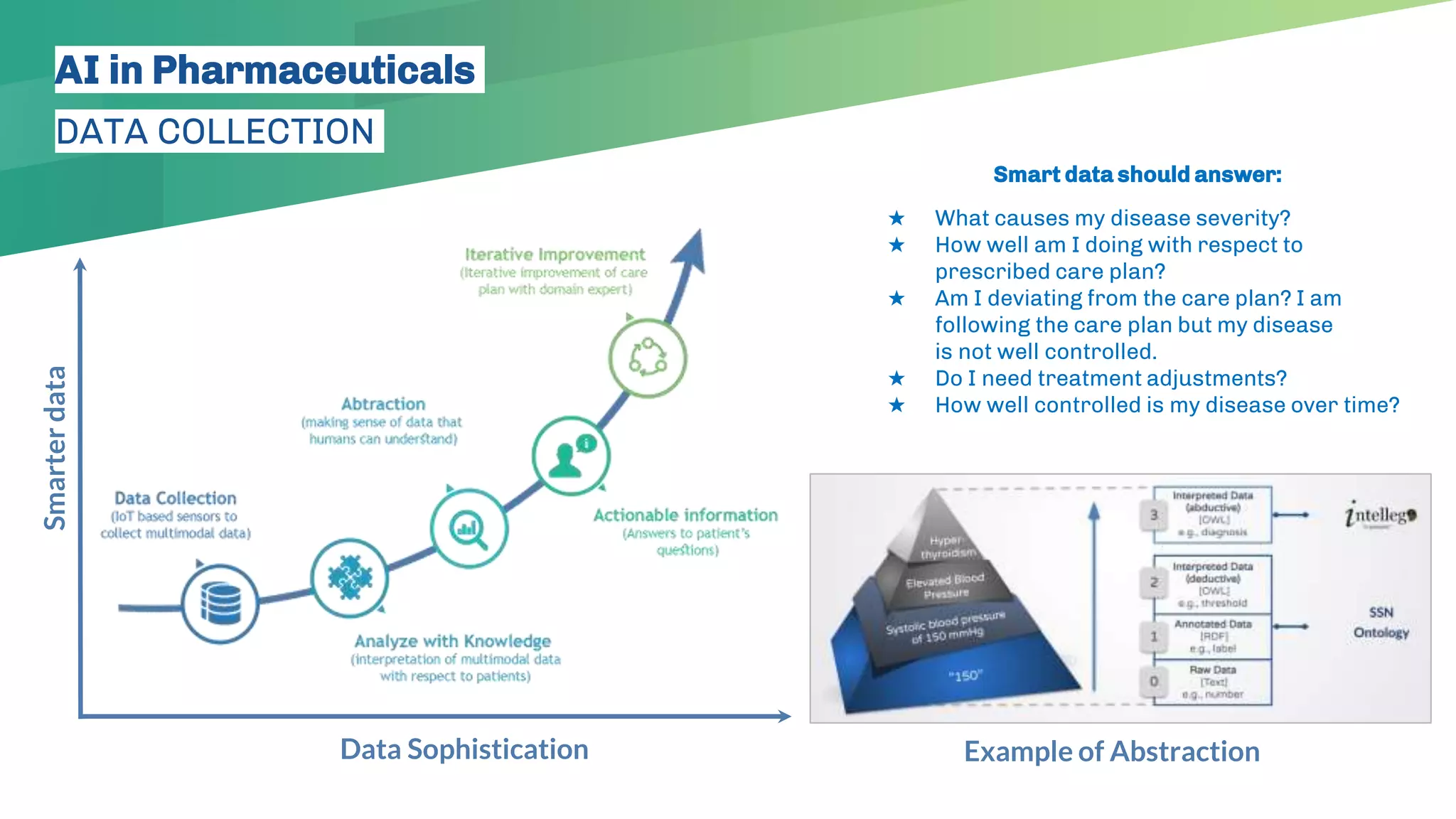
The presentation emphasizes the crucial role of big data and artificial intelligence (AI) in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly in transforming drug discovery and patient safety through data analysis techniques. It advocates for integrating data science skills among pharmacy students, highlighting the shift from traditional lab sciences to data-driven methodologies, and discusses various applications of AI such as patient monitoring and pharmacovigilance. The document also notes the substantial investment by pharmaceutical companies in research and development and the increasing use of AI and machine learning in various healthcare processes.