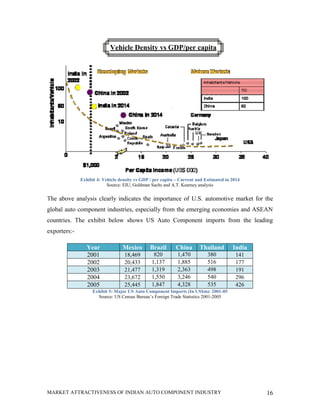
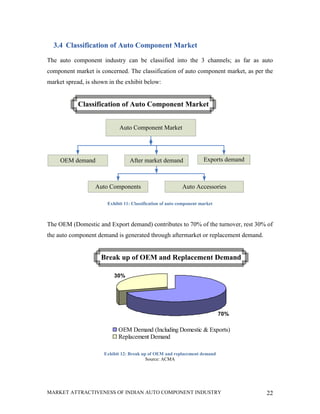
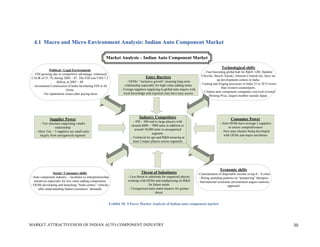
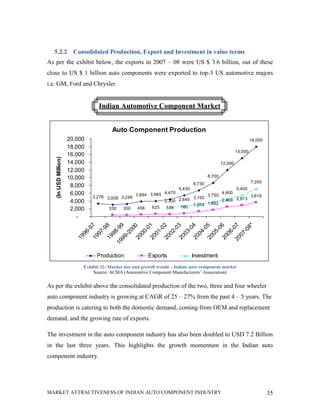
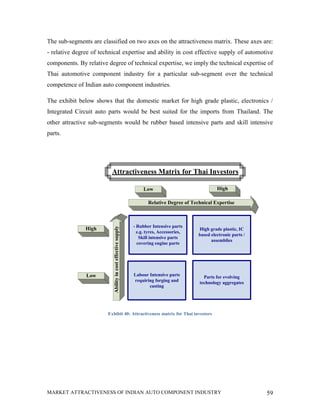
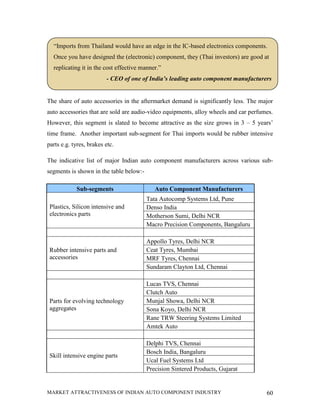
This document analyzes the market attractiveness of the auto component industry in India. It begins with an executive summary that outlines the size and growth forecasts of the OEM and replacement markets in India. It then discusses the government's foreign investment policies in the auto component sector and identifies attractive sub-segments for potential entry strategies. The rest of the document provides an in-depth analysis of trends in the global and Indian auto component industries, including market size estimates, production and export figures, major players, and growth forecasts through 2025. It also examines the OEM and replacement markets in India and how components are sourced.