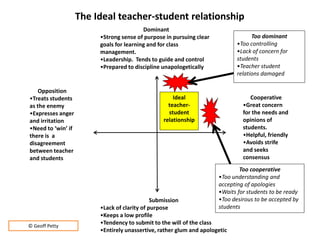
The document provides strategies for effective classroom behavior management. It recommends addressing all student behavior, understanding context, involving peers, setting clear expectations aligned with industry, sharing practices with colleagues, and leading by positive example. Ineffective strategies include being inconsistent, focusing only on visible problems, not assisting students, sending students away without follow up, and not collaborating with others. Key strategies shown to decrease disruptions are building positive teacher-student relationships, establishing clear rules and procedures, using disciplinary interventions appropriately, and developing self-awareness of one's mental state when responding to issues.