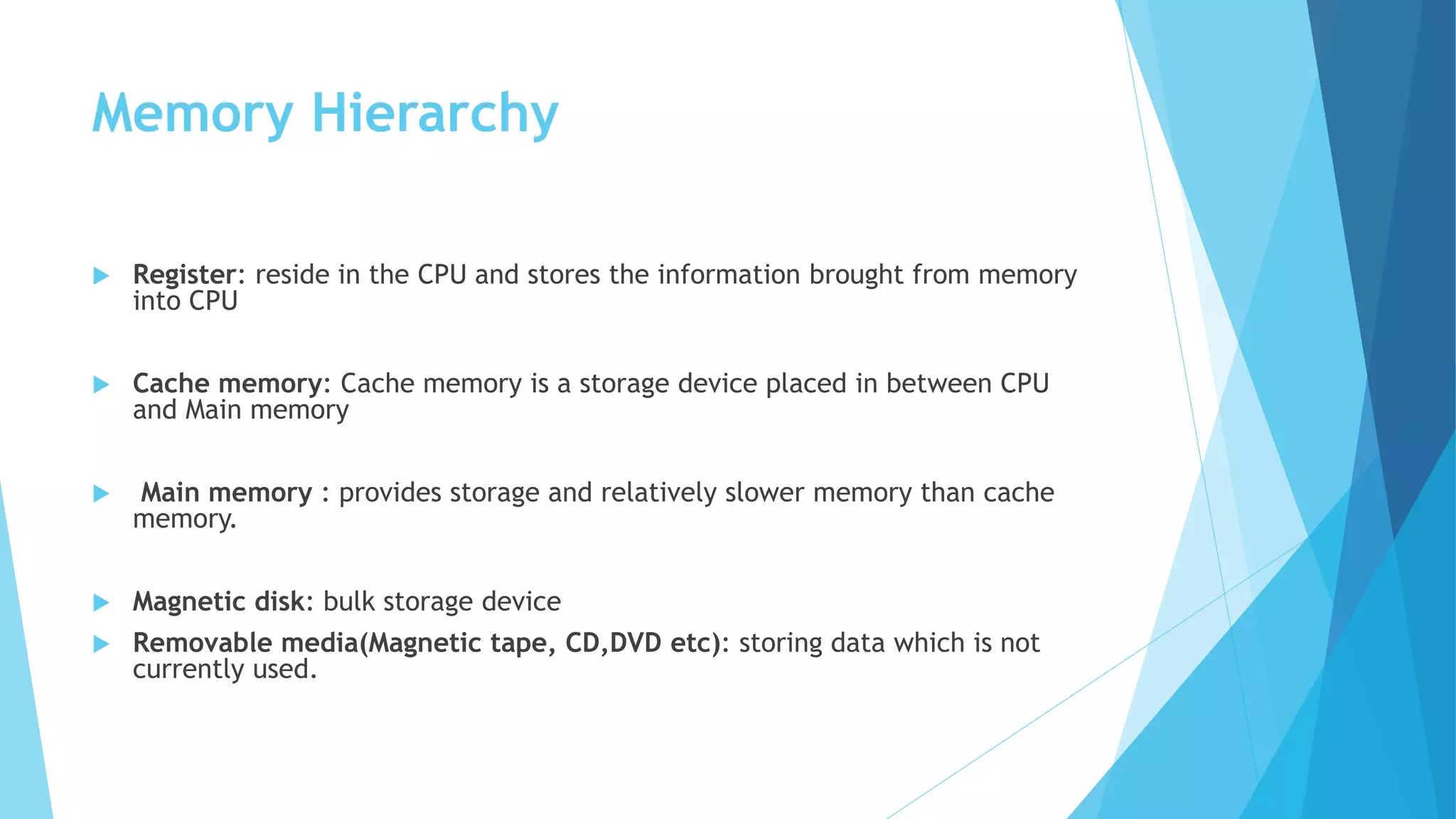
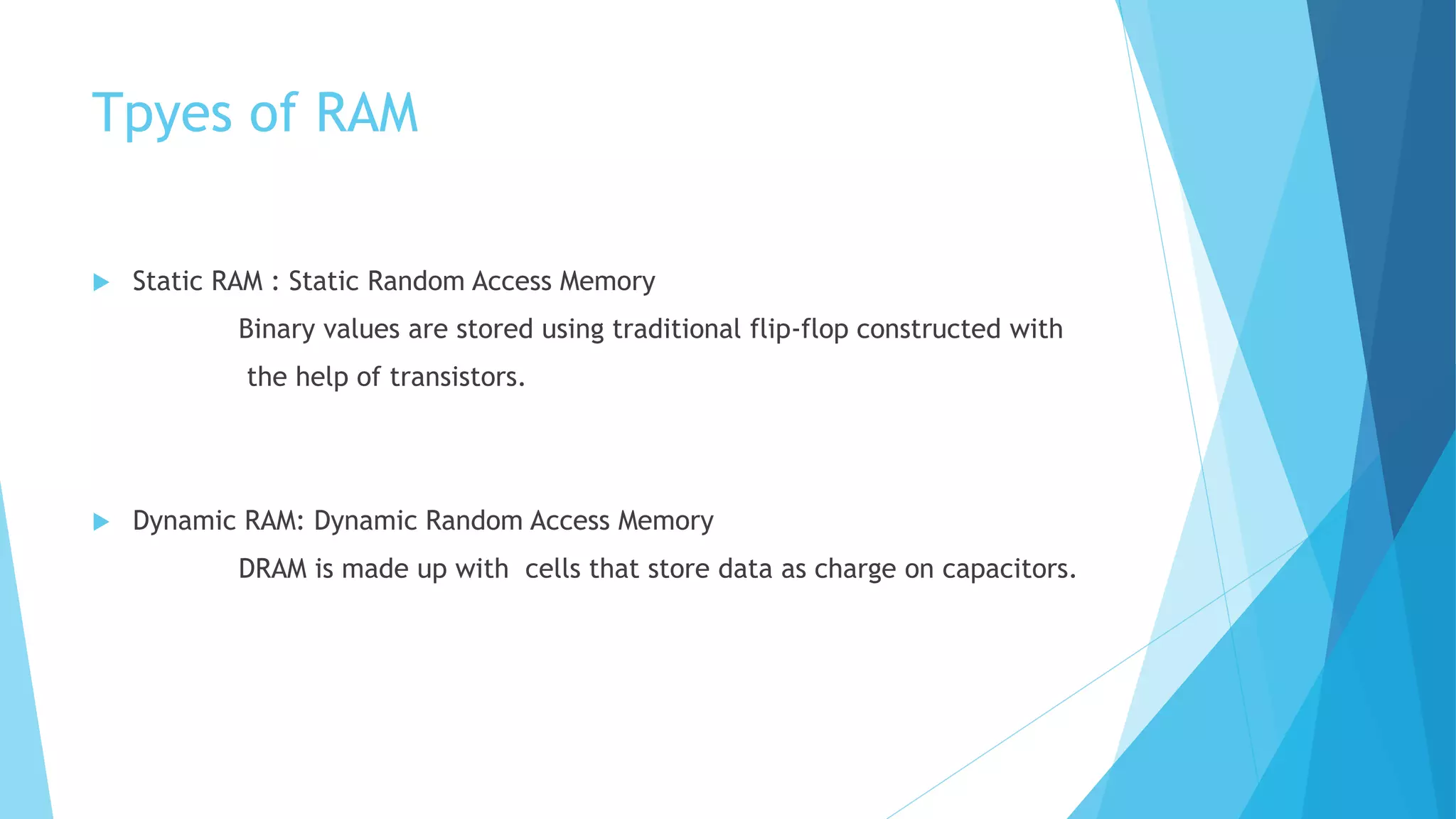
This document discusses basic concepts of memory. It describes the memory hierarchy from fastest to slowest as registers, cache memory, main memory, magnetic disks, and removable media. It also covers different types of read-only memory (ROM) like PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM. RAM types static RAM and dynamic RAM are compared in terms of cell design, density, cost, refresh requirements, and speed. Memory access time and cycle time are also defined.