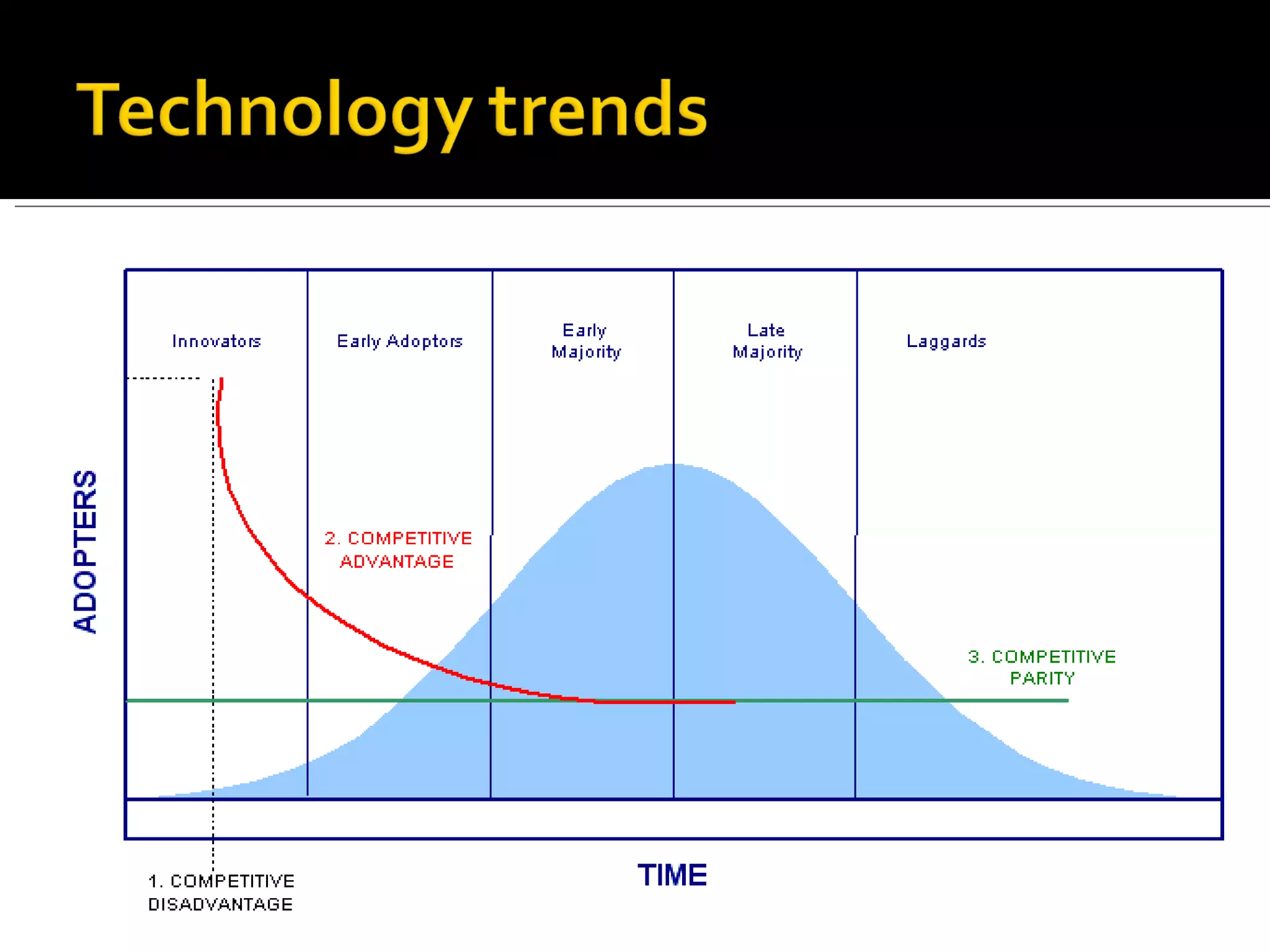
The four pillars of the financial system are savers, users, financial markets, and financial intermediaries. Banks are a key financial intermediary that mobilizes deposits from savers and lends to users, providing various financial services. While traditional banking has benefits like personal relationships, modern banking provides advantages such as accessibility, speed, and lower transaction costs through new technologies. Both systems have pros and cons, and majority of customers in India still prefer traditional banking.






























![Outsourcing (eg. IT and HR) RFID (Radio frequency identification) implementation. Managing competition: Marketing , Differentiated products CRM(customized products) Cope with the changing trends incorporating Para-banking activities[banc assurance, pension fund(CAGR- 122.44% 1999-00 to 2006-07)] Source: http://www.scribd.com/doc/18446435/banking-industry-overview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankinganalysis-120108032258-phpapp01/75/Banking-analysis-36-2048.jpg)


