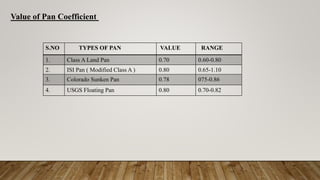
An atmometer is used to directly measure evaporation rates. It consists of a porous ceramic cup attached to a water reservoir. Water evaporates from the cup through a tube into the reservoir. Pan evaporation involves measuring the water loss from a metal pan over time to estimate evaporation from larger bodies of water, like reservoirs. Factors like pan type, location, and climate affect the pan coefficient used to extrapolate pan evaporation rates to actual reservoir evaporation. In the example, a Class A pan recorded 35mm of evaporation over a week, corresponding to an estimated 24.5mm of reservoir evaporation based on the Class A pan coefficient of 0.7.