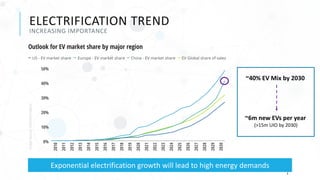
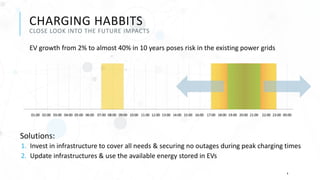
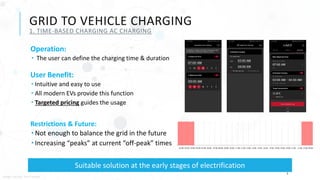
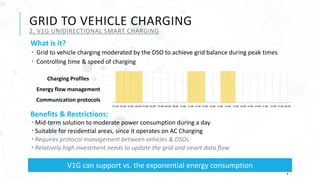
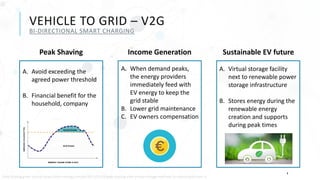
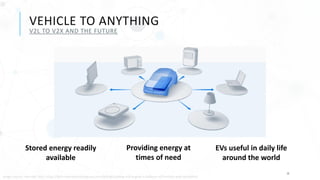
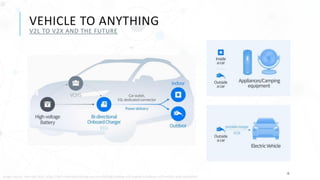
The document discusses various charging technologies for electric vehicles (EVs), including unidirectional smart charging (V1G) and bidirectional vehicle-to-grid (V2G) solutions. It emphasizes the importance of updating infrastructure to meet the growing energy demands anticipated with the increase of EVs, which could reach a 40% market mix by 2030. Additionally, it highlights the potential financial and environmental benefits of implementing V2G systems while addressing challenges such as high implementation costs and the need for better communication protocols.

![DEFINITIONS
Time based – User Defined Charging
Grid to Vehicle [V1G] - Unidirectional Controlled Smart Charging
Vehicle to Grid [V2G] - Bidirectional Controlled Smart Charging
V2x – Power supply from vehicle to its surroundings (V2L, V2H, etc.)
2
1
2
3
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6ioannisroussis-210331103306/85/Auto-Forum-2021-2-320.jpg)