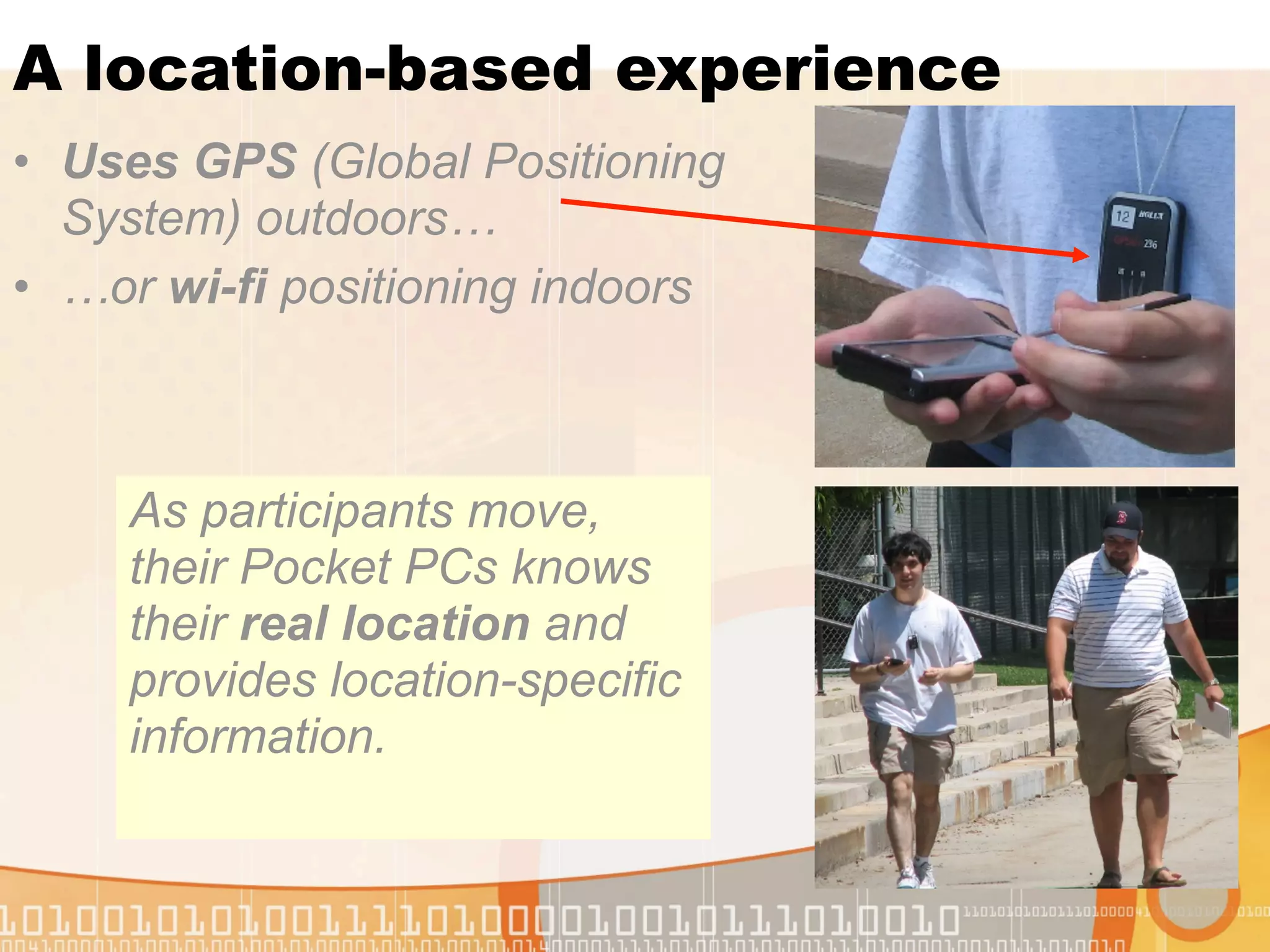
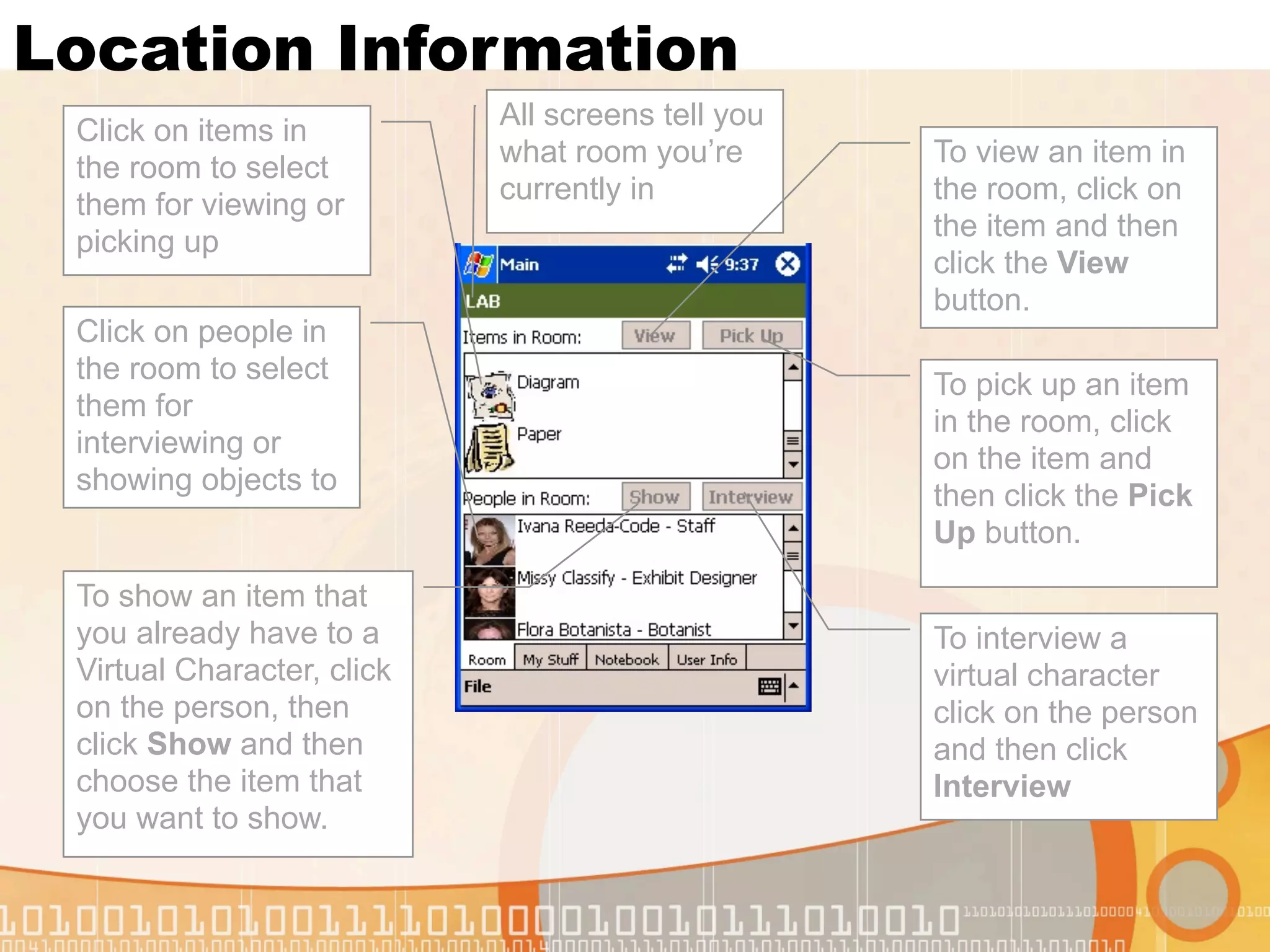
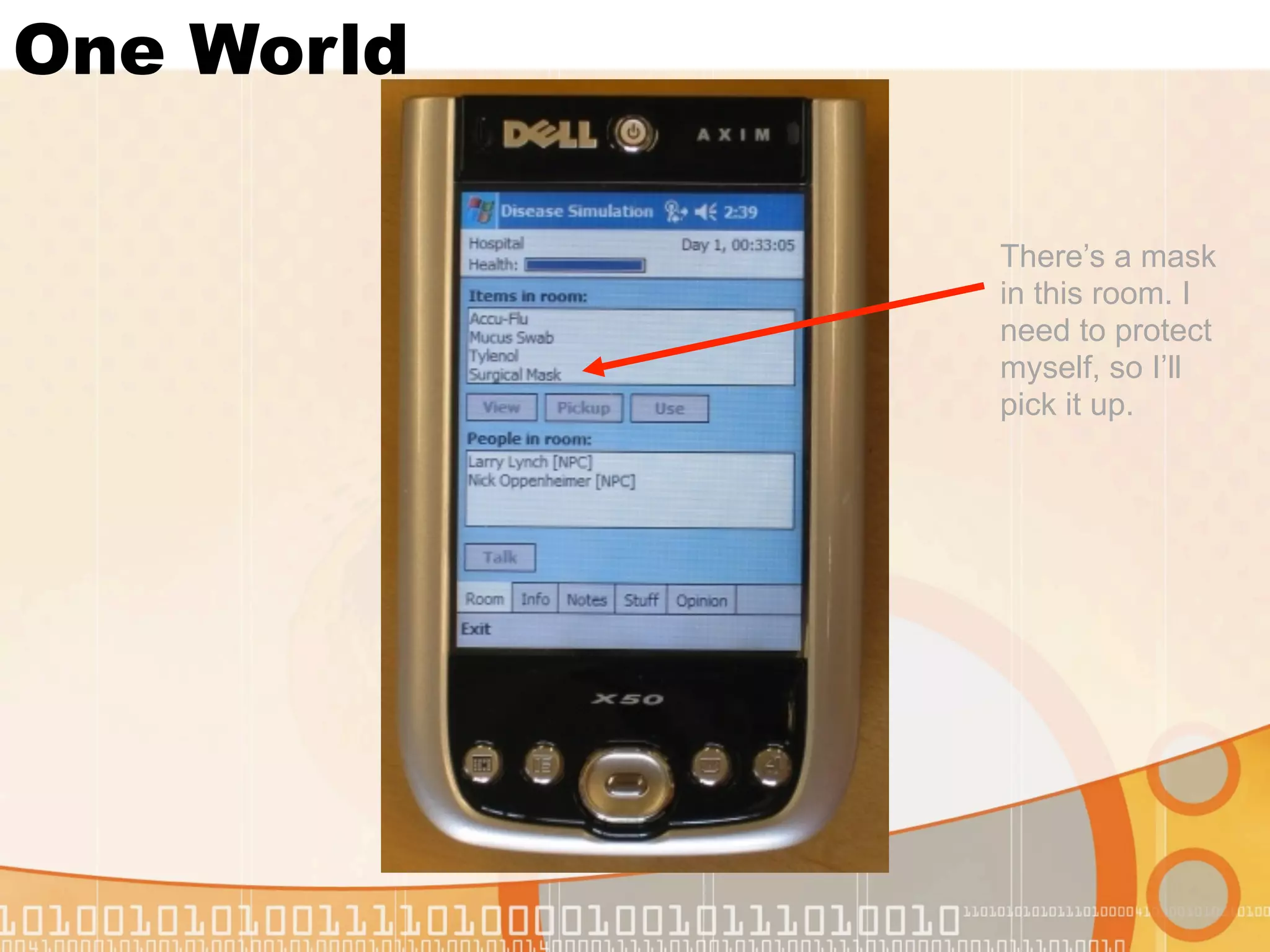
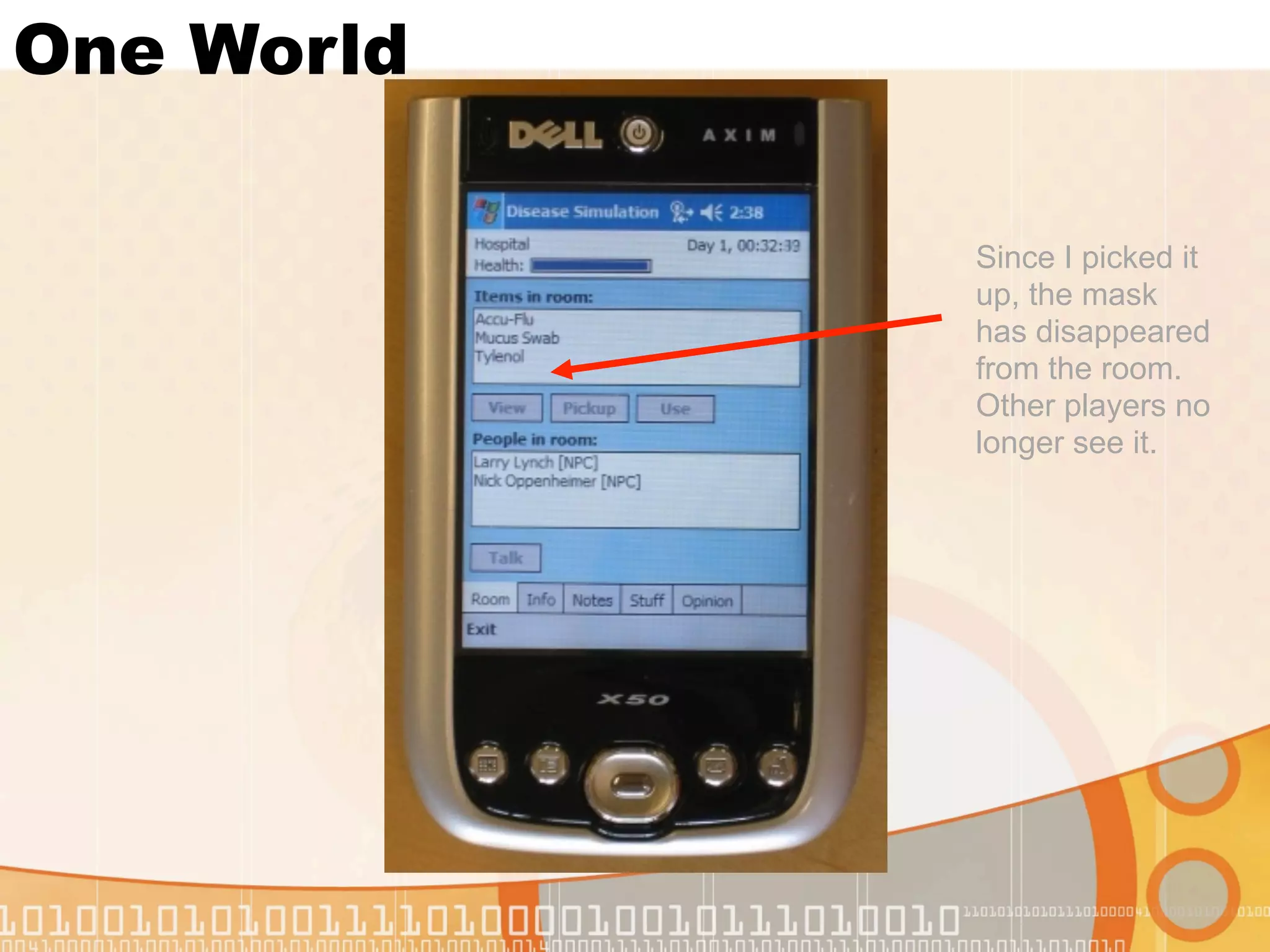
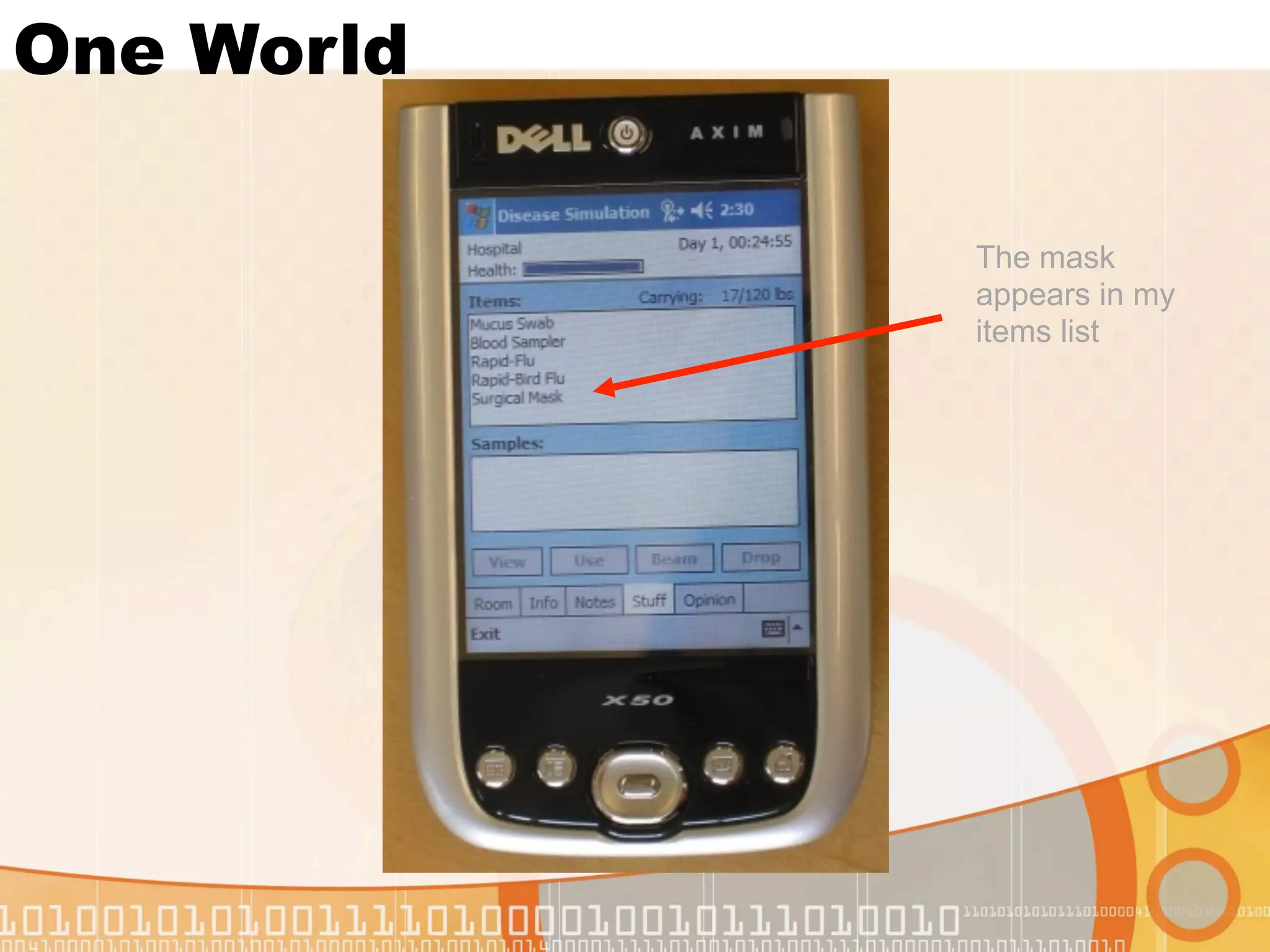
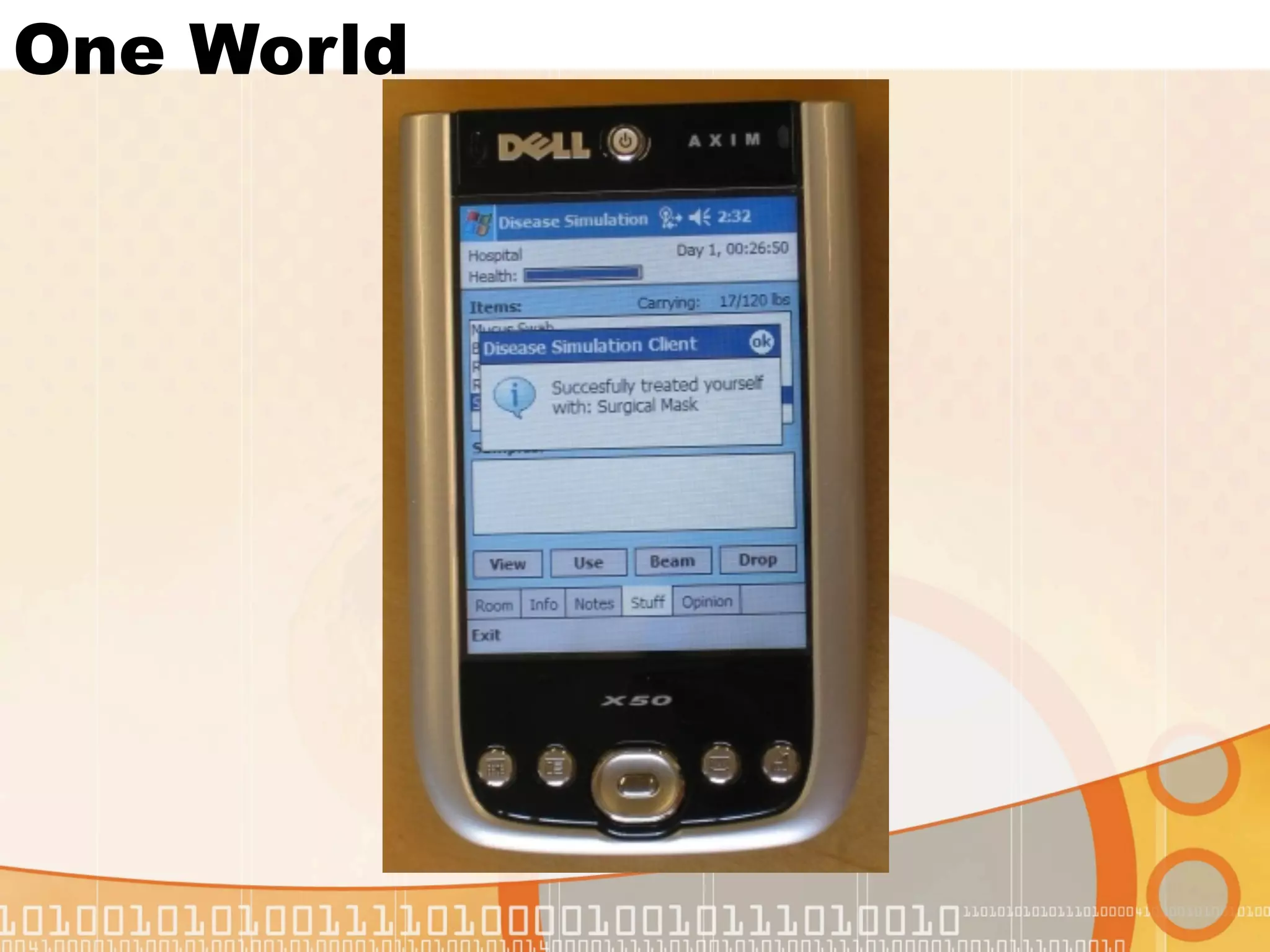
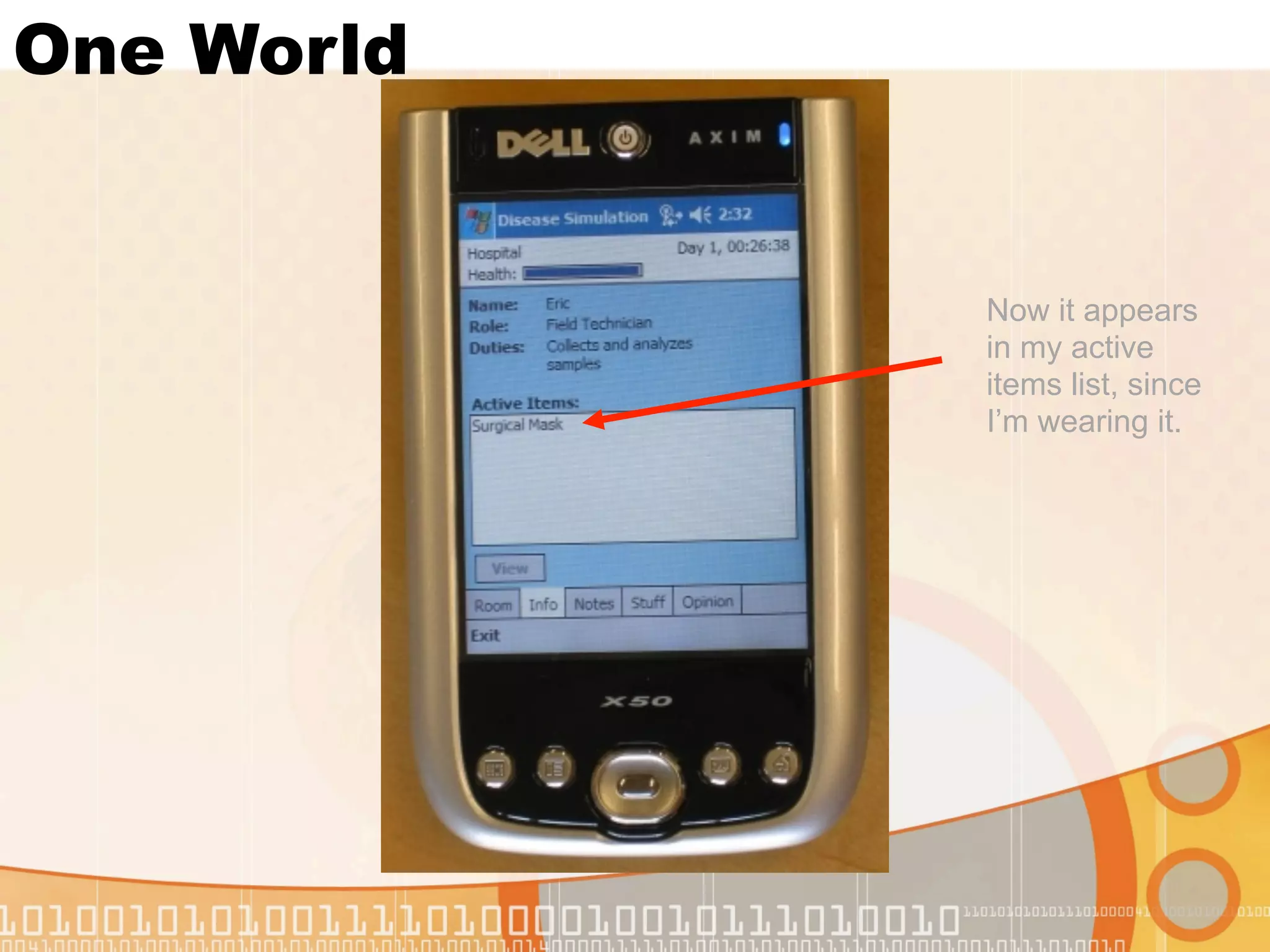
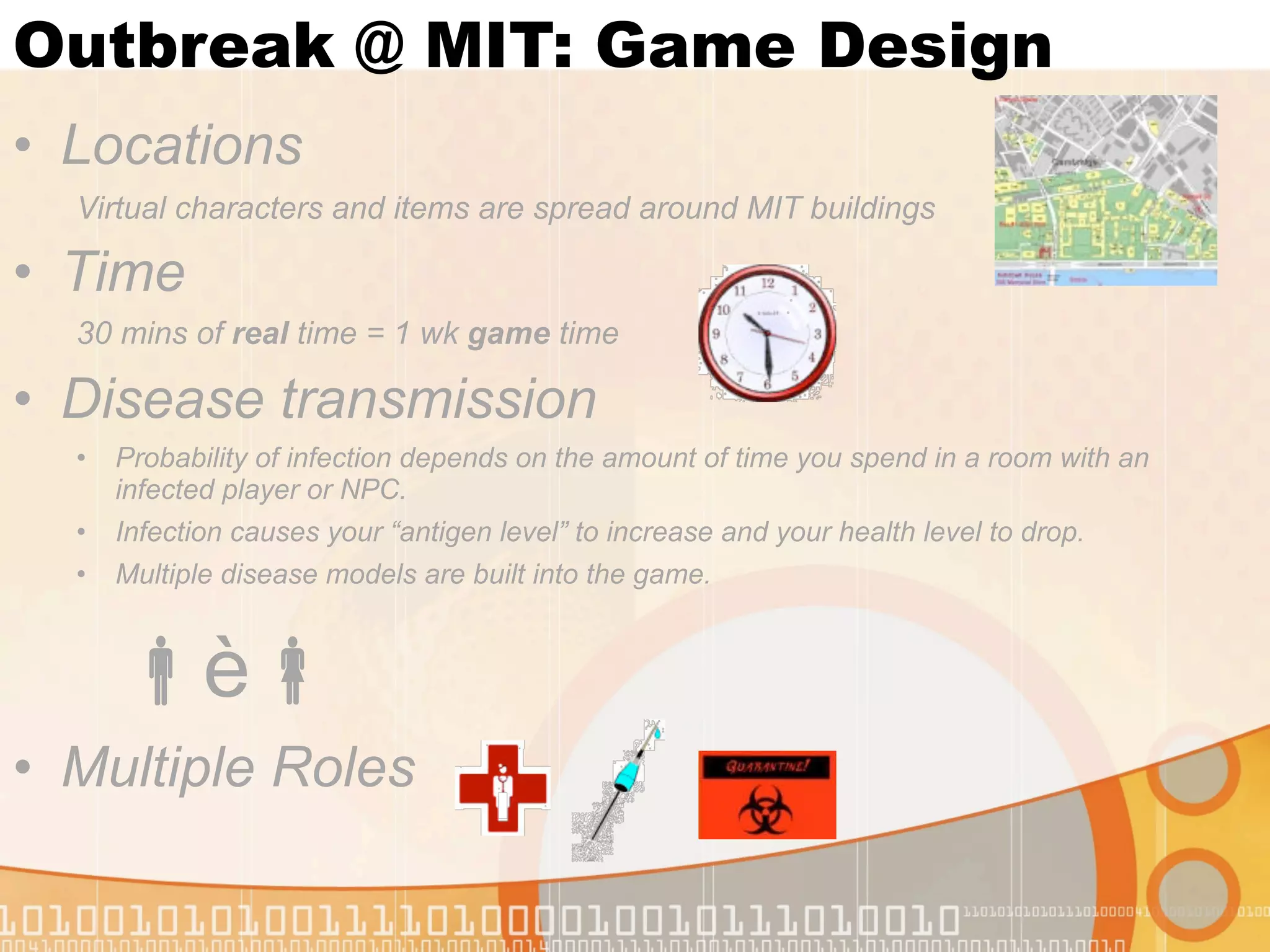
This document summarizes augmented reality simulations for education. It describes how augmented reality combines the physical and virtual world to engage learners in authentic situations. Examples are given of location-based augmented reality experiences using GPS or Wi-Fi to trigger educational simulations. Indoor and outdoor augmented reality advances are discussed. Specific augmented reality scenarios for public health and forensics are also outlined.