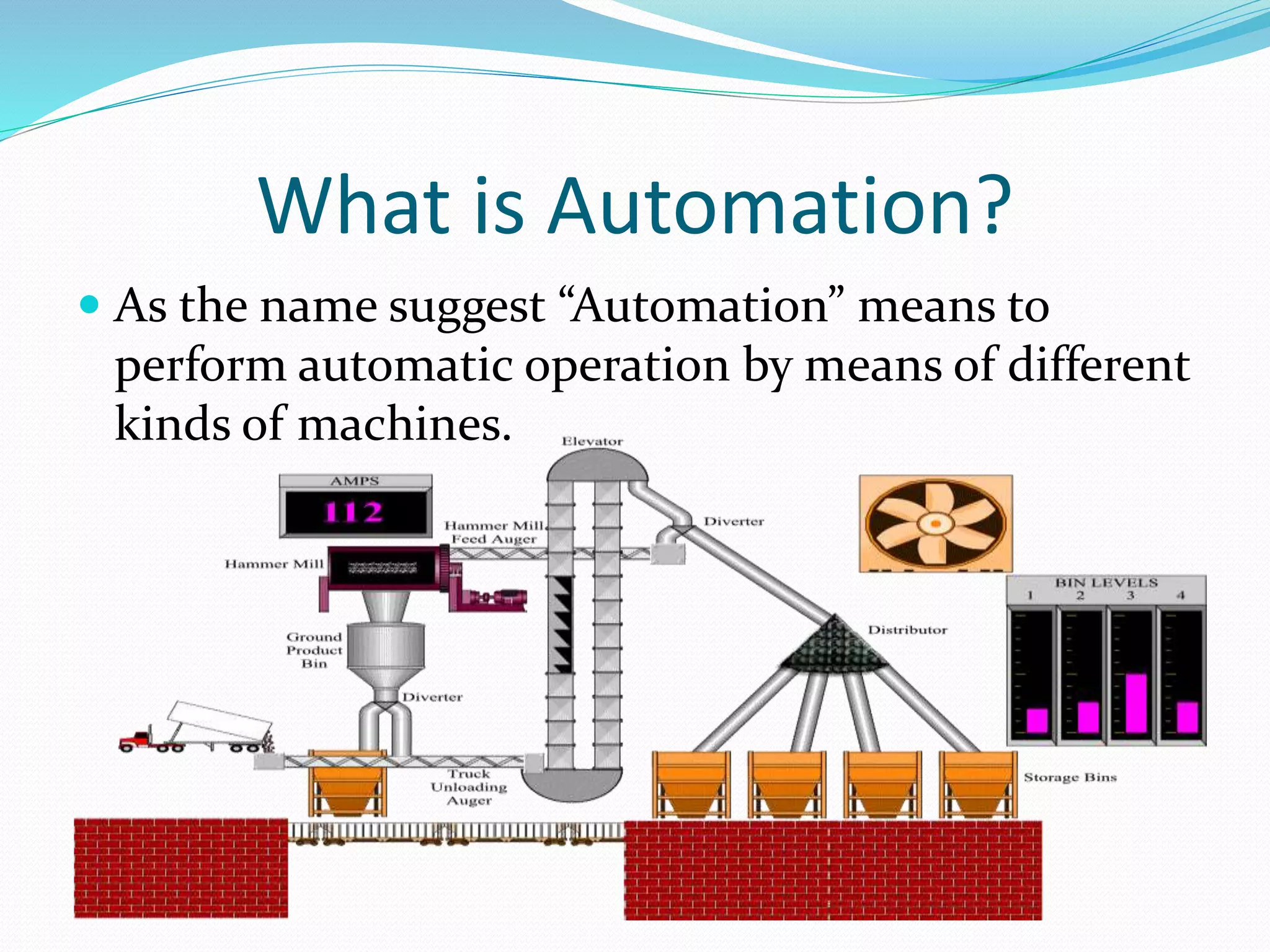
The document discusses automation and robotics. It defines automation as performing automatic operations using machines. It outlines the history and types of automation as well as common automation tools like PLCs, SCADA, sensors and robotics. SCADA refers to systems that collect data from sensors and includes components like HMIs, RTUs, PLCs and communication infrastructure. The document also defines robotics as using reprogrammable machines to replace humans in hazardous work, discusses the history and technologies of robotics, types of robots, and applications of automation and robotics in various industries.