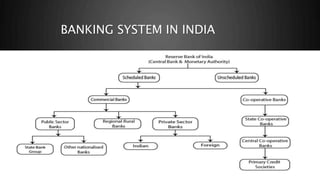
The document presents information on the banking system in India. It discusses that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India's central bank and was established in 1935. The RBI regulates scheduled and non-scheduled banks. Scheduled banks names appear in RBI's second schedule and include public sector banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, and regional rural banks. Co-operative banks primarily serve farming communities and include urban cooperative banks, state cooperative banks, and district cooperative banks. The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development provides financing for agriculture and rural development.