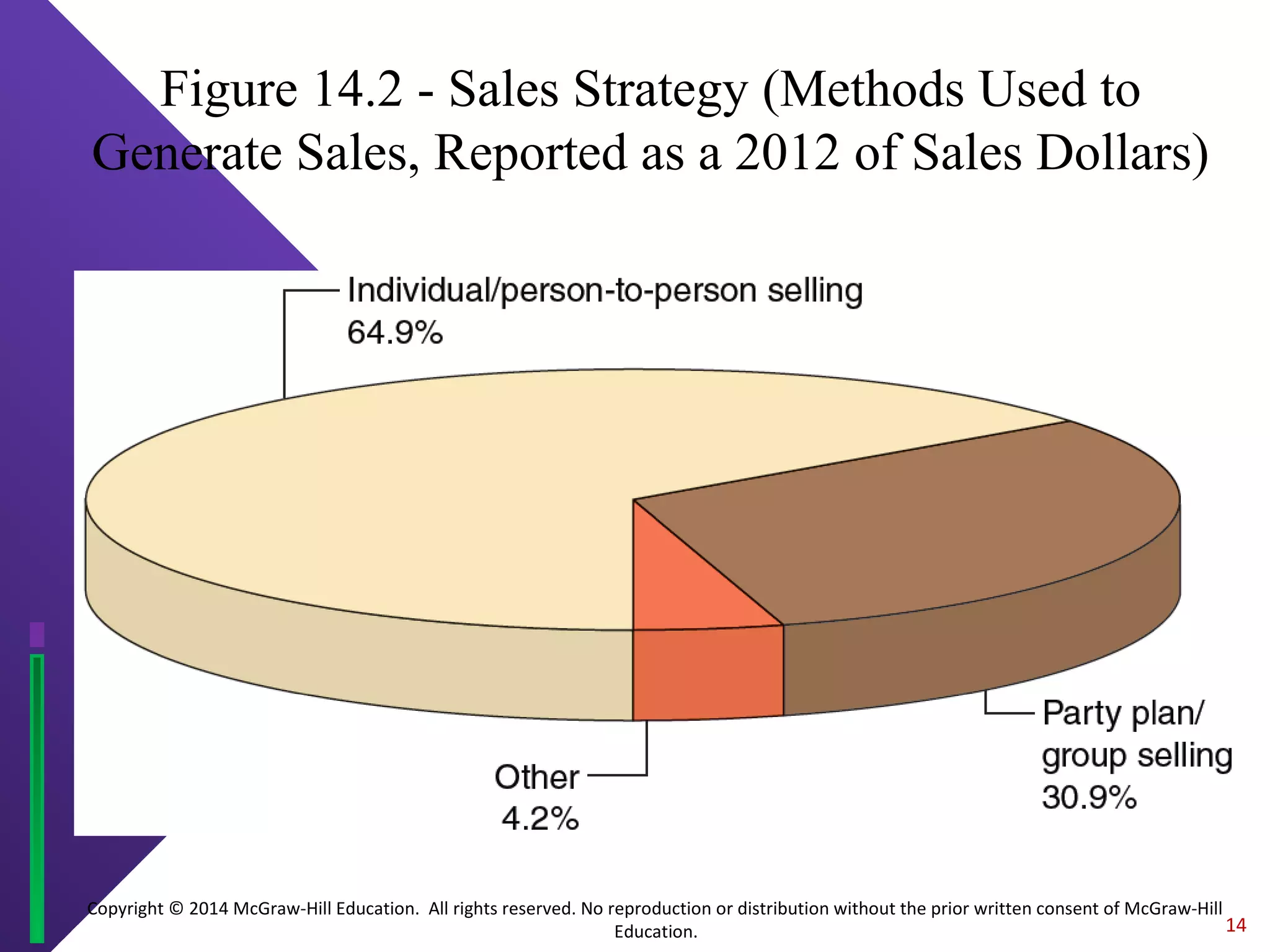
This document summarizes key aspects of direct marketing. It discusses direct marketing as an interactive system using advertising media to elicit a measurable response. Various direct marketing media are covered, including direct mail, catalogs, email, broadcast media, telemarketing and direct selling. Factors in the growth of direct marketing and how it fits into integrated marketing communications are also summarized. The document concludes with evaluating direct marketing effectiveness and advantages and disadvantages.