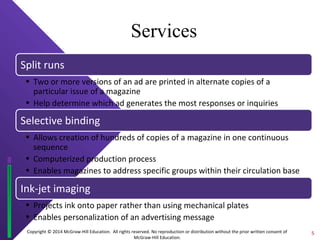
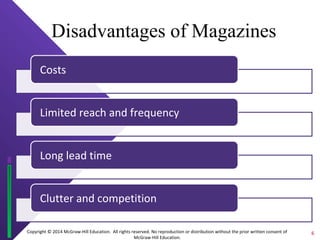
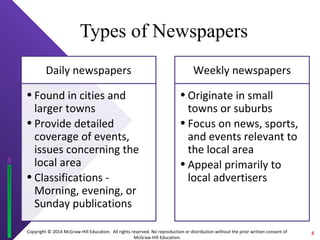
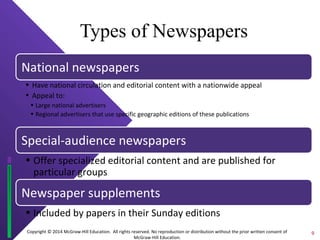
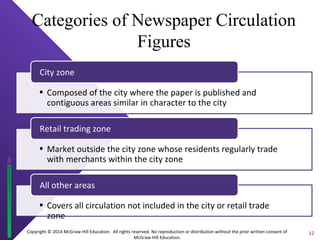
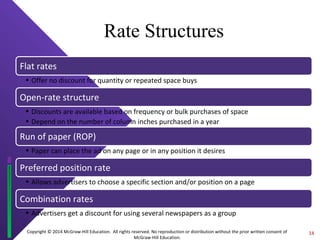
The document discusses print media evaluation, focusing on magazines and newspapers. It covers their advantages like selectivity and permanence for magazines. For newspapers, it discusses types like dailies and weeklies, and advertising methods like display and classified ads. Circulation figures and rates are also evaluated, such as guaranteed circulation for magazines and standard advertising units for newspapers.