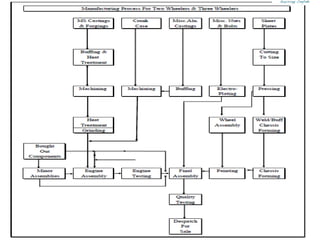
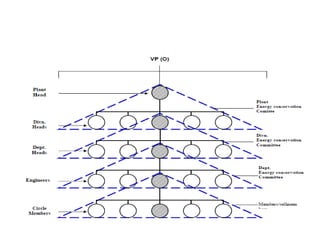
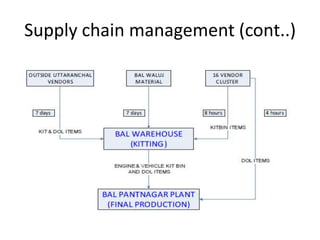
Bajaj Auto Limited is an Indian motorcycle manufacturer with multiple plant locations in India and Indonesia. It has transitioned its manufacturing model over the decades from a batch production approach in the 1980s-1990s with dedicated assembly lines and high inventories, to a lean manufacturing approach from the late 1990s onward with multi-model flexible assembly lines, statistical process control, direct material supply from vendors, and an emphasis on quality and reduced waste. Key results of the newer model include a 10-fold increase in productivity, dramatically reduced inventory levels, and greatly improved quality. The company also implements advanced supply chain management systems and outbound logistics tailored to different market segments.