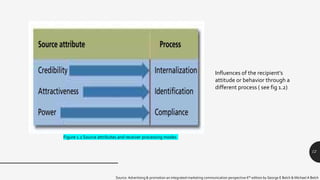
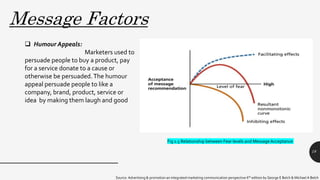
The document discusses key variables in the communication system relevant to advertising and promotional campaigns, focusing on source, message, and channel factors. It introduces the persuasion matrix, which helps marketers understand how these elements interact with consumer responses. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of source credibility, attractiveness, and message structure in effectively persuading consumers.