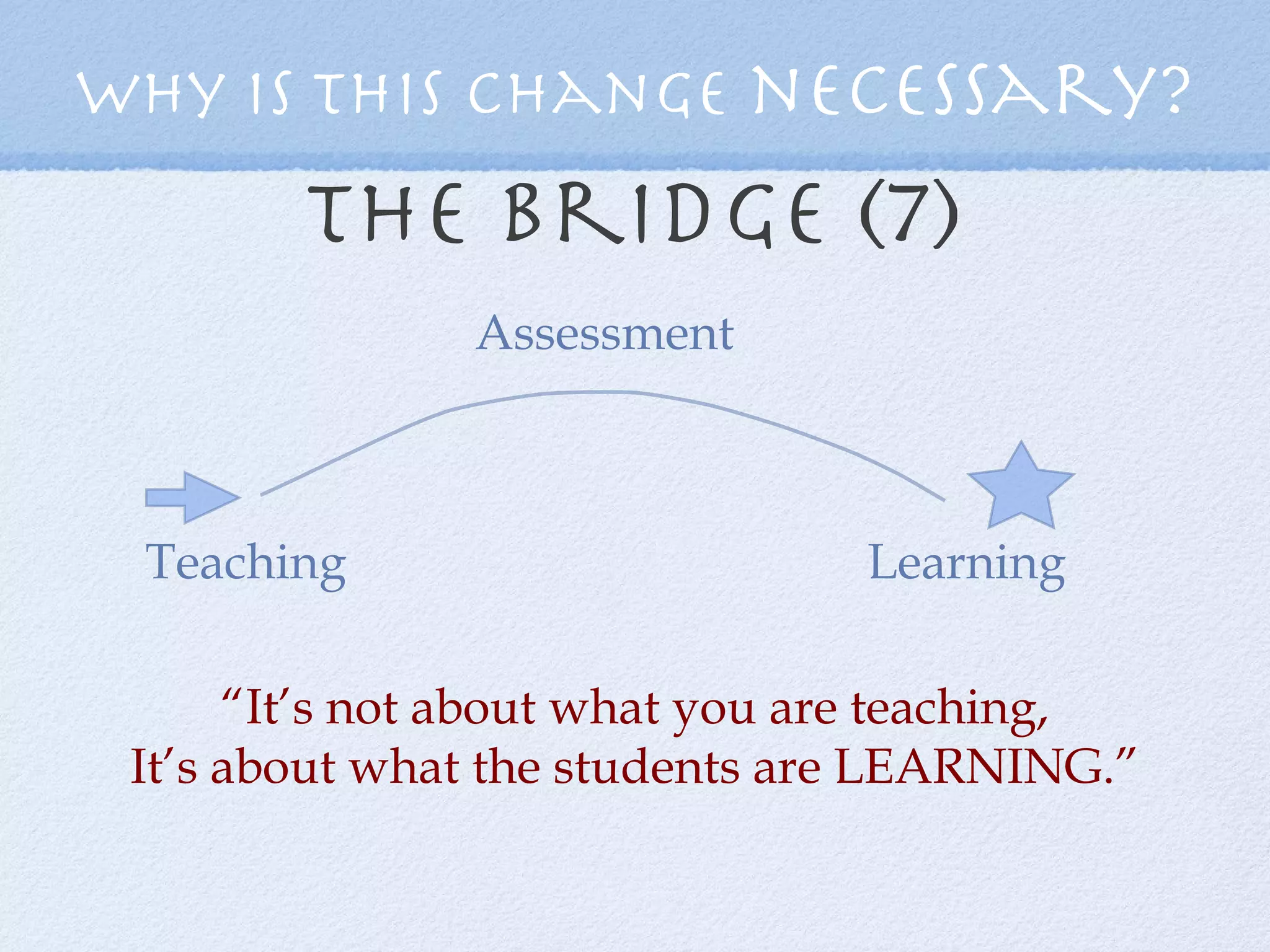
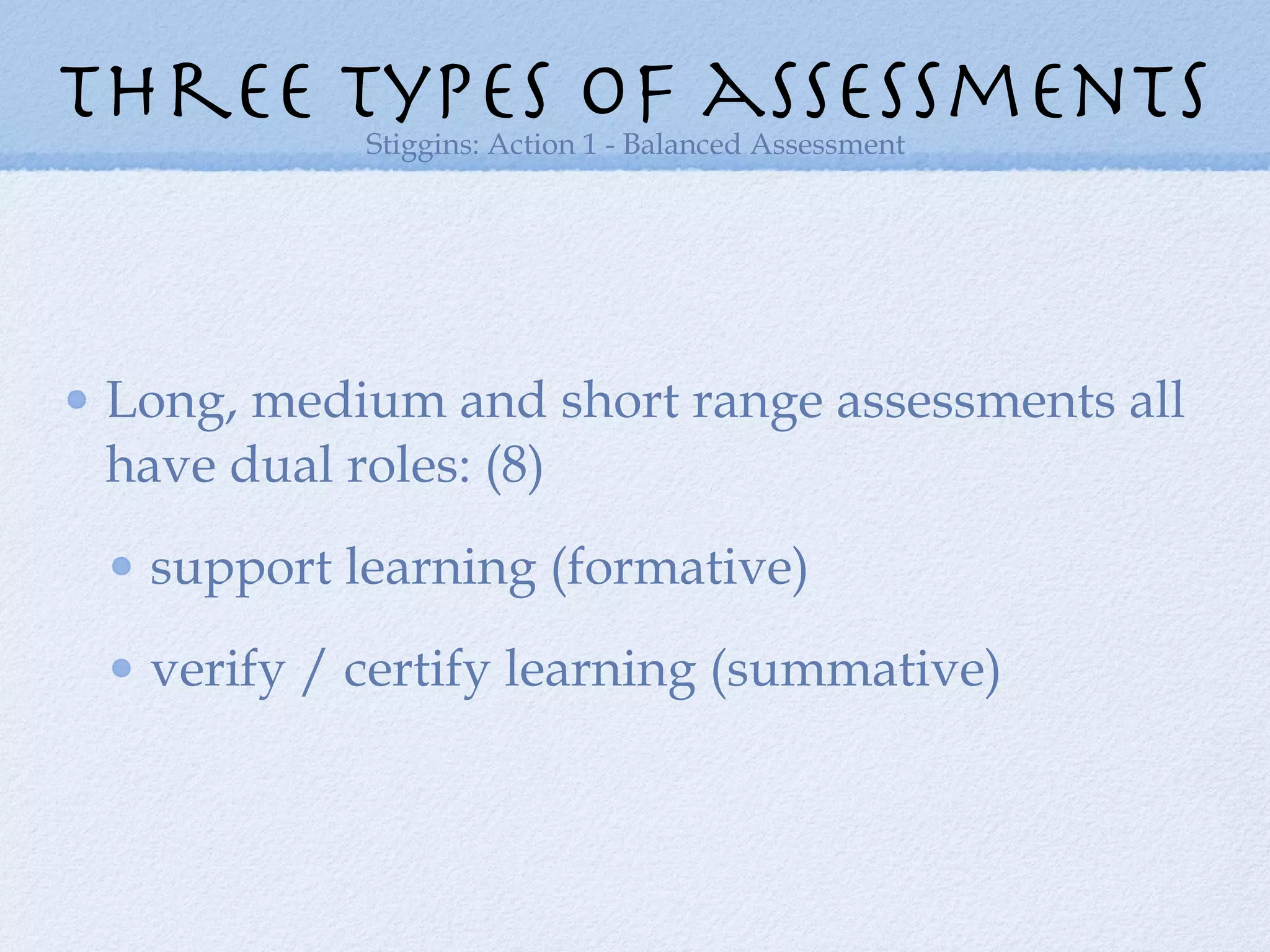
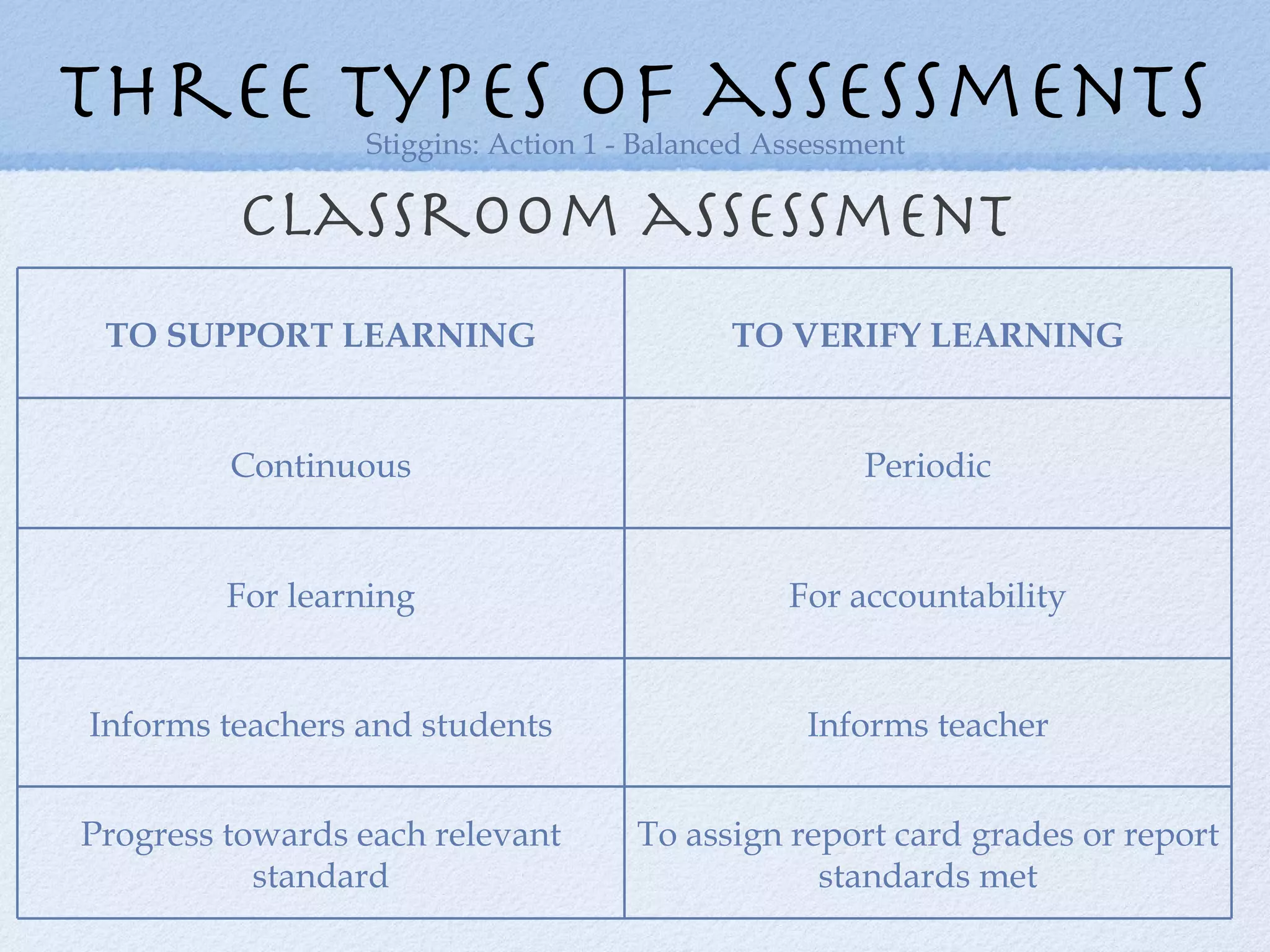
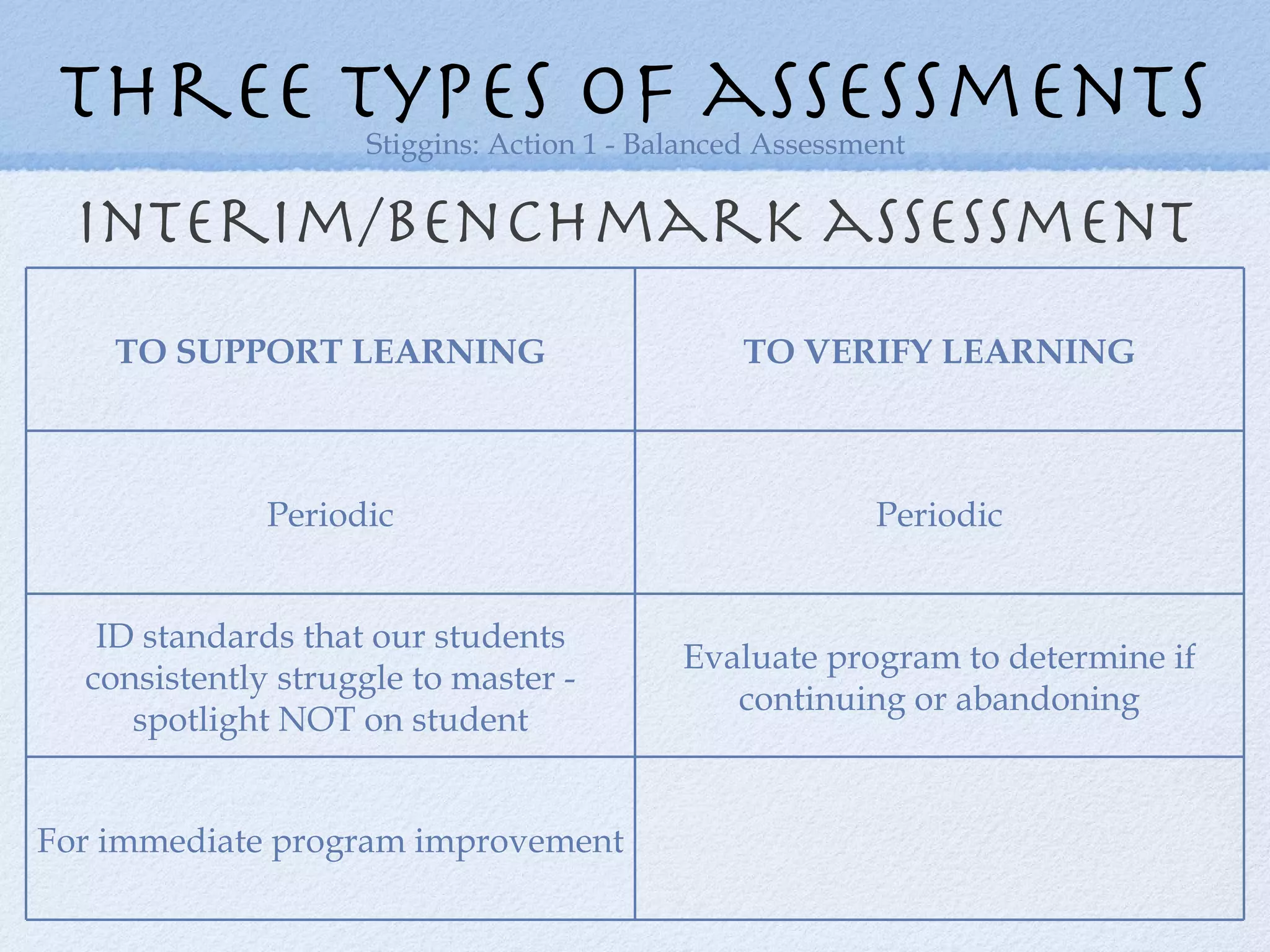
The document discusses the necessity of transforming assessment practices in education to effectively support student learning and reduce achievement gaps. It emphasizes the importance of formative assessment as a tool for improving teaching and highlights the role of professional learning communities in collaborative efforts towards enhancing educational outcomes. Key strategies include shifting focus from traditional methods to more interactive, student-driven approaches that emphasize learning over mere performance metrics.