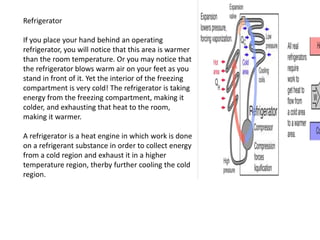
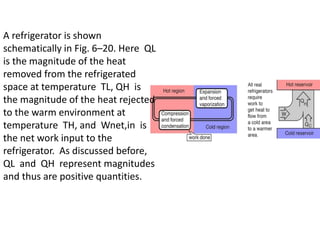
Refrigeration is a process that uses mechanical means to transfer heat from a low-temperature area to a high-temperature area, with applications including household refrigerators and freezers. The introduction of refrigerated rail cars in the 1800s allowed for expanded settlement in the United States by making it possible to transport perishable goods. Early Americans began using ice harvested in winter to refrigerate foods in the 1830s as iceboxes became more widely available. A refrigerator operates by using a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle with four main components - a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator - to absorb heat from the refrigerated interior and release it to the exterior environment.