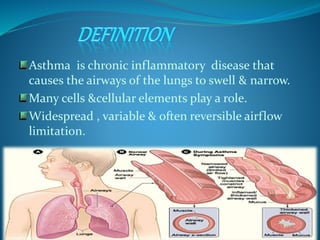
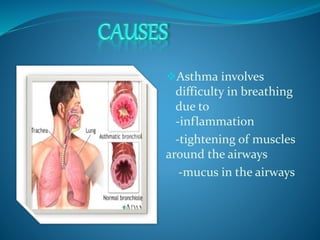
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by swelling and narrowing of the airways, leading to breathing difficulties and variable airflow limitation. It can be triggered by allergens, respiratory infections, and environmental factors, with symptoms that manifest in episodes and may worsen at night or with exercise. Management involves avoiding triggers, regular medical follow-ups, and medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids.