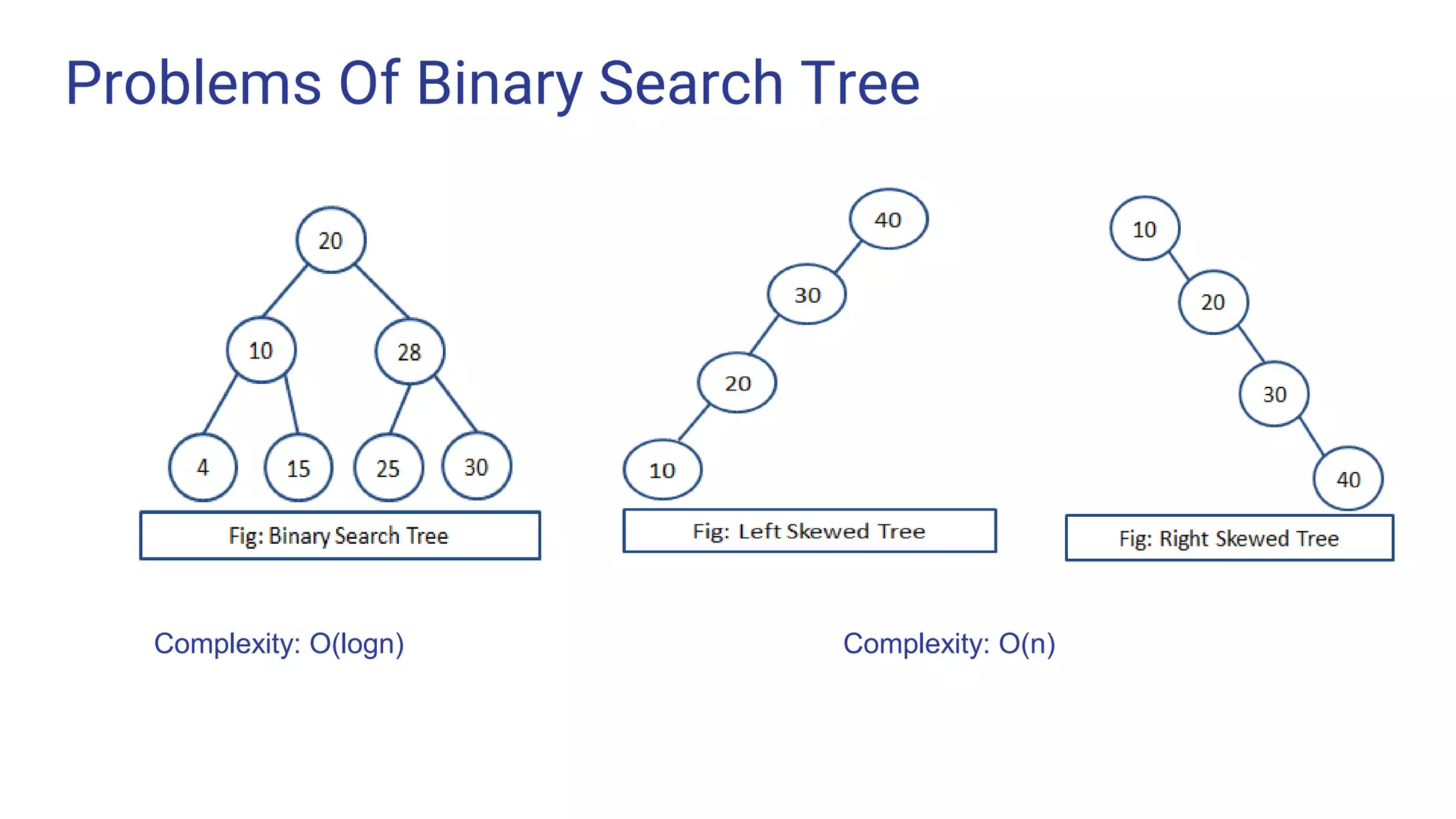
This document discusses AVL trees, which are self-balancing binary search trees where the heights of the left and right subtrees of every node differ by at most one. It covers the definition of AVL trees, problems with regular binary search trees, properties of AVL trees including balance factors, and algorithms for insertion and deletion that rebalance the tree through rotations. The time complexity of operations on an AVL tree is O(log n). Four cases for rebalancing after an insertion are described - left-left, right-right, left-right, and right-left - along with the rotations needed to resolve each case. Deletion is also explained as removing the node and then rebalancing through rotations if needed.