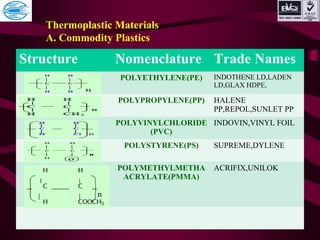
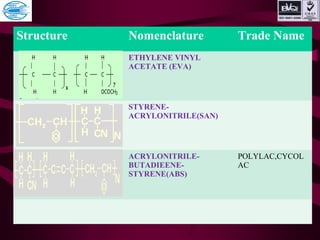
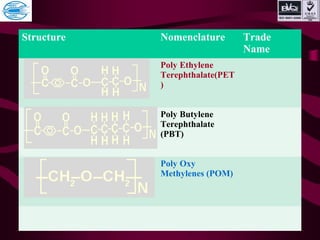
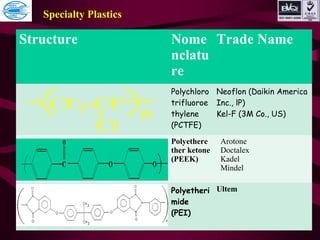
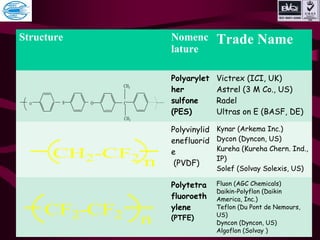
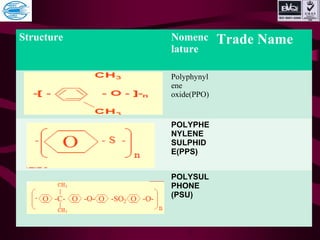
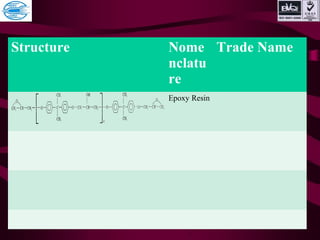
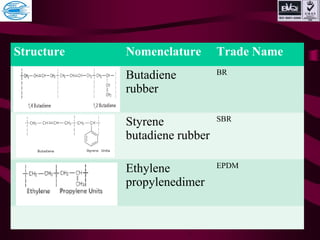
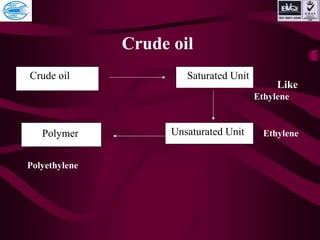
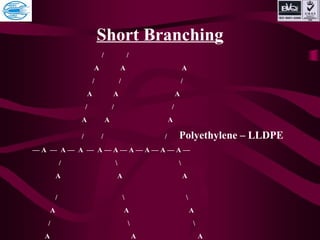
This document discusses various types of plastics and polymers. It provides 13 reasons why plastics are commonly used, including being lightweight, low cost, and available in various colors and forms. It then covers polymerization processes and how monomers link together to form polymers. The rest of the document categorizes and classifies different types of polymers based on their structure, manufacturing method, processing type, crystallinity, and applications. Key polymer types discussed include polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, nylons, and rubbers.




![Chemical unit should unsaturated like double or triple bond
between C — C atom.
Polymerization
n M —[M]n
—
Monomer Polymer
n No. of repeating unit
Monomer to Polymer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpolymer-170430061007/85/Basic-of-polymer-6-320.jpg)







![Types of Co-polymer
Alternative Co-polymer
— A — B — A — B —A — B — A — B — —PP
Random Co-Polymer
— A — B — A — A — A — B — B — A — A — A — A —
Block Co-Polymer
[— A — A — A — A — A — A —]n
[— B — B — B — B — B —]m
For example, PS-b-PMMA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpolymer-170430061007/85/Basic-of-polymer-15-320.jpg)


![ADDITION POLYMER
1. nM Polymerization [M]n
2. No by-product are formed.
• 3. Total molecular weight of monomer is
equivalent to molecular weight of polymer.
4. EXAMPLE
PE
PP
PVC
PS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpolymer-170430061007/85/Basic-of-polymer-18-320.jpg)
![CONDENSATION POLYMER
• n MA
+ n MB
[Polymer] + nH2
O
• During reaction by-products are formed e.g.
Water etc..
• Molecular weight of polymer is less than
molecular weight of total monomer.
• These polymer require pre-drying before
processing
EXAMPLE
• Nylon
• Polyester PET, PBT
• PC
• Thermoset](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpolymer-170430061007/85/Basic-of-polymer-19-320.jpg)