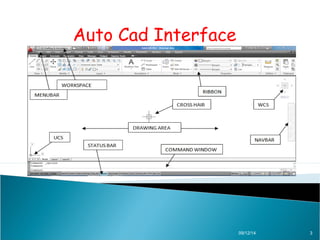
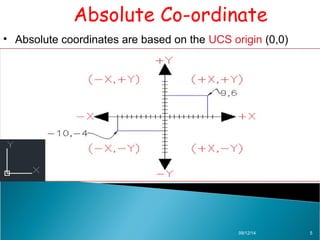
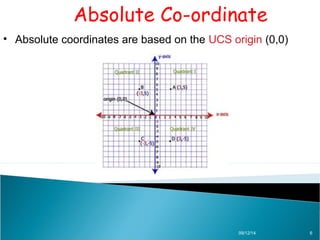
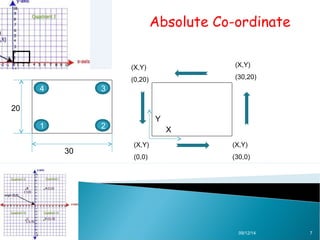
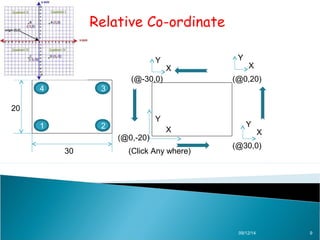
AutoCAD is a CAD software developed by Autodesk in 1982, originally used in DOS and now available on Windows, serving various fields such as mechanical, civil, and electrical design. The document explains different types of coordinates used in AutoCAD, including absolute, relative, and polar coordinates, and how to utilize them. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these coordinate systems for effective use of the software.