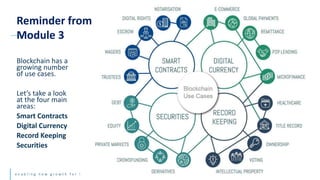
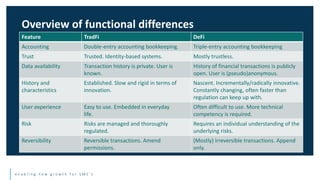
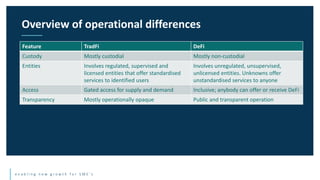
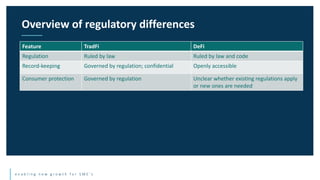
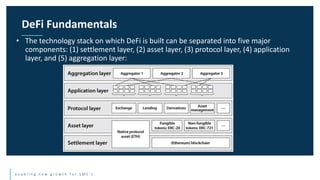
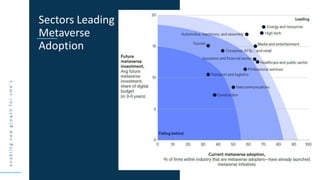
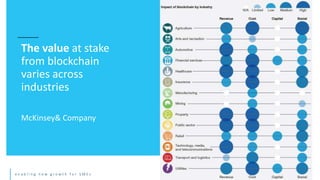
This document discusses the future of blockchain technology and applications. It describes how the European Commission aims to support the development of blockchain standards and applications in Europe. It then explores current and potential future uses of blockchain, including non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized finance (DeFi), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and decentralized metaverses. The module aims to help understand both the valuable aspects of blockchain as a technology as well as its potential scope in the future.