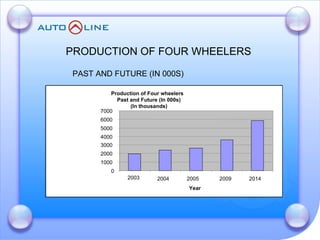
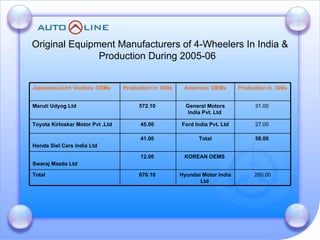
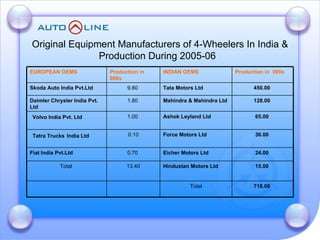
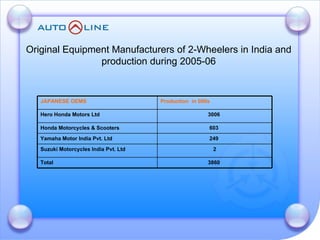
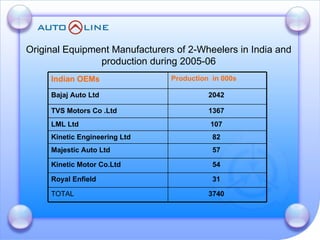
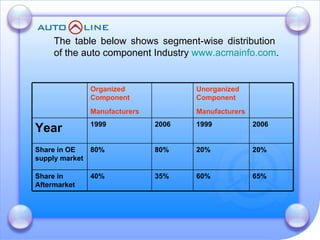
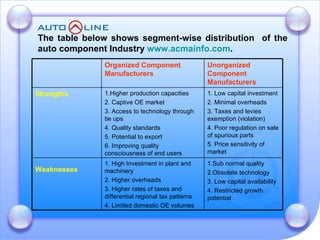
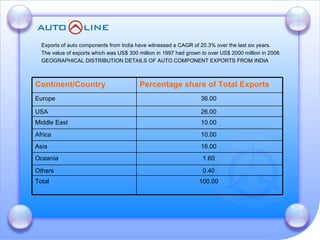
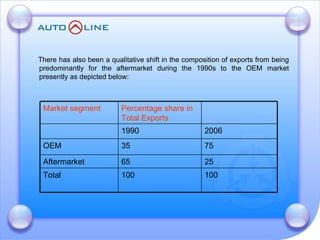
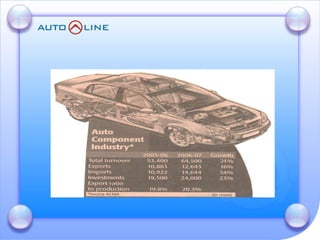
The document discusses the future prospects of the Indian auto component industry. It notes that the domestic market for four-wheelers is projected to grow at 9% annually, providing good growth opportunities. It also outlines factors driving primary OEM and aftermarket demand, and lists the major auto manufacturers in India and their 2005-06 production levels. The industry is transitioning from low-volume and fragmented to competitive, adopting global standards and consolidation.