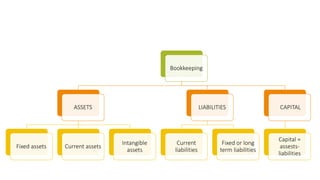
The document outlines the fundamentals of accounting, emphasizing the importance of analyzing and evaluating economic results for organizations. It details the classifications of assets, liabilities, and capital, explaining their roles and relationships in financial statements. Ultimately, it highlights accounting as a crucial discipline for managing finances and ensuring compliance with regulations.