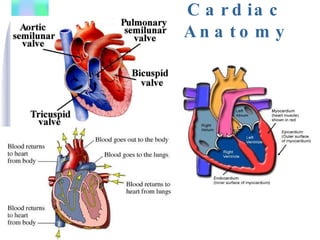
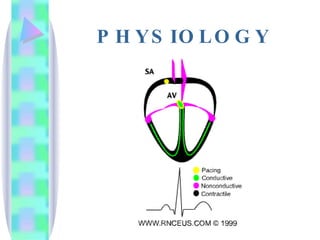
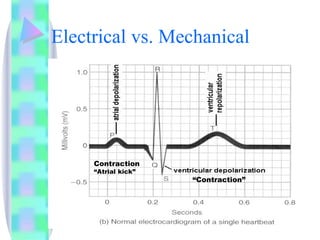
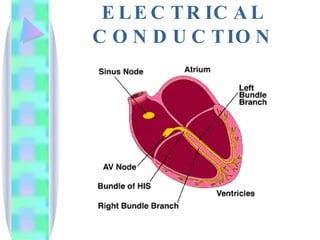
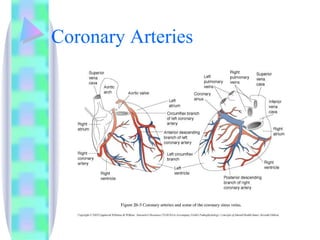
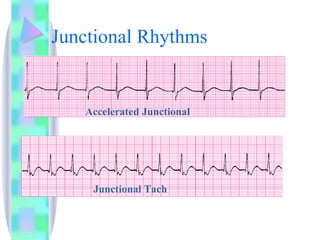
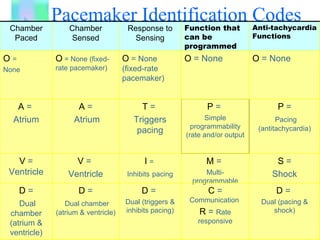
1. The document provides an overview of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and different types of cardiac rhythms including sinus rhythms, junctional rhythms, atrial rhythms, ventricular rhythms, and pacemaker rhythms.
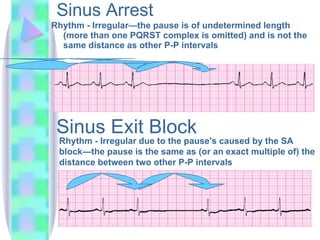
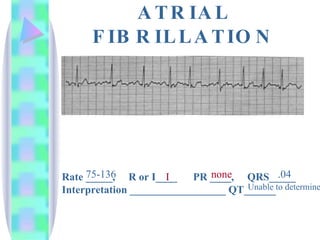
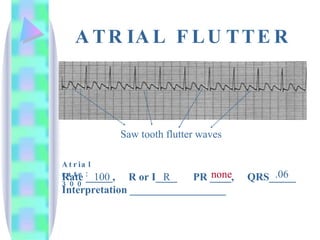
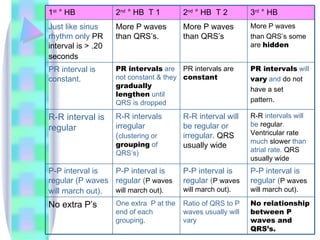
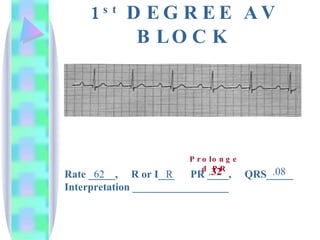
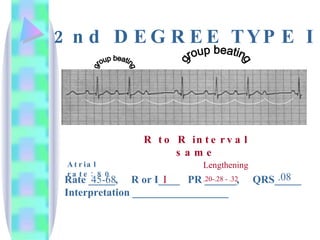
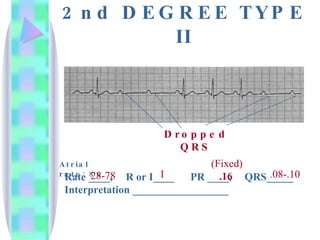
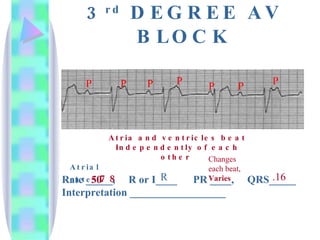
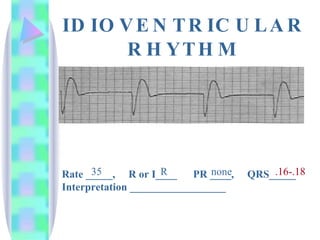
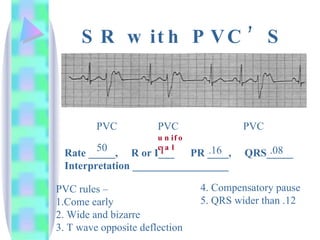
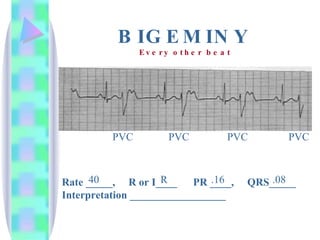
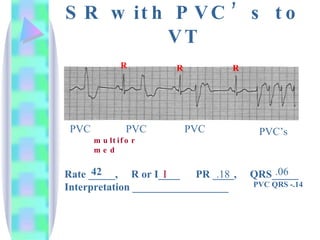
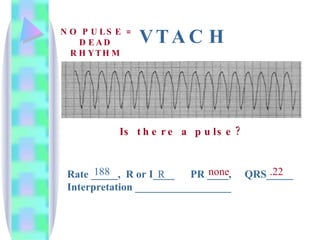
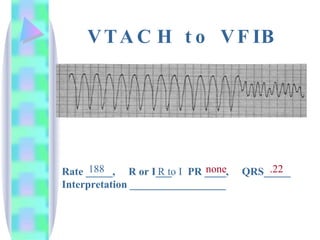
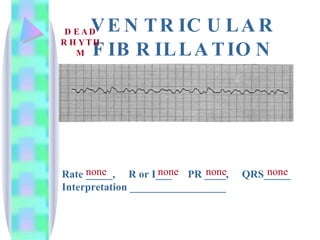
2. Key details are provided about identifying characteristics of different rhythms like atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, various types of heart block, premature ventricular contractions, ventricular tachycardia, and more.
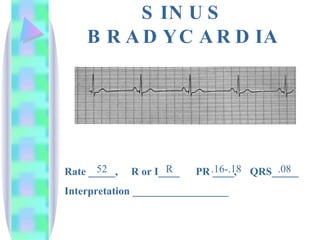
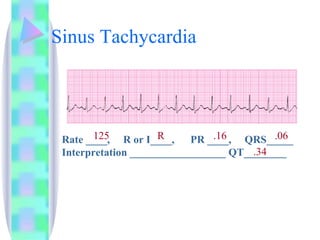
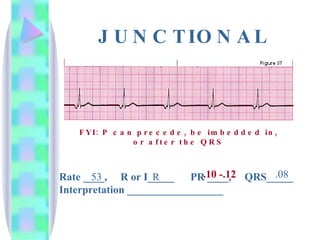
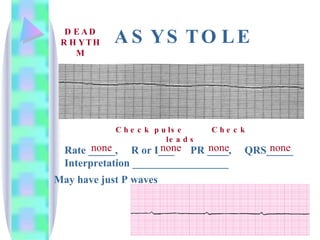
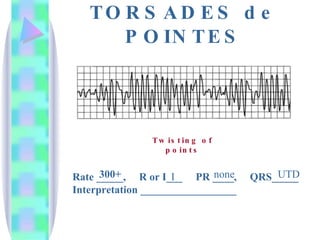
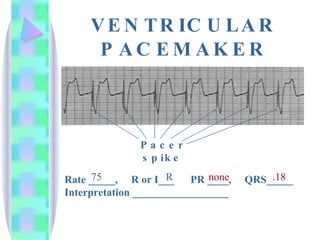
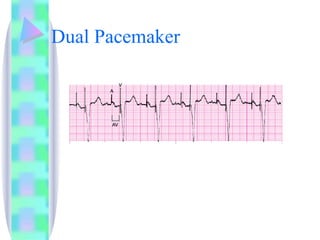
3. Guidelines are given for interpreting EKG strips and determining the rate, regularity, P wave presence, PR and QRS intervals, and overall rhythm interpretation.