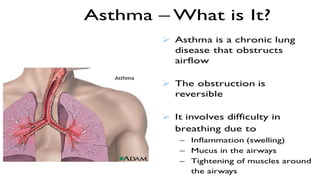
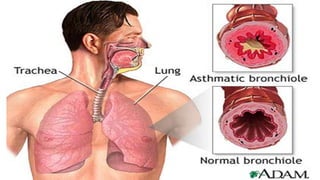
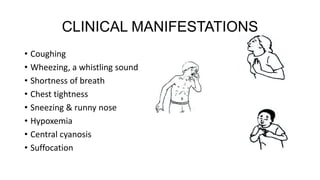
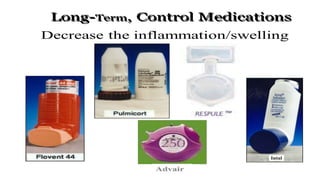
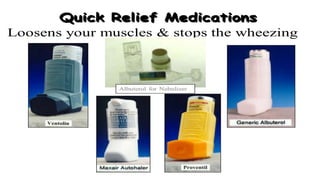
This document defines asthma as a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Asthma is caused by narrowing of the bronchi and bronchioles due to smooth muscle spasms, swelling of the mucosa, and excess mucus production in response to allergens, irritants, infections or other triggers in genetically predisposed individuals. The document then classifies asthma by severity and discusses its clinical manifestations, management through medical treatment, diet, and nursing care, as well as complications like status asthmaticus and the importance of prevention.