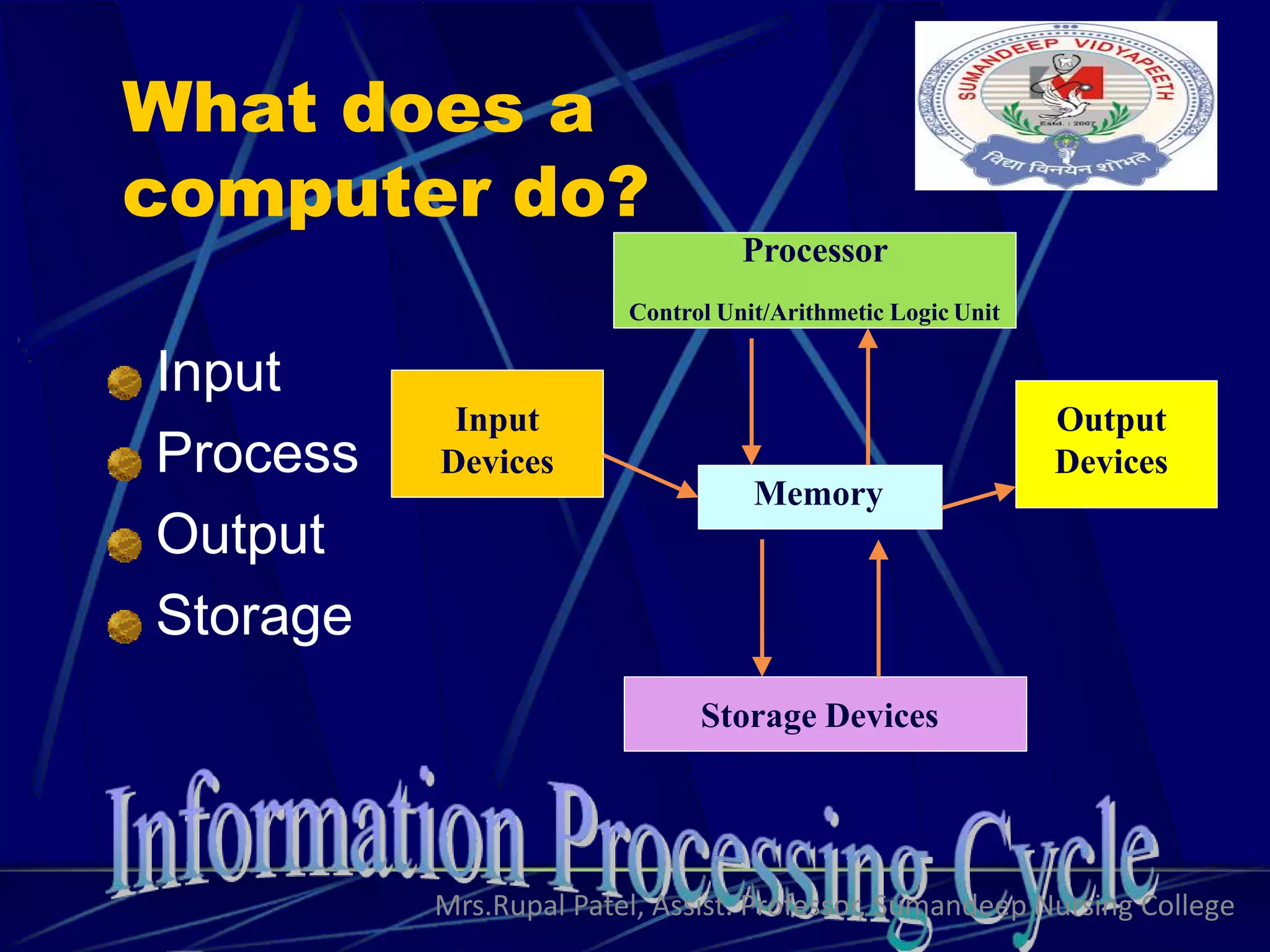
The document discusses basic computer concepts including definitions of a computer, common computer components, input and output devices, storage devices, the system unit, communications devices, types of computers, computer software, networks, the internet, the world wide web, web browsers, common applications, and electronic commerce. It provides descriptions and examples for each concept.