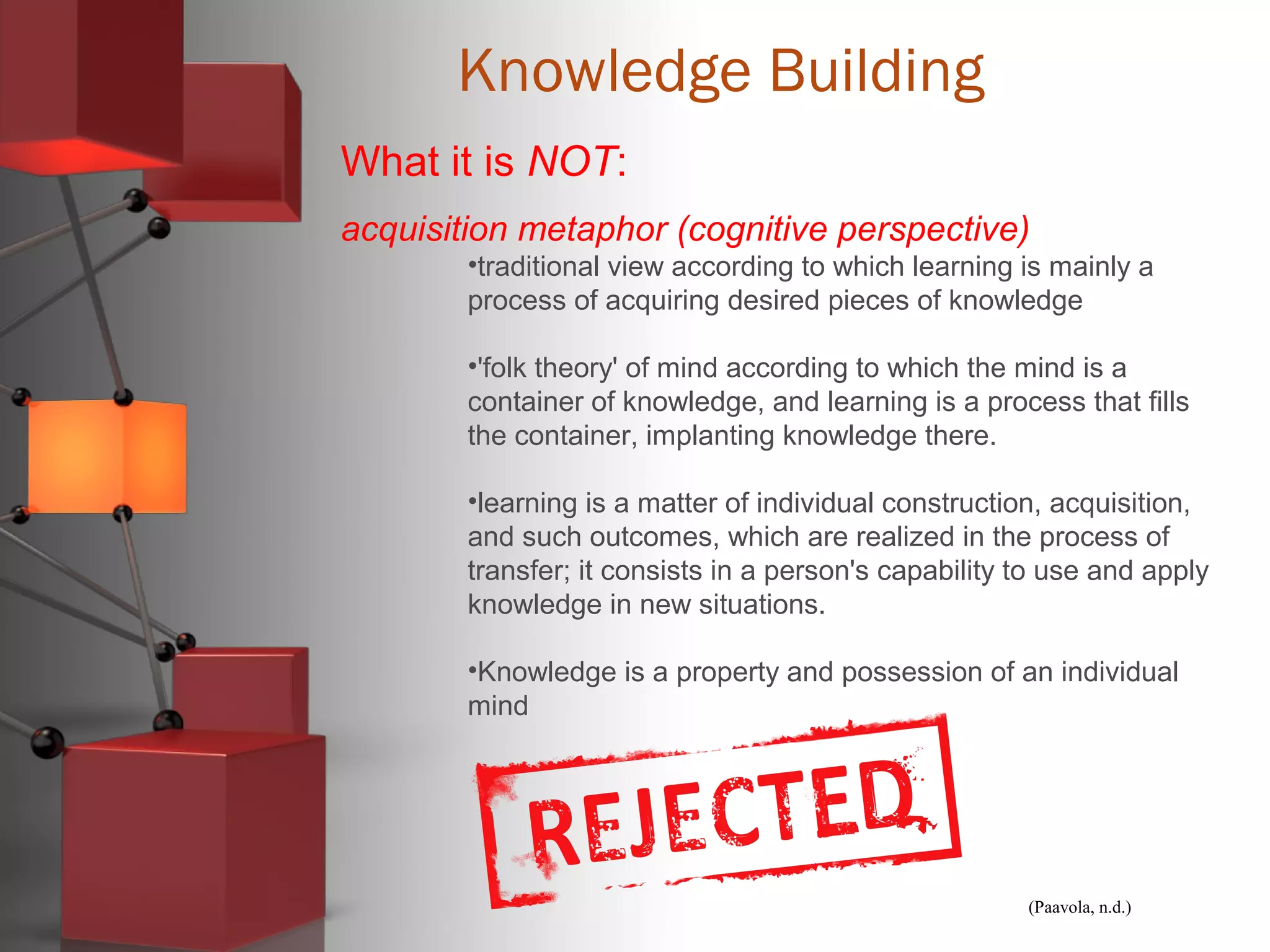
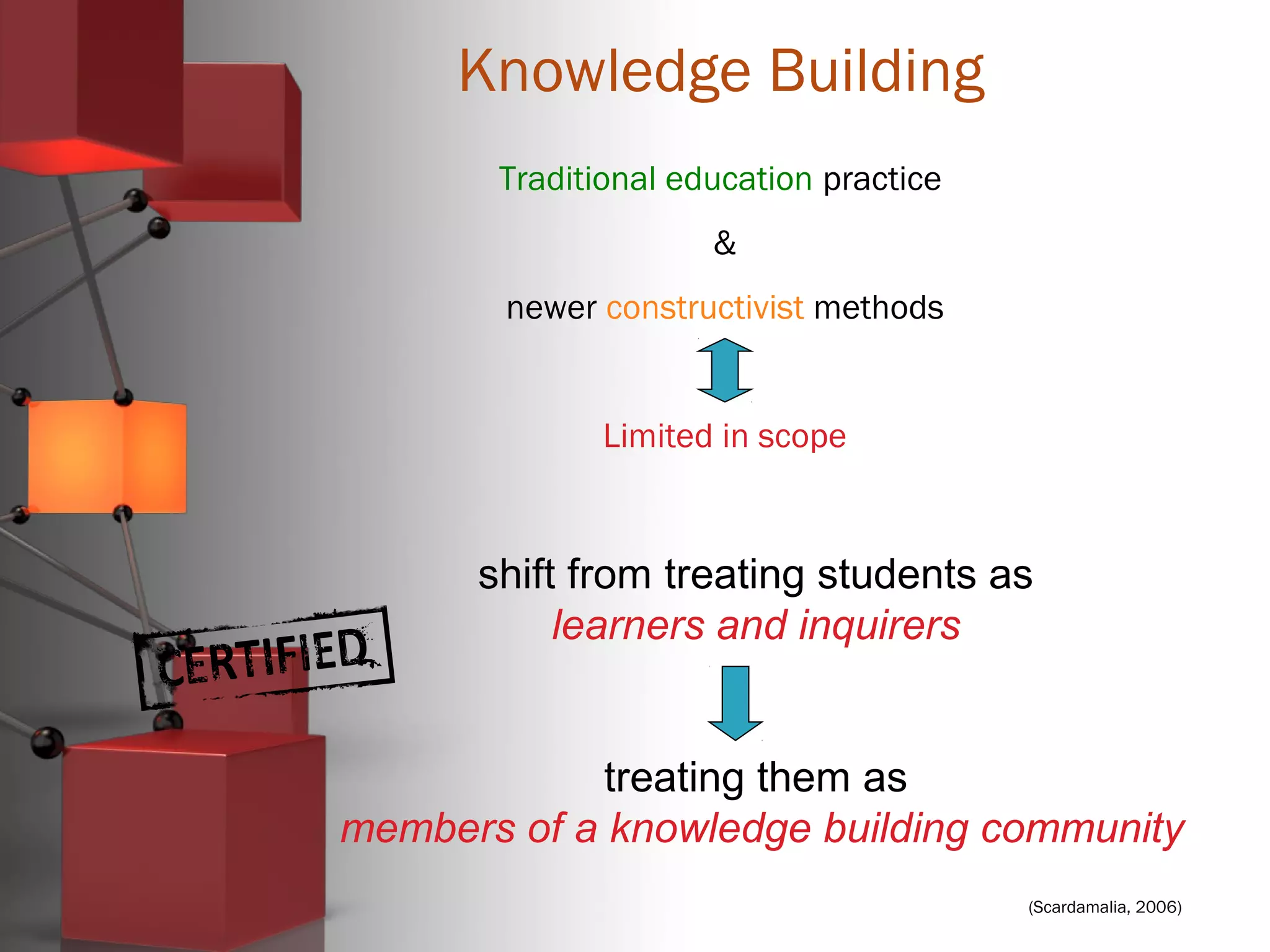
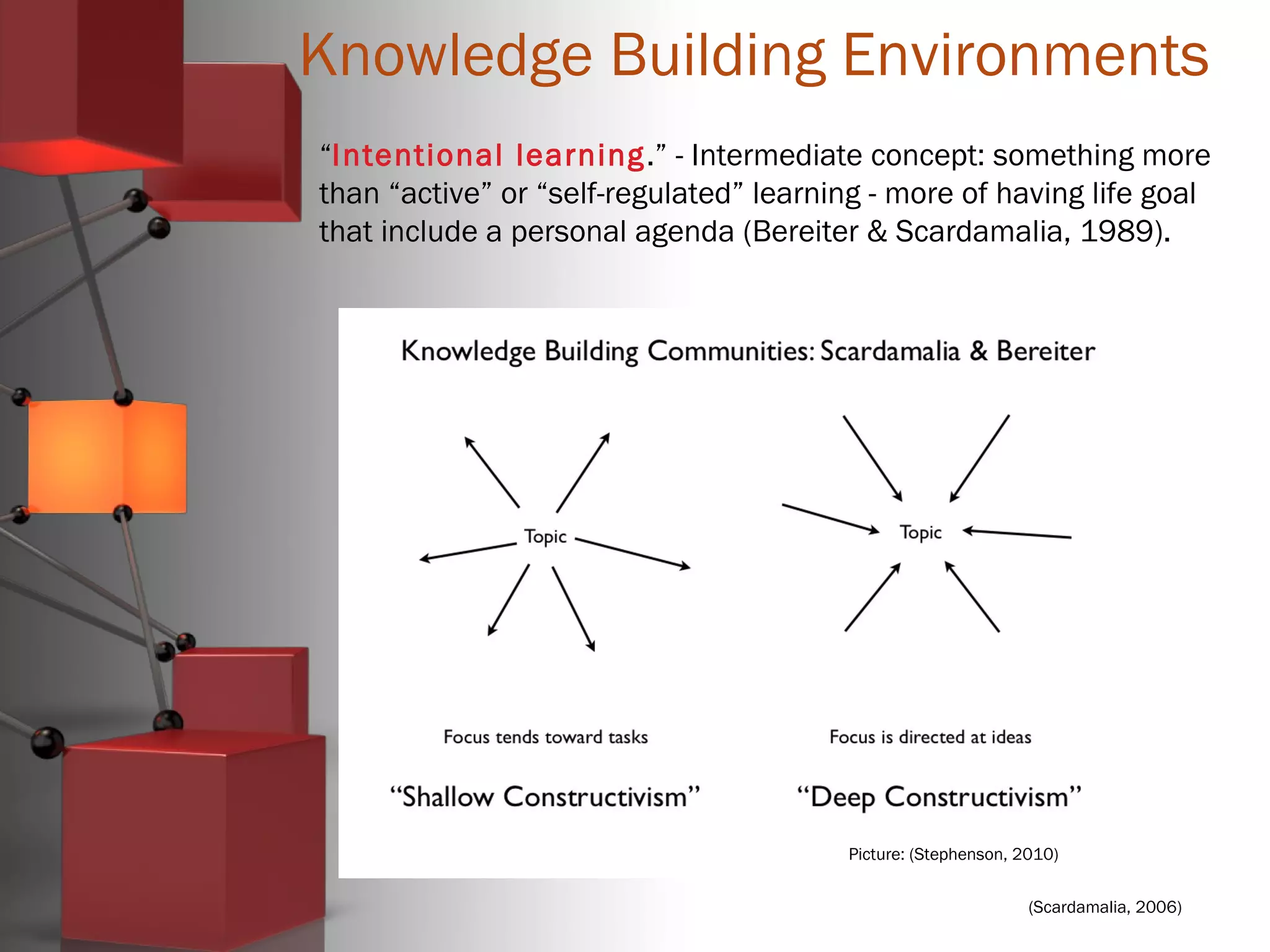
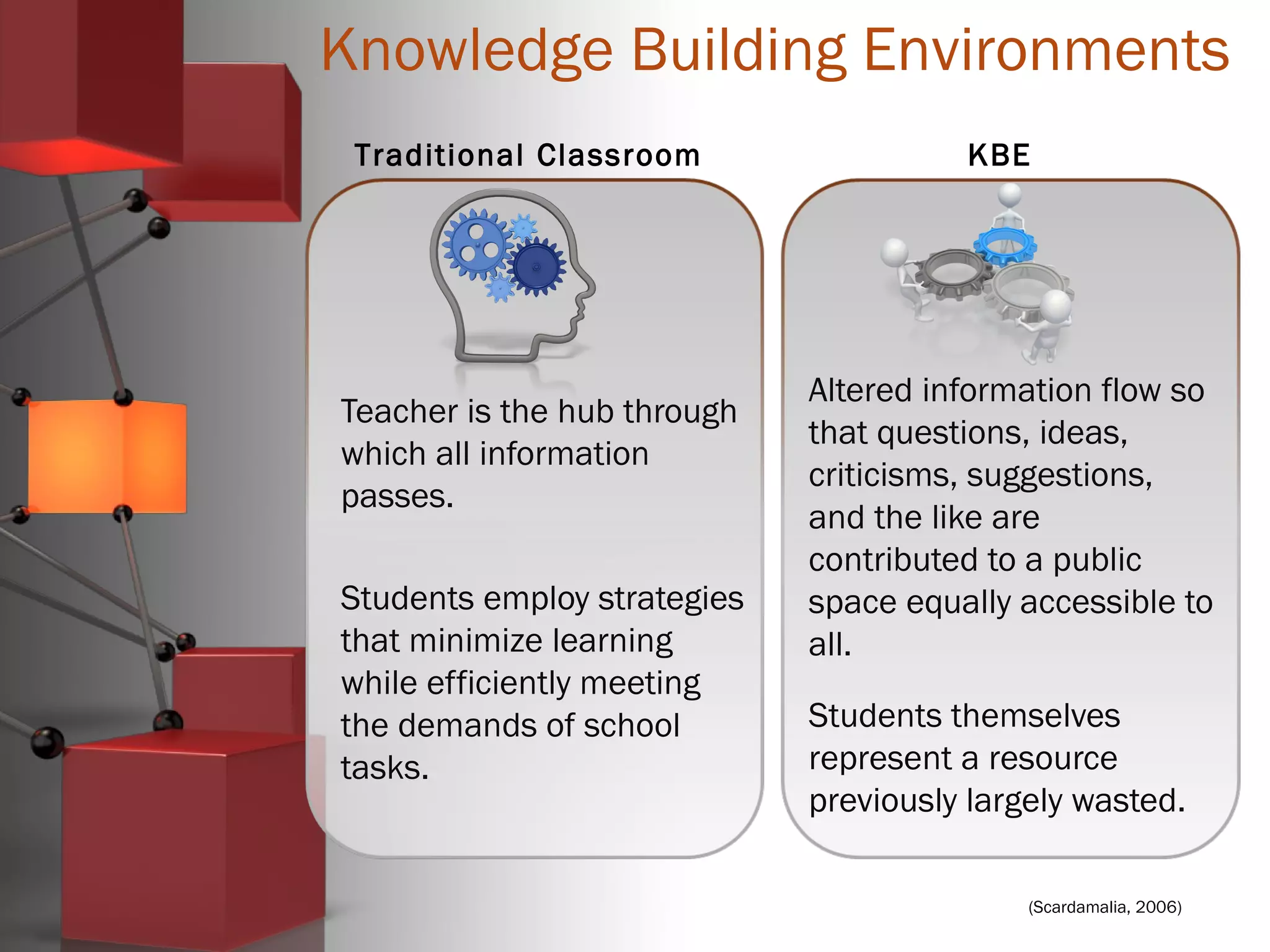
Carl Bereiter is a professor emeritus at the University of Toronto who co-founded the Institute for Knowledge Innovation & Technology. He developed CSILE, the first networked system for collaborative learning, and later Knowledge Forum. Knowledge building environments aim to treat students as members of a knowledge building community rather than just learners. They emphasize knowledge advancement for the community rather than individual achievement and focus on improving ideas rather than acquiring knowledge. Discourse is collaborative problem solving rather than argumentation, and emergent understandings are valued over authoritative knowledge.






















![References
Bereiter, C. (1985). Toward a solution of the learning paradox. Review of
Educational Research, 55, 201-226.
Bereiter, C. (1991). Implications of connectionism for thinking about rules.
Educational Researcher, 20, 10-16.
Bereiter, C. (1992). Referent-centered and problem-centered knowledge:
Elements of an educational epistemology. Interchange, 23, 337-362.
Bereiter, C. (1994). Implications of postmodernism for science, or, Science as
progressive discourse. Educational Psychologist, 29(1), 3-12.
Bereiter, C. (2002). Education and mind in the knowledge age. Mahwah, NJ:
Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (1989). Intentional learning as a goal of
instruction. In L. B. Resnick (Eds.), Knowing, learning, and instruction:
Essays in honor of Robert Glaser (pp. 361-392). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence
Erlbaum Associates.
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (2003). Learning to work creatively with
knowledge. In E. D. Corte, L. Verschaffel, N. Entwistle, & J. V. Merri ]
boer (Eds.), Powerful learning environments: Unravelling basic
components and dimensions (pp. 73-78). Oxford: Elsevier Science.
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (in press). Models of teaching and instruction
in the Knowledge Age. In P. A. Alexander and P. H. Winne (Eds.),
Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence
Erlbaum Associates.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/woodward-theorypresentation-101028125644-phpapp01/75/Bereiter-theory-presentation-38-2048.jpg)

![References
Hicks, D. (1996). Contextual inquiries: A discourse-oriented study of
classroom learning. In D. Hicks (Ed.), Discourse, learning and schooling
(pp. 104-141). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Koschmann, T. (2002). Dewey's contribution to the foundations of CSCL
research. In G. Stahl (Ed.), Computer support for collaborative learning:
Foundations for a CSCL community: Proceedings of CSCL 2002 (pp. 17-
22). Boulder, CO: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Lakatos, I. (1976). Proofs and refutations : The logic of mathematical
discovery. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Lave, J., & Wenger, E. (1991). Situated learning: Legitimate peripheral
participation. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
LeBaron, C. (2002). Technology does not exist independent of its use. In T.
Koschmann, R. Hall & N. Miyake (Eds.), CSCL 2: Carrying forward the
conversation (pp. 433-439). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
LeFever, L., & LeFever, S. (2007, April 23). RSS in plain English, [Video].
Retrieved from http://www.commoncraft.com/rss_plain_english
LeFever, L., & LeFever, S. (2007, May 29). Wikis in plain English, [Video].
Retrieved from http://www.commoncraft.com/video-wikis-plain-english
LeFever, L., & LeFever, S. (2007, November 30). Blogs in plain English,
[Video]. Retrieved from http://www.commoncraft.com/blogs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/woodward-theorypresentation-101028125644-phpapp01/75/Bereiter-theory-presentation-40-2048.jpg)
![References
LeFever, L., & LeFever, S. (2008, April 21). Podcasting in plain English,
[Video]. Retrieved from http://www.commoncraft.com/podcasting
LeFever, L., & LeFever, S. (2010, May 5). Wikipedia explained by common
craft [Video]. Retrieved from http://www.commoncraft.
com/wikipedia-video
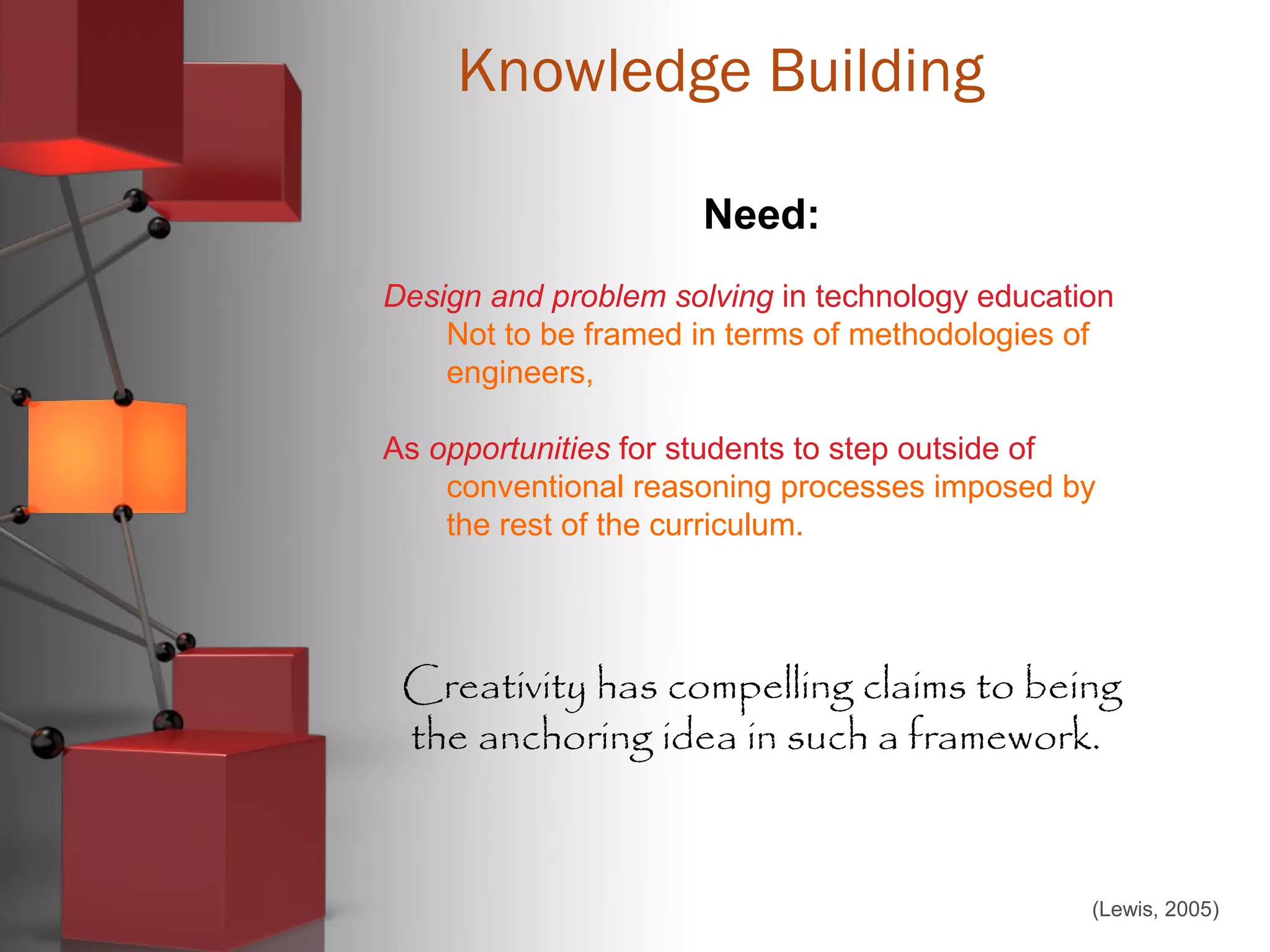
Lewis, T., (2005). Creativity – A framework for the design/problem solving
discourse in technology education. In Journal of Technology Education
17(1). Retrieved from
http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/ejournals/JTE/v17n1/lewis.html
Mader, S. (2008, March 29). How do you use a wiki? Poll result [Web log].
Retrieved from http://blogs.atlassian
.com/news/2008/03/how_do_you_use.html
Nicolopoulou, A., & Cole, M. (1993). Generation and transmission of shared
knowledge in the culture of collaborative learning: The fifth dimension,
its playworld and its institutional contexts. In E. Forman, N. Minnick &
C. A. Stone (Eds.), Contexts for learning: Sociocultural dynamics in
children's development. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Pascual-Leone , J. (1980). Constructive problems for constructive theories:
The current relevance of Piaget's work and a critique of information
processing simulation psychology. In R. H. Kluwe & H. Spada
(eds.), Developmental models of thinking (pp. 263-296). New York:
Academic Press.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/woodward-theorypresentation-101028125644-phpapp01/75/Bereiter-theory-presentation-41-2048.jpg)

