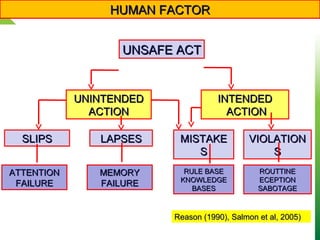
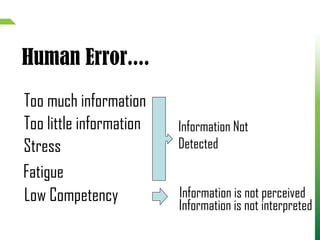
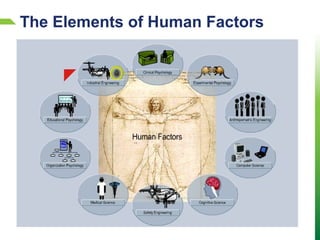
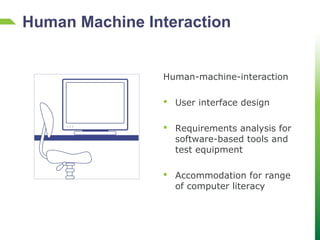
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang tantangan rekayasa keselamatan lalu lintas di Indonesia dan dunia. Dokumen ini menjelaskan bahwa faktor manusia sangat berpengaruh terhadap kecelakaan lalu lintas, seperti kesalahan, ketidakfokusan, dan kelalaian. Oleh karena itu, diperlukan pemahaman akan faktor manusia untuk mencegah kecelakaan. Dokumen ini juga menjelaskan berbagai disiplin ilmu