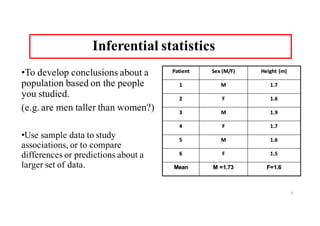
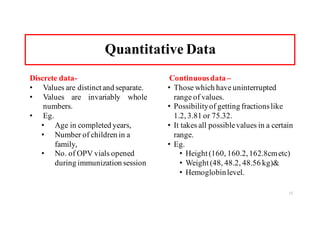
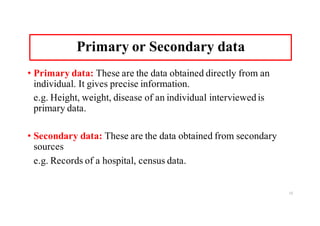
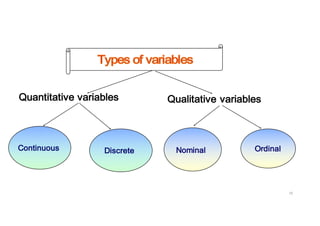
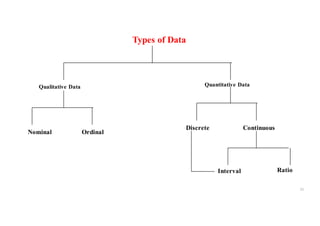
The document provides an introduction to biostatistics, covering essential concepts such as data, information, statistics, variables, and scales of measurement. It distinguishes between qualitative and quantitative data, and explains types of statistics like descriptive and inferential statistics. Additionally, it outlines the importance of understanding primary and secondary data, the role of variables in research, and the appropriate use of continuous versus categorical data.