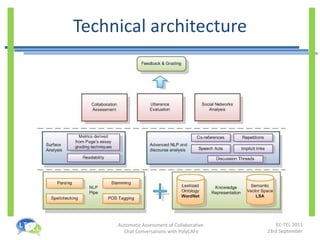
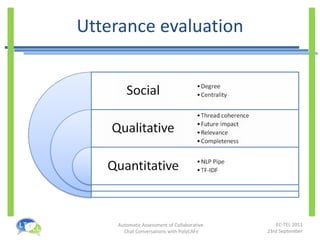
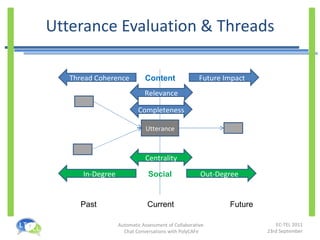
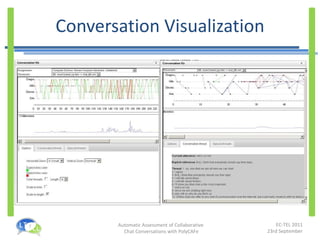
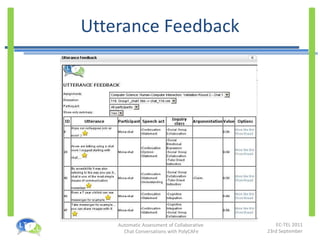
- PolyCAFe is an automatic assessment tool that analyzes collaborative chat conversations and provides feedback without requiring tutor time.
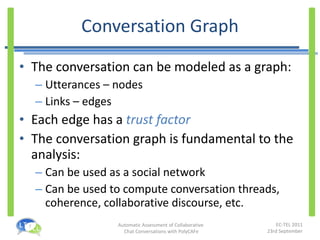
- It uses natural language processing, social network analysis, and information retrieval techniques to evaluate utterances, measure collaboration, and generate feedback.
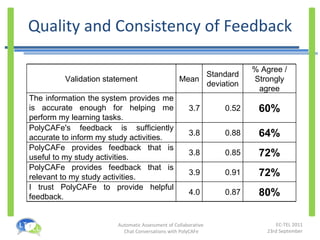
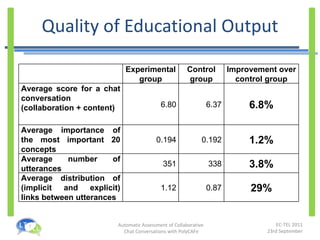
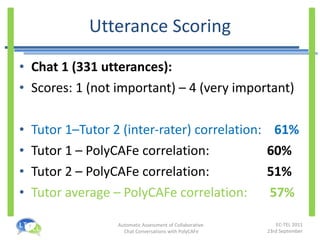
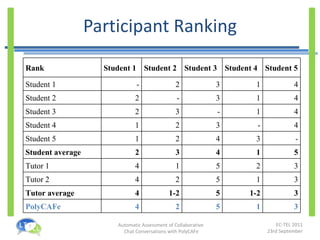
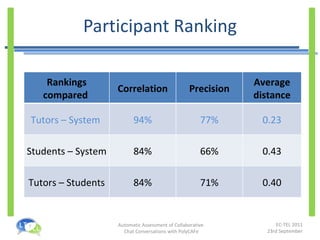
- An experiment found that tutors could prepare feedback 35% faster with PolyCAFe and that students found its feedback useful, accurate, and helpful for their learning.