basic 1 lecture.ppt
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•3 views
The document summarizes key aspects of the vertebrate nervous system including: 1. It describes the two main cell types - neurons and neuroglia. Neurons transmit signals while neuroglia nourish and protect neurons. 2. It outlines the structure of neurons including dendrites, cell body, axon and terminal. It also describes different types of neurons. 3. It provides an overview of the electrical signals in neurons including action potentials and graded potentials and how they are used to communicate signals short and long distances.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Nerve impulse synapses

The nerve impulse is an electrical signal transmitted by neurons in the nervous system. It occurs when voltage-gated sodium channels in the neuron's membrane open, allowing sodium ions to flow into the neuron and depolarize it. This then causes voltage-gated potassium channels to open, allowing potassium ions to flow out and repolarize the neuron, restoring the resting potential. The nerve impulse travels rapidly along the axon via this process of local depolarization and repolarization. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic neuron, which can either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron, determining whether or not an impulse continues along the nerve circuit.
Neuron 

Neurons are electrically excitable cells that communicate with each other and the body. The human nervous system contains around 100 billion neurons. There are three main types of neurons - sensory neurons relay signals from sense organs to the central nervous system, motor neurons relay signals from the CNS to effector organs, and interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons. Each neuron has a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates an action potential down its axon via changes in membrane potential. Neurotransmitters are released at synapses to transmit signals between neurons.
Communication and Homeostasis (Part two)

Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and transmit this information as nerve impulses along neurons. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, generating an action potential if the threshold is reached. Myelination speeds up signal transmission along long neurons. Communication between neurons allows homeostasis to be maintained.
Neuron & its structural & functional type by Murtaza Syed

This document discusses neurons and their structural and functional types. It begins by defining neurons as the functional units of the nervous system, consisting of a cell body, axon, and dendrites. It then describes the three main types of neurons based on their structures - unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. The document also covers the functional classifications of neurons into sensory, motor and interneurons. It provides details on the structural components of neurons including axons, nerve fibers, and synapses. Finally, it explains the phases and propagation of action potentials in neurons.
neurons and synapses

Neurons transmit electrical signals along their axons via action potentials. At synapses, neurons interact and transmit signals to other neurons or effector cells. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, neurotransmitters are released, which can modulate the signal transmission. Propagation occurs as local currents depolarize successive parts of the axon, causing each section to reach the threshold potential and fire an action potential.
components of the xray machine- xray tube

They are produced when high-velocity electrons collide with the metal plates, thereby giving the energy as the X-Rays and themselves absorbed by the metal plate.
The X-Ray beam travels through the air and comes in contact with the body tissues, and produces an image on a metal film.
Soft tissue like organs and skin, cannot absorb the high-energy rays, and the beam passes through them.
Dense materials inside our bodies, like bones, absorb the radiation.he X-Rays properties are given below:
They have a shorter wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Requires high voltage to produce X-Rays.
They are used to capture the human skeleton defects.
They travel in a straight line and do not carry an electric charge with them.
They are capable of travelling in a vacuum.Medical science recognizes different types of X-Rays. A few important types of X-Rays are given in the points below.
Standard Computed Tomography
Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder X-ray
Teeth and bones X-rays
Chest X-rays
Lungs X-rays
Abdomen X-rays
synapse.pdf

This document provides an overview of synapses, including their definition, structure, function, types of transmission (electrical vs. chemical), neurotransmitters, and various properties like synaptic delay, fatigue, summation, and more. It discusses excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters and how convergence and divergence allow signals to be dispersed or combined. Clinical implications are that problems with synaptic transmission can cause diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
The synapse

This document provides an overview of synapses, including their definition, structure, function, types of transmission (electrical vs. chemical), neurotransmitters, and various properties like synaptic delay, fatigue, summation, and more. It discusses excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters and how convergence and divergence allow signals to be dispersed or combined. Clinical implications are that problems with synaptic transmission can cause diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
Recommended
Nerve impulse synapses

The nerve impulse is an electrical signal transmitted by neurons in the nervous system. It occurs when voltage-gated sodium channels in the neuron's membrane open, allowing sodium ions to flow into the neuron and depolarize it. This then causes voltage-gated potassium channels to open, allowing potassium ions to flow out and repolarize the neuron, restoring the resting potential. The nerve impulse travels rapidly along the axon via this process of local depolarization and repolarization. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic neuron, which can either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron, determining whether or not an impulse continues along the nerve circuit.
Neuron 

Neurons are electrically excitable cells that communicate with each other and the body. The human nervous system contains around 100 billion neurons. There are three main types of neurons - sensory neurons relay signals from sense organs to the central nervous system, motor neurons relay signals from the CNS to effector organs, and interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons. Each neuron has a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates an action potential down its axon via changes in membrane potential. Neurotransmitters are released at synapses to transmit signals between neurons.
Communication and Homeostasis (Part two)

Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and transmit this information as nerve impulses along neurons. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, generating an action potential if the threshold is reached. Myelination speeds up signal transmission along long neurons. Communication between neurons allows homeostasis to be maintained.
Neuron & its structural & functional type by Murtaza Syed

This document discusses neurons and their structural and functional types. It begins by defining neurons as the functional units of the nervous system, consisting of a cell body, axon, and dendrites. It then describes the three main types of neurons based on their structures - unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. The document also covers the functional classifications of neurons into sensory, motor and interneurons. It provides details on the structural components of neurons including axons, nerve fibers, and synapses. Finally, it explains the phases and propagation of action potentials in neurons.
neurons and synapses

Neurons transmit electrical signals along their axons via action potentials. At synapses, neurons interact and transmit signals to other neurons or effector cells. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, neurotransmitters are released, which can modulate the signal transmission. Propagation occurs as local currents depolarize successive parts of the axon, causing each section to reach the threshold potential and fire an action potential.
components of the xray machine- xray tube

They are produced when high-velocity electrons collide with the metal plates, thereby giving the energy as the X-Rays and themselves absorbed by the metal plate.
The X-Ray beam travels through the air and comes in contact with the body tissues, and produces an image on a metal film.
Soft tissue like organs and skin, cannot absorb the high-energy rays, and the beam passes through them.
Dense materials inside our bodies, like bones, absorb the radiation.he X-Rays properties are given below:
They have a shorter wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Requires high voltage to produce X-Rays.
They are used to capture the human skeleton defects.
They travel in a straight line and do not carry an electric charge with them.
They are capable of travelling in a vacuum.Medical science recognizes different types of X-Rays. A few important types of X-Rays are given in the points below.
Standard Computed Tomography
Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder X-ray
Teeth and bones X-rays
Chest X-rays
Lungs X-rays
Abdomen X-rays
synapse.pdf

This document provides an overview of synapses, including their definition, structure, function, types of transmission (electrical vs. chemical), neurotransmitters, and various properties like synaptic delay, fatigue, summation, and more. It discusses excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters and how convergence and divergence allow signals to be dispersed or combined. Clinical implications are that problems with synaptic transmission can cause diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
The synapse

This document provides an overview of synapses, including their definition, structure, function, types of transmission (electrical vs. chemical), neurotransmitters, and various properties like synaptic delay, fatigue, summation, and more. It discusses excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters and how convergence and divergence allow signals to be dispersed or combined. Clinical implications are that problems with synaptic transmission can cause diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
Neuronal conduction.pptx

Neural signals are transmitted through both electrical and chemical means. An electrical signal travels down a neuron's dendrites to its cell body. If the signal reaches the axon hillock's threshold, the axon is activated and fires, transmitting an electrical signal down the axon. At the axon terminals, neurotransmitters are released across the synaptic cleft to the next cell. The membrane potential, maintained by ion concentration gradients and sodium-potassium pumps, underlies the neuron's resting potential. When neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the post-synaptic cell, they generate graded excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials that are integrated and can trigger an all-or-none action potential for signal transmission along the ax
HAP 1 anatomy physiology and pathophysio

The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. It detects changes inside and outside the body and responds through electrical signals called nerve impulses. Neurons conduct these impulses while neuroglia provide support. There are two main types of synapses - electrical and chemical. At chemical synapses, a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic neuron and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Nerve Impulse Conduction & Synapses

Nerve Impulse is defined as a wave of electrical chemical changes across the neuron that helps in the generation of the action potential in response to the stimulus. This transmission of a nerve impulse across the neuron membrane as a result of a change in membrane potential is known as Nerve impulse conduction.
Mechanism of Nerve Impulse Conduction
Nerve impulse conduction is a major process occurring in the body responsible for organized functions of the body. So, for conduction of nerve impulse there are two mechanisms:
Continuous conduction
Saltatory conduction
Nervous Transduction

These slides contain the basic information and principle of nervous transduction, It also includes the information about the type of the neurons, structure of the neuron, resting and active membrane potential, synapes and events occurring in it, and introduction to the neurotransmitters.
Nervous coordination

The nervous system allows for coordination in the body through electrochemical signaling between neurons. It consists of neurons and neuroglia. Neurons receive and transmit signals via dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. There are three types of neurons - sensory, motor, and inter. A nerve impulse is generated through changes in the neuron's membrane potential and the opening and closing of ion channels, causing the signal to propagate along the axon. At a synapse, neurotransmitters transmit the signal to the next neuron. Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli.
Neurotransmission

Neurotransmission involves the release of neurotransmitters from the axon terminal of one neuron that bind to and react with receptors on another neuron. Nerve signals travel as electrical nerve impulses along neurons. A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals. When a neuron is stimulated, sodium ions enter the cell causing an action potential to propagate along the axon. At synaptic junctions, neurotransmitters are released from vesicles and bind to receptors, causing excitation or inhibition of the downstream neuron. Neurotransmitters are then removed from the synapse to terminate signaling.
Cell membrane potential

1) Neuron membranes maintain a resting potential through ion gradients established by sodium-potassium pumps.
2) When stimulated, voltage-gated ion channels allow sodium to enter and potassium to leave, depolarizing the membrane and initiating an action potential.
3) Action potentials propagate as waves down axons through local currents, transmitting nerve impulses as electrical signals along the length of neurons.
NERVE PHYSIOLOGY

DESCRIBES THE ACTION POTENTIAL OCCURING IN THE NERVE. IT ALSO TACKLES ON THE NUERON AND ITS 3 BASIC PARTS NAMELY 1)DENDRITES 2) BODY 3) AXON
NeuronsJFJKJFJKDFJKJKFKJGJKERGJEFGJEGJKEDJKFKDFDKF.pptx

Neurons have four main parts: dendrites, axon, presynaptic terminals, and soma. The resting membrane potential of a neuron is maintained by sodium-potassium pumps and leak channels. When the membrane potential changes enough to reach the threshold, an action potential is generated and propagated down the axon via voltage-gated ion channels. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic terminal and bind to receptors, producing excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. There are ongoing advances in understanding neural stem cells and their potential role in brain repair.
Nerve Impulse 

An action potential occurs when a neuron reaches its membrane threshold. This causes sodium channels to open, allowing sodium ions to enter the neuron and depolarize the membrane. Then, potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit the neuron and repolarize the membrane back to its resting potential. This process of depolarization and repolarization propagates as a self-sustaining wave along the neuron, conducting the nerve impulse. Myelinated neurons enhance conduction velocity through salutatory conduction, where the action potential jumps between nodes of Ranvier.
Biology- Control and Coordination.pdf

This document discusses the nervous system and how it coordinates the activities of sensory receptors, decision making in the central nervous system, and effectors like muscles and glands. It describes the three types of neurons - sensory, intermediate, and motor neurons. It explains how motor neurons transmit impulses from the CNS to effectors and discusses their structure. The document also covers myelin sheaths, nodes of Ranvier, reflex arcs, impulse transmission through action potentials, and synaptic transmission between neurons.
Neurophysiology kritika

The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system. It describes the structure and types of neurons, how nerve impulses are conducted and propagated, and the mechanisms of pain perception and transmission. Specifically, it covers the electrochemistry of the nerve membrane and action potentials, impulse propagation in myelinated and unmyelinated nerves, and theories of pain including the gate control theory and chemical mediators of pain such as bradykinin and substance P.
lec 5 NERVOUS SYSTEM_SYNAPSES_PPT_AKUNGA.pptx

The document discusses the nervous system and synapses. It describes how synapses allow neurons to communicate via either electrical or chemical transmission. At chemical synapses, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing changes in its membrane potential. Excitatory synapses cause depolarization via EPSPs, while inhibitory synapses cause hyperpolarization or stabilization via IPSPs. Spatial and temporal summation of EPSPs at synapses can bring the postsynaptic neuron to threshold to fire an action potential. Neurotransmitters are removed from synapses via reuptake or degradation to terminate signals. Drugs can modify synaptic transmission by affecting neurotransmitter synthesis, storage, release, receptor activation, or reupt
Local anesthesia

Local anesthesia is the reversible loss of sensation in a body area caused by inhibiting nerve conduction. This document discusses the introduction, composition, mechanism of action, and dose calculation of local anesthesia. It covers topics like nerve physiology, electrophysiology of nerve conduction, impulse propagation, and the site and mode of action of local anesthetics. The document provides details on how local anesthetics work by blocking sodium channels and raising the firing threshold of nerves.
Homeostasis Topic 6.5 

The document summarizes the structure and function of the human nervous system. It describes the three main types of neurons - sensory, motor, and interneurons - and how they transmit nerve impulses via electrical and chemical signals. It also explains the process of synaptic transmission between neurons and how homeostasis is maintained through negative feedback mechanisms that monitor and respond to changes in the internal environment.
Generation and conduction of action potential.

The document discusses the generation and conduction of action potentials in neurons. It covers several key topics:
1) An action potential is initiated when the membrane potential reaches threshold, opening voltage-gated sodium channels and causing rapid sodium influx. This depolarizes the membrane.
2) The membrane then repolarizes as sodium channels close and potassium channels open, allowing potassium efflux.
3) Action potentials propagate along axons via contiguous conduction, with adjacent segments of membrane depolarizing sequentially. Myelination allows faster saltatory conduction.
4) At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic terminals and bind to receptors, sometimes depolarizing the postsynaptic cell and propagating the impulse.
Nerve physiology

The document summarizes key aspects of nerve physiology:
- The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is further divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
- A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. Neurons transmit electrical signals called action potentials via their axons.
- An action potential occurs when a neuron is stimulated - sodium ions rush into the neuron, depolarizing the membrane. Then potassium ions exit, repolarizing the membrane back to its resting potential. This allows signals to propagate along axons.
Nerve and muscle physiology .ppt

The document discusses the basics of neural communication and motor control. It describes how neural communication works, including how the resting potential is established across cell membranes and how action potentials are generated and propagated. It explains how ions are involved in maintaining the resting potential and how action potentials are initiated by sodium ion influx and terminated by potassium ion efflux. It also discusses how myelination allows for faster saltatory conduction along axons. Additionally, it summarizes the key aspects of synaptic transmission, including the roles of neurotransmitters, ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, and how excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials influence neural signaling. Finally, it provides an overview of the hierarchical organization of the motor system and identifies primary motor cortex, prem
Nervous system and sense organs

The document discusses the nervous system and sense organs. It begins by describing the basic functions and components of the nervous system, including neurons, action potentials, and synapses. It then provides details on the types of neurons, glial cells, and how the resting membrane potential and action potentials work. The document also discusses the evolution of nervous systems in invertebrates and vertebrates. It concludes by describing the peripheral nervous system and different types of sense organs.
Communication-I.pptx

This presentation contains the data about neurons, its types and the nerve conduction process extracted from Hickman's Integrated Principles of Zoology
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/kqbnxVAZs-0
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/SINlygW1Mpc
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
More Related Content
Similar to basic 1 lecture.ppt
Neuronal conduction.pptx

Neural signals are transmitted through both electrical and chemical means. An electrical signal travels down a neuron's dendrites to its cell body. If the signal reaches the axon hillock's threshold, the axon is activated and fires, transmitting an electrical signal down the axon. At the axon terminals, neurotransmitters are released across the synaptic cleft to the next cell. The membrane potential, maintained by ion concentration gradients and sodium-potassium pumps, underlies the neuron's resting potential. When neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the post-synaptic cell, they generate graded excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials that are integrated and can trigger an all-or-none action potential for signal transmission along the ax
HAP 1 anatomy physiology and pathophysio

The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. It detects changes inside and outside the body and responds through electrical signals called nerve impulses. Neurons conduct these impulses while neuroglia provide support. There are two main types of synapses - electrical and chemical. At chemical synapses, a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic neuron and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Nerve Impulse Conduction & Synapses

Nerve Impulse is defined as a wave of electrical chemical changes across the neuron that helps in the generation of the action potential in response to the stimulus. This transmission of a nerve impulse across the neuron membrane as a result of a change in membrane potential is known as Nerve impulse conduction.
Mechanism of Nerve Impulse Conduction
Nerve impulse conduction is a major process occurring in the body responsible for organized functions of the body. So, for conduction of nerve impulse there are two mechanisms:
Continuous conduction
Saltatory conduction
Nervous Transduction

These slides contain the basic information and principle of nervous transduction, It also includes the information about the type of the neurons, structure of the neuron, resting and active membrane potential, synapes and events occurring in it, and introduction to the neurotransmitters.
Nervous coordination

The nervous system allows for coordination in the body through electrochemical signaling between neurons. It consists of neurons and neuroglia. Neurons receive and transmit signals via dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. There are three types of neurons - sensory, motor, and inter. A nerve impulse is generated through changes in the neuron's membrane potential and the opening and closing of ion channels, causing the signal to propagate along the axon. At a synapse, neurotransmitters transmit the signal to the next neuron. Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli.
Neurotransmission

Neurotransmission involves the release of neurotransmitters from the axon terminal of one neuron that bind to and react with receptors on another neuron. Nerve signals travel as electrical nerve impulses along neurons. A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals. When a neuron is stimulated, sodium ions enter the cell causing an action potential to propagate along the axon. At synaptic junctions, neurotransmitters are released from vesicles and bind to receptors, causing excitation or inhibition of the downstream neuron. Neurotransmitters are then removed from the synapse to terminate signaling.
Cell membrane potential

1) Neuron membranes maintain a resting potential through ion gradients established by sodium-potassium pumps.
2) When stimulated, voltage-gated ion channels allow sodium to enter and potassium to leave, depolarizing the membrane and initiating an action potential.
3) Action potentials propagate as waves down axons through local currents, transmitting nerve impulses as electrical signals along the length of neurons.
NERVE PHYSIOLOGY

DESCRIBES THE ACTION POTENTIAL OCCURING IN THE NERVE. IT ALSO TACKLES ON THE NUERON AND ITS 3 BASIC PARTS NAMELY 1)DENDRITES 2) BODY 3) AXON
NeuronsJFJKJFJKDFJKJKFKJGJKERGJEFGJEGJKEDJKFKDFDKF.pptx

Neurons have four main parts: dendrites, axon, presynaptic terminals, and soma. The resting membrane potential of a neuron is maintained by sodium-potassium pumps and leak channels. When the membrane potential changes enough to reach the threshold, an action potential is generated and propagated down the axon via voltage-gated ion channels. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic terminal and bind to receptors, producing excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. There are ongoing advances in understanding neural stem cells and their potential role in brain repair.
Nerve Impulse 

An action potential occurs when a neuron reaches its membrane threshold. This causes sodium channels to open, allowing sodium ions to enter the neuron and depolarize the membrane. Then, potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit the neuron and repolarize the membrane back to its resting potential. This process of depolarization and repolarization propagates as a self-sustaining wave along the neuron, conducting the nerve impulse. Myelinated neurons enhance conduction velocity through salutatory conduction, where the action potential jumps between nodes of Ranvier.
Biology- Control and Coordination.pdf

This document discusses the nervous system and how it coordinates the activities of sensory receptors, decision making in the central nervous system, and effectors like muscles and glands. It describes the three types of neurons - sensory, intermediate, and motor neurons. It explains how motor neurons transmit impulses from the CNS to effectors and discusses their structure. The document also covers myelin sheaths, nodes of Ranvier, reflex arcs, impulse transmission through action potentials, and synaptic transmission between neurons.
Neurophysiology kritika

The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system. It describes the structure and types of neurons, how nerve impulses are conducted and propagated, and the mechanisms of pain perception and transmission. Specifically, it covers the electrochemistry of the nerve membrane and action potentials, impulse propagation in myelinated and unmyelinated nerves, and theories of pain including the gate control theory and chemical mediators of pain such as bradykinin and substance P.
lec 5 NERVOUS SYSTEM_SYNAPSES_PPT_AKUNGA.pptx

The document discusses the nervous system and synapses. It describes how synapses allow neurons to communicate via either electrical or chemical transmission. At chemical synapses, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing changes in its membrane potential. Excitatory synapses cause depolarization via EPSPs, while inhibitory synapses cause hyperpolarization or stabilization via IPSPs. Spatial and temporal summation of EPSPs at synapses can bring the postsynaptic neuron to threshold to fire an action potential. Neurotransmitters are removed from synapses via reuptake or degradation to terminate signals. Drugs can modify synaptic transmission by affecting neurotransmitter synthesis, storage, release, receptor activation, or reupt
Local anesthesia

Local anesthesia is the reversible loss of sensation in a body area caused by inhibiting nerve conduction. This document discusses the introduction, composition, mechanism of action, and dose calculation of local anesthesia. It covers topics like nerve physiology, electrophysiology of nerve conduction, impulse propagation, and the site and mode of action of local anesthetics. The document provides details on how local anesthetics work by blocking sodium channels and raising the firing threshold of nerves.
Homeostasis Topic 6.5 

The document summarizes the structure and function of the human nervous system. It describes the three main types of neurons - sensory, motor, and interneurons - and how they transmit nerve impulses via electrical and chemical signals. It also explains the process of synaptic transmission between neurons and how homeostasis is maintained through negative feedback mechanisms that monitor and respond to changes in the internal environment.
Generation and conduction of action potential.

The document discusses the generation and conduction of action potentials in neurons. It covers several key topics:
1) An action potential is initiated when the membrane potential reaches threshold, opening voltage-gated sodium channels and causing rapid sodium influx. This depolarizes the membrane.
2) The membrane then repolarizes as sodium channels close and potassium channels open, allowing potassium efflux.
3) Action potentials propagate along axons via contiguous conduction, with adjacent segments of membrane depolarizing sequentially. Myelination allows faster saltatory conduction.
4) At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic terminals and bind to receptors, sometimes depolarizing the postsynaptic cell and propagating the impulse.
Nerve physiology

The document summarizes key aspects of nerve physiology:
- The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is further divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
- A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. Neurons transmit electrical signals called action potentials via their axons.
- An action potential occurs when a neuron is stimulated - sodium ions rush into the neuron, depolarizing the membrane. Then potassium ions exit, repolarizing the membrane back to its resting potential. This allows signals to propagate along axons.
Nerve and muscle physiology .ppt

The document discusses the basics of neural communication and motor control. It describes how neural communication works, including how the resting potential is established across cell membranes and how action potentials are generated and propagated. It explains how ions are involved in maintaining the resting potential and how action potentials are initiated by sodium ion influx and terminated by potassium ion efflux. It also discusses how myelination allows for faster saltatory conduction along axons. Additionally, it summarizes the key aspects of synaptic transmission, including the roles of neurotransmitters, ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, and how excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials influence neural signaling. Finally, it provides an overview of the hierarchical organization of the motor system and identifies primary motor cortex, prem
Nervous system and sense organs

The document discusses the nervous system and sense organs. It begins by describing the basic functions and components of the nervous system, including neurons, action potentials, and synapses. It then provides details on the types of neurons, glial cells, and how the resting membrane potential and action potentials work. The document also discusses the evolution of nervous systems in invertebrates and vertebrates. It concludes by describing the peripheral nervous system and different types of sense organs.
Communication-I.pptx

This presentation contains the data about neurons, its types and the nerve conduction process extracted from Hickman's Integrated Principles of Zoology
Similar to basic 1 lecture.ppt (20)
NeuronsJFJKJFJKDFJKJKFKJGJKERGJEFGJEGJKEDJKFKDFDKF.pptx

NeuronsJFJKJFJKDFJKJKFKJGJKERGJEFGJEGJKEDJKFKDFDKF.pptx
Recently uploaded
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/kqbnxVAZs-0
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/SINlygW1Mpc
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
The Best Ayurvedic Antacid Tablets in India

Treat the symptoms of indigestion, heartburn and stomach reflux with the 10 Best Ayurvedic Antacid Tablets in India.
Top-Vitamin-Supplement-Brands-in-India List

Swisschem Dermacare provides the Top 10 Vitamin Supplement Brands in India. To know more about us give us call at our official number
Ketone bodies and metabolism-biochemistry

This slide consists of all the topics of ketone . This can be used for exam purpose for writing about Diabetic keto acidosis etc . Thank you
Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...

Learn about body grief and ways to cope with it. We will also explore methods to heal from this challenging experience.
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

It includes regulation of combination products and medical devices. FDA and industry liaisons.
A Classical Text Review on Basavarajeeyam

Basavarajeeyam is a Sreshta Sangraha grantha (Compiled book ), written by Neelkanta kotturu Basavaraja Virachita. It contains 25 Prakaranas, First 24 Chapters related to Rogas& 25th to Rasadravyas.
Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx

In some case, your chronic prostatitis may be related to over-masturbation. Generally, natural medicine Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill can help mee get a cure.
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Local Advanced Lung Cancer: Artificial Intelligence, Synergetics, Complex Sys...

Overall life span (LS) was 1671.7±1721.6 days and cumulative 5YS reached 62.4%, 10 years – 50.4%, 20 years – 44.6%. 94 LCP lived more than 5 years without cancer (LS=2958.6±1723.6 days), 22 – more than 10 years (LS=5571±1841.8 days). 67 LCP died because of LC (LS=471.9±344 days). AT significantly improved 5YS (68% vs. 53.7%) (P=0.028 by log-rank test). Cox modeling displayed that 5YS of LCP significantly depended on: N0-N12, T3-4, blood cell circuit, cell ratio factors (ratio between cancer cells-CC and blood cells subpopulations), LC cell dynamics, recalcification time, heparin tolerance, prothrombin index, protein, AT, procedure type (P=0.000-0.031). Neural networks, genetic algorithm selection and bootstrap simulation revealed relationships between 5YS and N0-12 (rank=1), thrombocytes/CC (rank=2), segmented neutrophils/CC (3), eosinophils/CC (4), erythrocytes/CC (5), healthy cells/CC (6), lymphocytes/CC (7), stick neutrophils/CC (8), leucocytes/CC (9), monocytes/CC (10). Correct prediction of 5YS was 100% by neural networks computing (error=0.000; area under ROC curve=1.0).
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis is an increasing cause of morbidity among the elderly.
In this document , a brief outline of osteoporosis is given , including the risk factors of osteoporosis fractures , the indications for testing bone mineral density and the management of osteoporosis
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Swisschem Dermacare has mentioned the List of The Best Antifungal Soap In India 2022. All of these soaps are trusted by various Dermatology Experts.
Recently uploaded (20)
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad
Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...

Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx
Vestibulocochlear Nerve by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Vestibulocochlear Nerve by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx

Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx
CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf

CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes
Local Advanced Lung Cancer: Artificial Intelligence, Synergetics, Complex Sys...

Local Advanced Lung Cancer: Artificial Intelligence, Synergetics, Complex Sys...
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India
basic 1 lecture.ppt
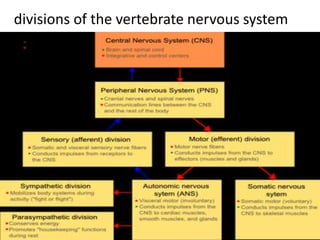
- 1. divisions of the vertebrate nervous system
- 4. NERVOUS SYSTEM It consist of two cells NEURONS NEUROGLIA . Larger than neuralgia .Smaller than neurons . Mainly has ability to .They support nourish & respond to a stimulus & protect the neurons & convert into an action maintain homeostasis potential. in the interstitial fluids.
- 6. A Typical Neuron Overview • Dentrites • Cell Body • Axon • Terminal
- 7. TYPES OF NEURONS Multipolar Bipolar Unipolar Severaldendrites one main dendrites & One axon. dendrite & axon fuse & eg: Brain, spinalcord one axon divide into eg: Retina of eye branches
- 9. ELECTRICAL SIGNALS OF NEURONS ACTION POTENTIAL GRADED POTENTIAL Electrical signal that >Used for short distance Travels along the surface communication. Of the membrane of Neurons. Communicates over short & long distances With in body.
- 10. ION CHANNELS LEAKAGE LIGAND GATED CHANNELS CHANNELS VOLTAGE GATED MECHANICALLY CHANNELS GATED CHANNELS
- 12. DESCRIPTION 1. Leakage channels : These randomly alternate b/w open & closed positions.Has more K ion leakage channels than Na ion. 2. Voltage gated : This opens in response to change in membrane potential .Participate in generation & conduction of action potential. 3. Ligand gated : open & closes in response to specific chemical stimulus eg hormones, neurotransmitters (ACH) by binding to a portion of channel protein or indirectly via membrane protein ( G protein). 4. Mechanically gated : By mechanical stimulation (vibration).
- 14. Synapse
- 15. SIGNAL TRANSMISSION AT CHEMICAL SYNAPSE
- 16. Synapse
- 17. Principles of Chemical Synaptic Transmission • Basic Steps – Neurotransmitter synthesis – Load neurotransmitter into synaptic vesicles – Vesicles fuse to presynaptic terminal – Neurotransmitter spills into synaptic cleft – Binds to postsynaptic receptors – Biochemical/Electrical response elicited in postsynaptic cell – Removal of neurotransmitter from synaptic cleft
- 18. Synaptic Transmission: Four Easy Steps I. Synthesis and Storage of Neurotransmitters II. Neurotransmitter Release III. Neurotransmitter Postsynaptic Receptors IV. Inactivation of Neurotransmitters
- 19. Step 1. The neurotransmitter is manufactured by the neuron and stored in vesicles at the axon terminal
- 20. Step 2. When the action potential reaches the axon terminal, it causes the vesicles to release the neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft
- 21. Step 3. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the cleft and binds to receptors on the post-synaptic cell. Step 4. The activated receptors cause changes in the activity of the post- synaptic neuron.
- 22. Step 5. The neurotransmitter molecules are released from the receptors and diffuse back into the synaptic cleft
- 23. Step 6. The Neurotransmitter is re-absorbed by the post synaptic neuron. This process is known as Reuptake.
- 24. Myelinated Axons The axon is a single long, thin extension that sends impulses to another neuron. They vary in length and are surrounded by a many-layered lipid and protein covering called the myelin sheath, produced by the schwann cells.
- 25. Myelination • Most mammalian axons are myelinated. • The myelin sheath is provided by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. • Myelin is insulating, preventing passage of ions over the membrane.
- 26. Resting Potential In a resting neuron (one that is not conducting an impulse), there is a difference in electrical charges on the outside and inside of the plasma membrane. The outside has a positive charge and the inside has a negative charge.
- 27. Trigger Zone: Cell Integration and Initiation of AP • Excitatory signal: depolarizes, reduces threshold • Inhibitory signal: hyperpolarizes, increases threshold
- 28. Action Potential When the cell membranes are stimulated, there is a change in the permeability of the membrane to sodium ions (Na+). The membrane becomes more permeable to Na+ and K+, therefore sodium ions diffuse into the cell down a concentration gradient. The entry of Na+ disturbs the resting potential and causes the inside of the cell to become more positive relative to the outside.
- 29. Course of the Action Potential • The action potential begins with a partial depolarization (e.g. from firing of another neuron ) [A]. • When the excitation threshold is reached there is a sudden large depolarization [B]. • This is followed rapidly by repolarization [C] and a brief hyperpolarization [D]. • There is a refractory period immediately after the action potential where no depolarization can occur [E] Membrane potential (mV) [A] [B] [C] [D] excitation threshold Time (msec) -70 +40 0 0 1 2 3
- 30. Action Potential Stages: Overview
- 31. Membrane & Channel Changes during an Action Potential
- 32. Refractory Period There are two types of refractory period: Absolute Refractory Period – Na+ channels are inactivated and no matter what stimulus is applied they will not re-open to allow Na+ in & depolarise the membrane to the threshold of an action potential. • Relative Refractory Period - Some of the Na+ channels have re- opened but the threshold is higher than normal making it more difficult for the activated Na+ channels to raise the membrane potential to the threshold of excitation.
- 33. Saltatory Conduction • Myelinated regions of axon are electrically insulated. • Electrical charge moves along the axon rather than across the membrane. • Action potentials occur only at unmyelinated regions: nodes of Ranvier. Myelin sheath Node of Ranvier