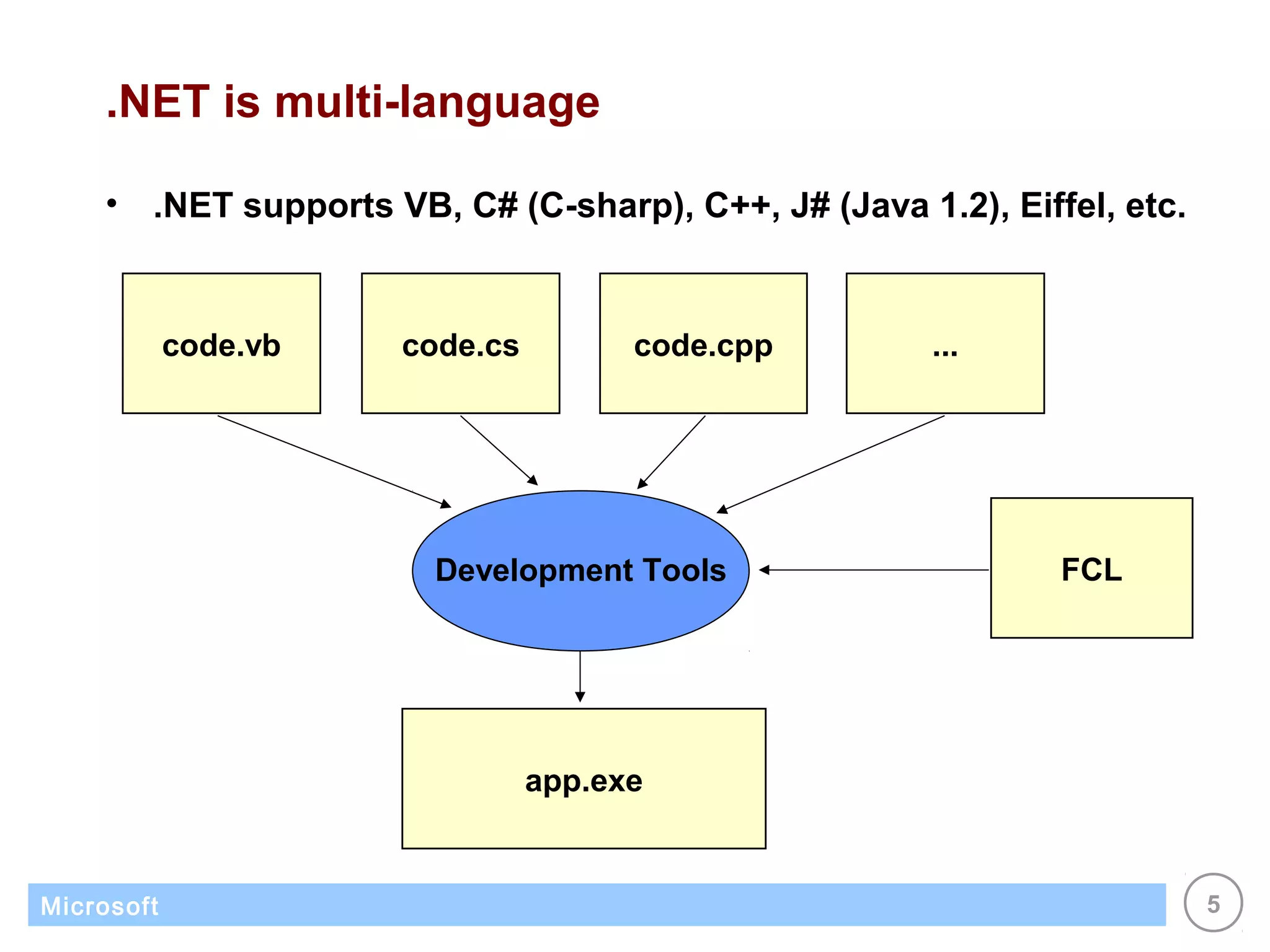
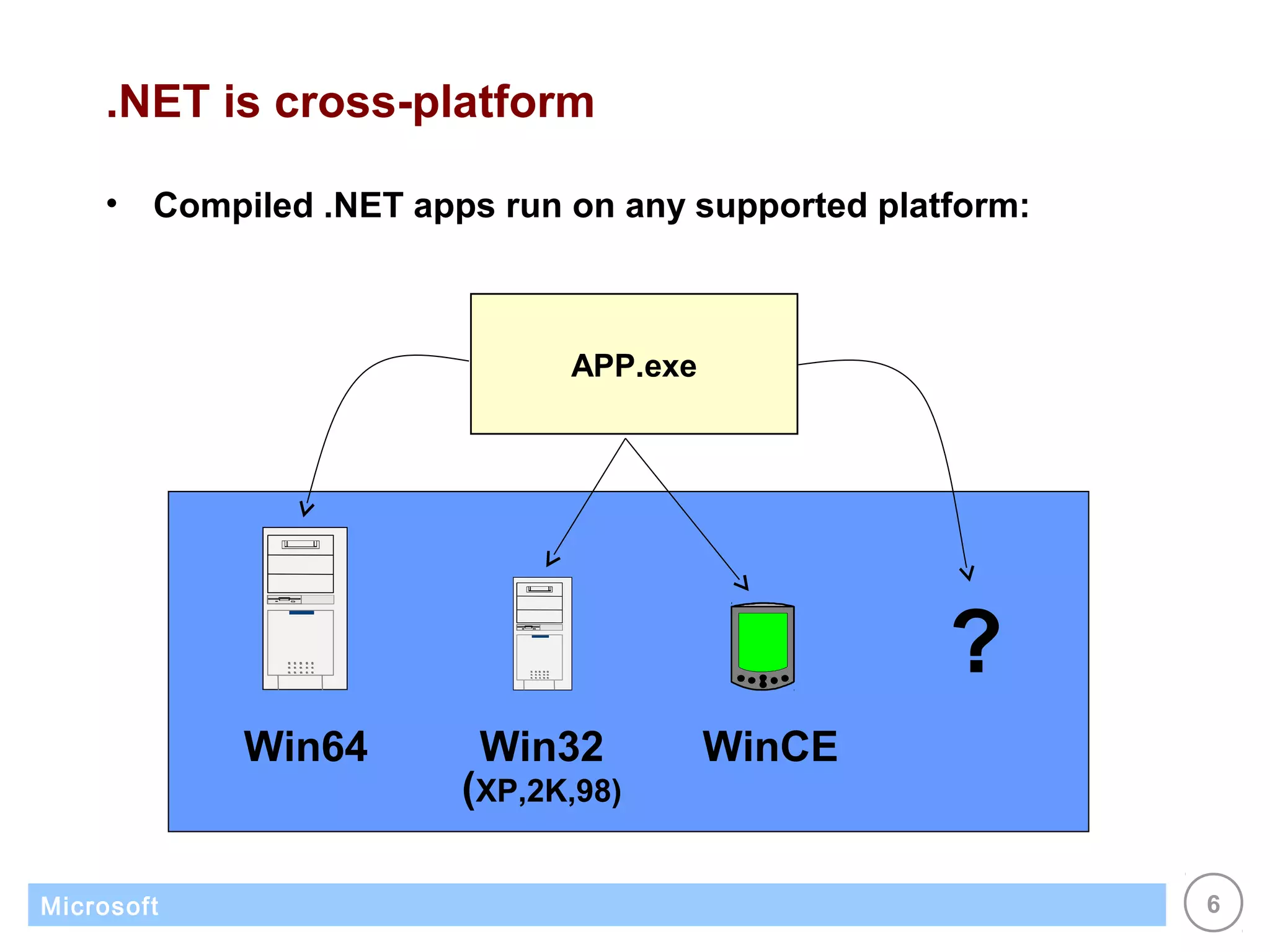
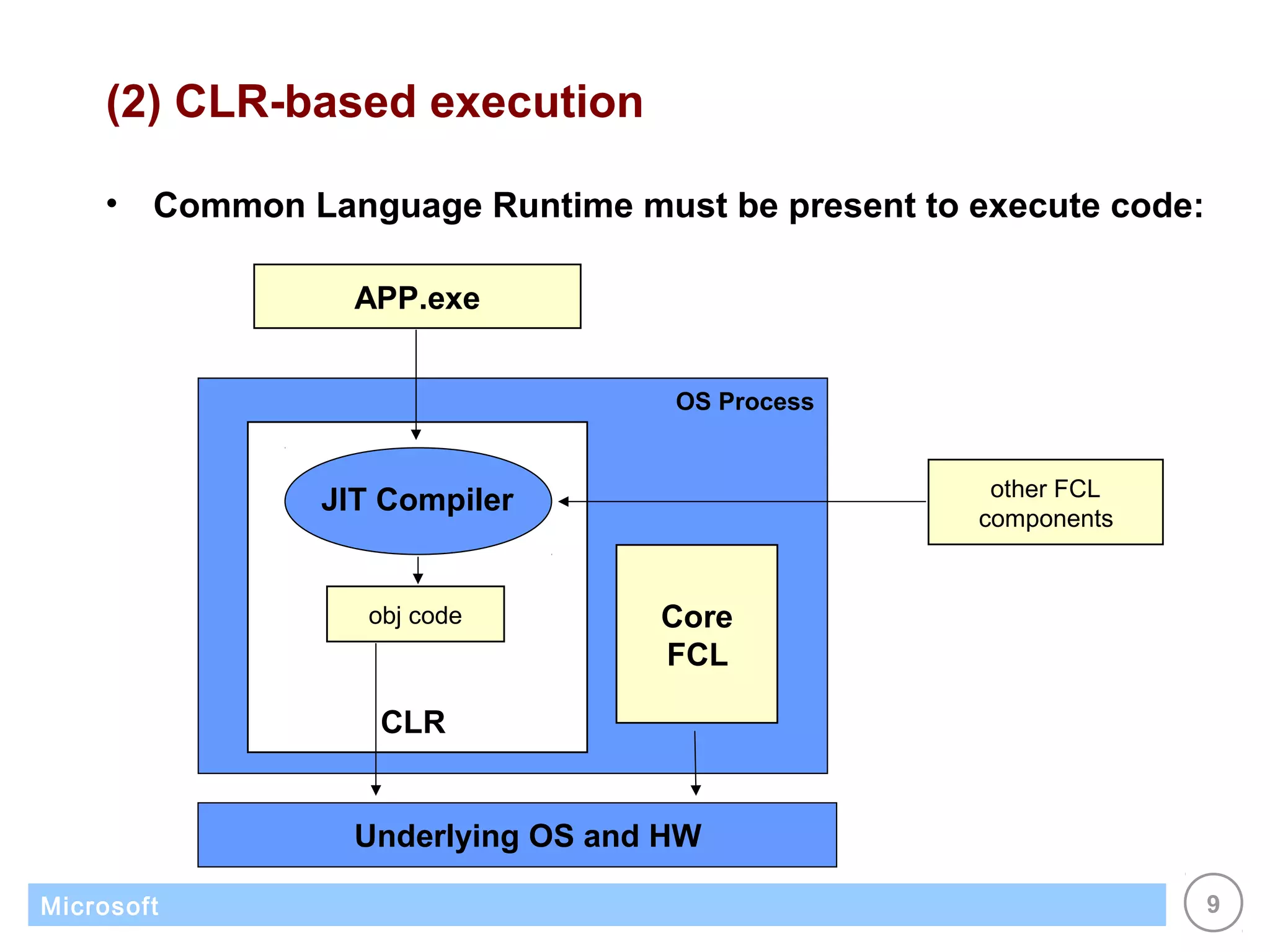
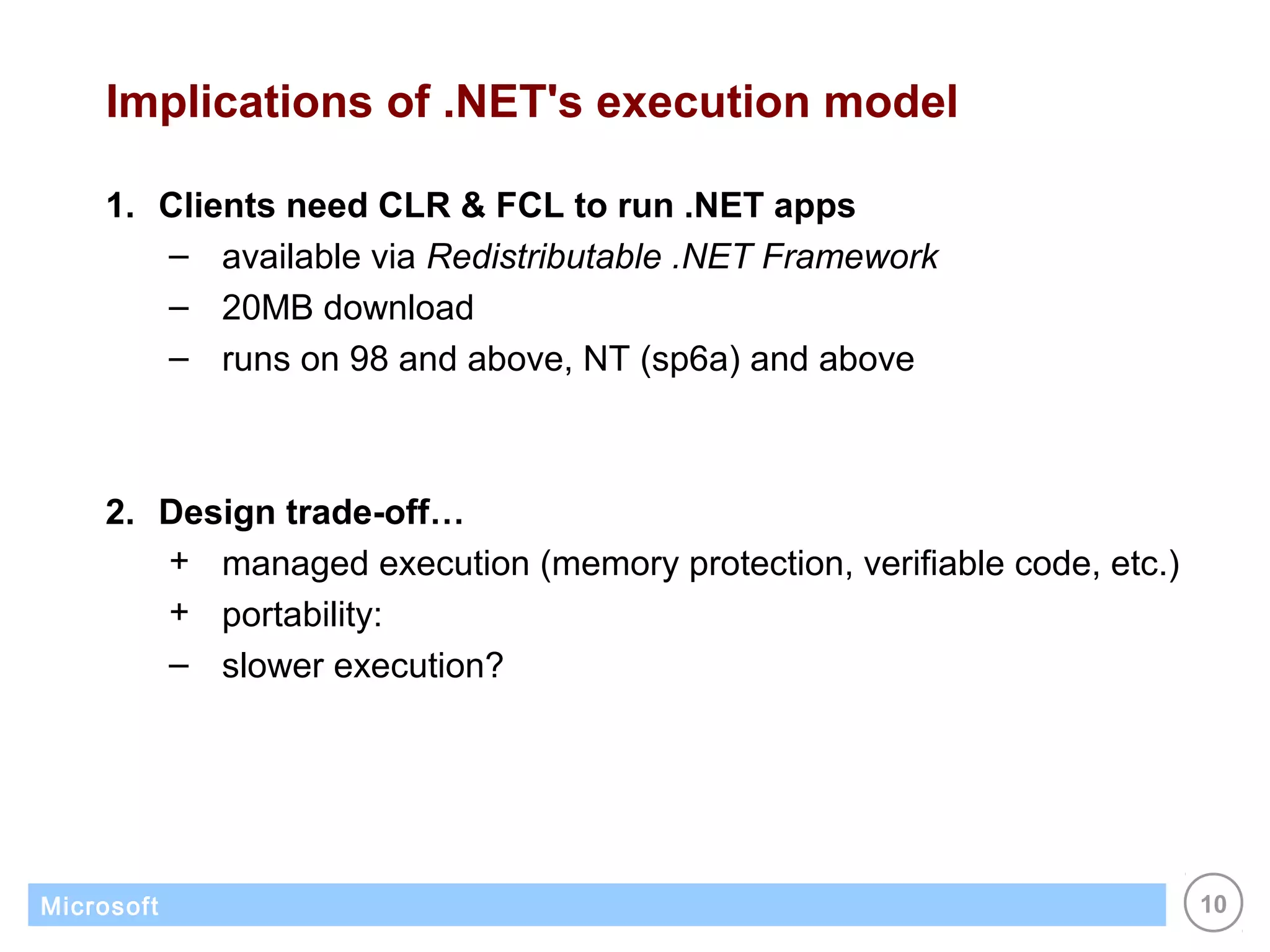
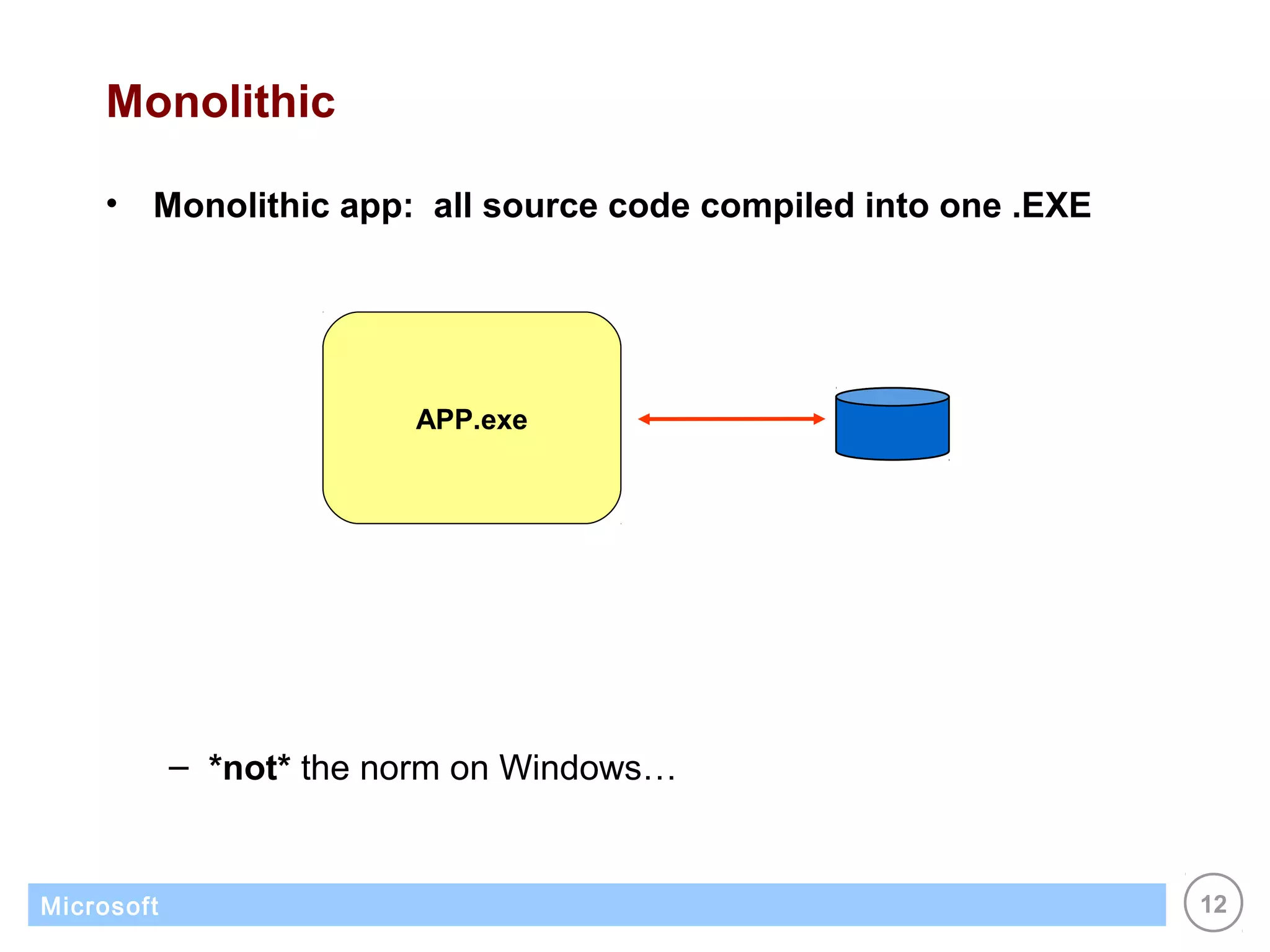
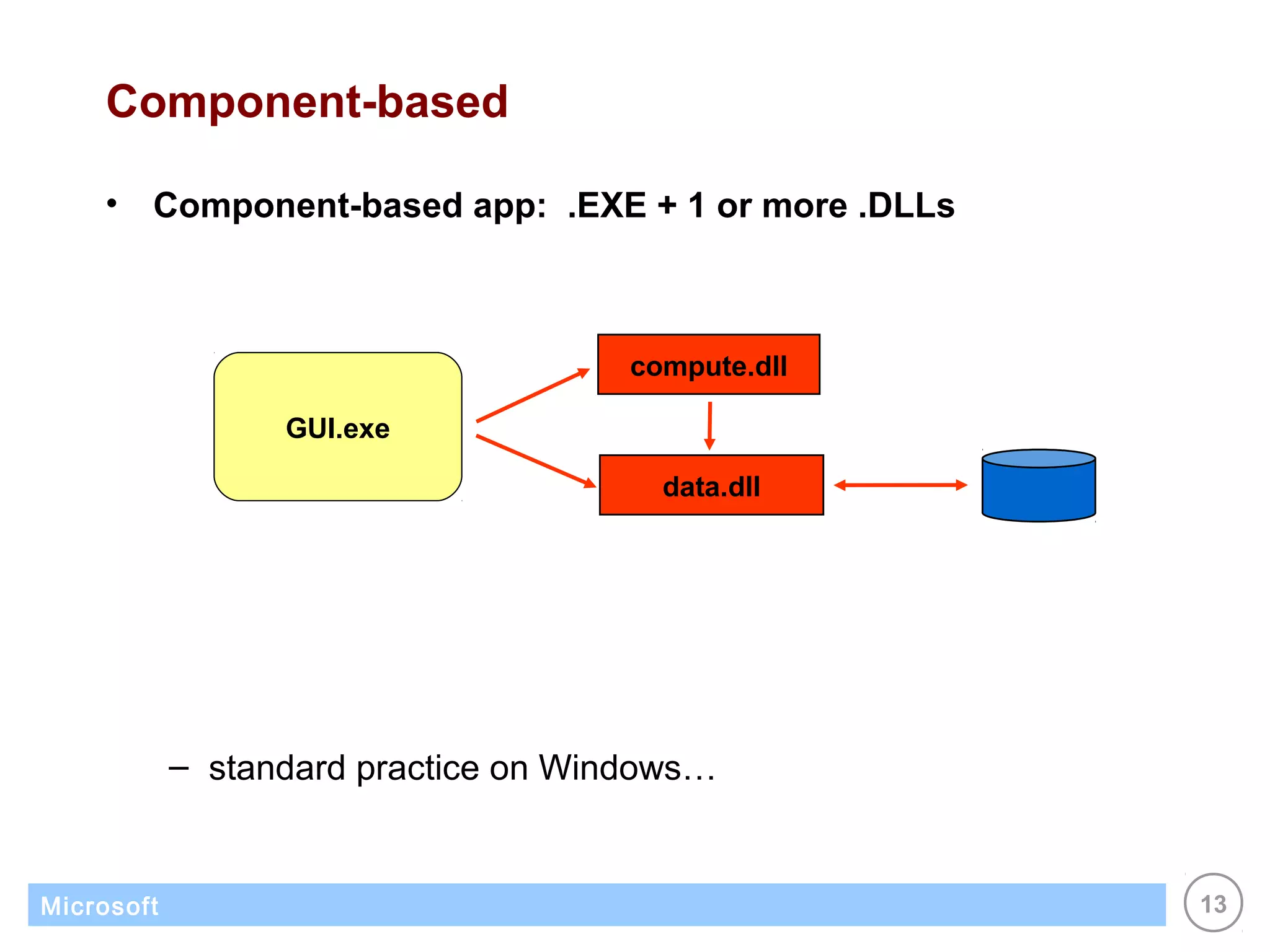
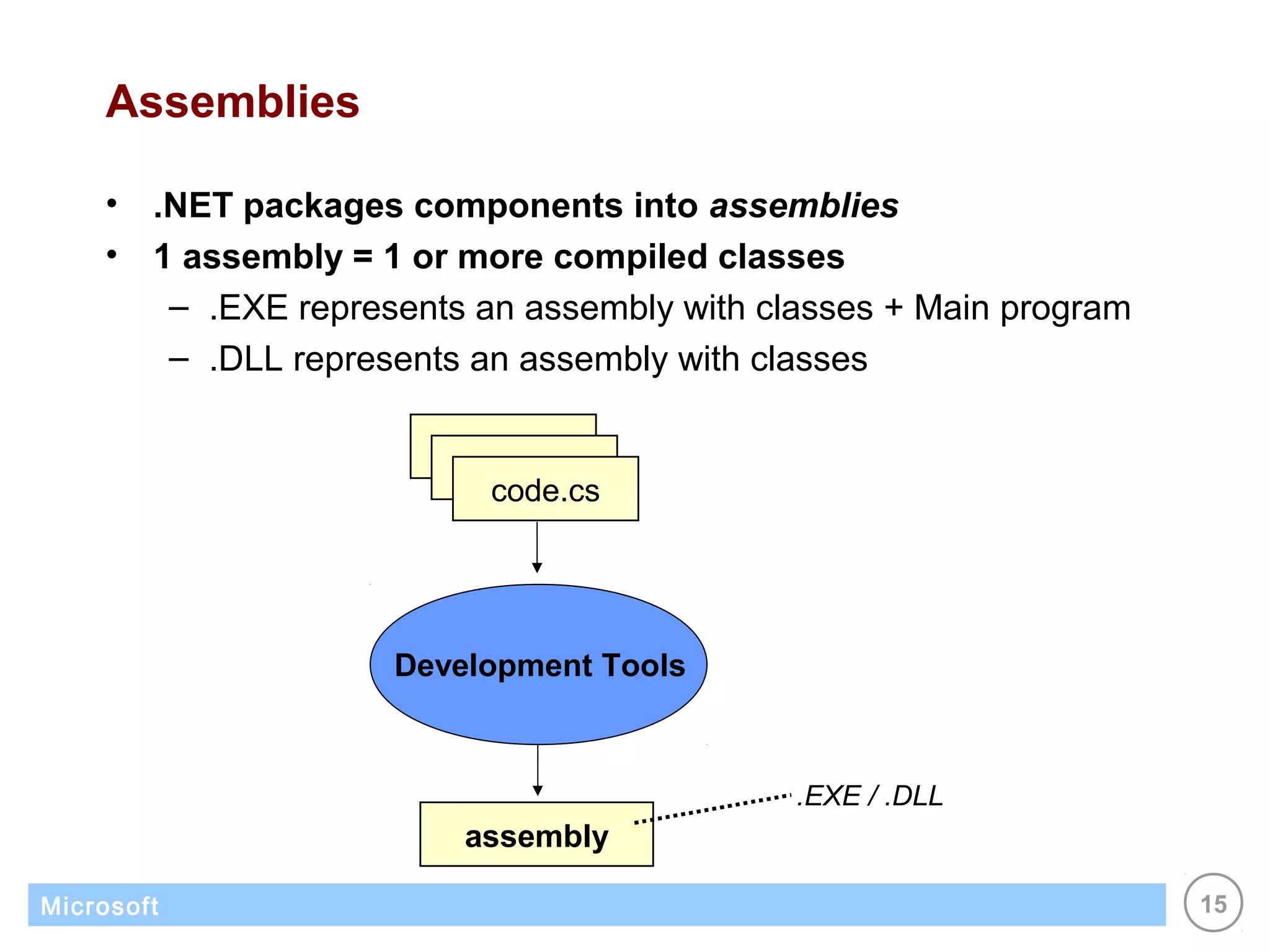
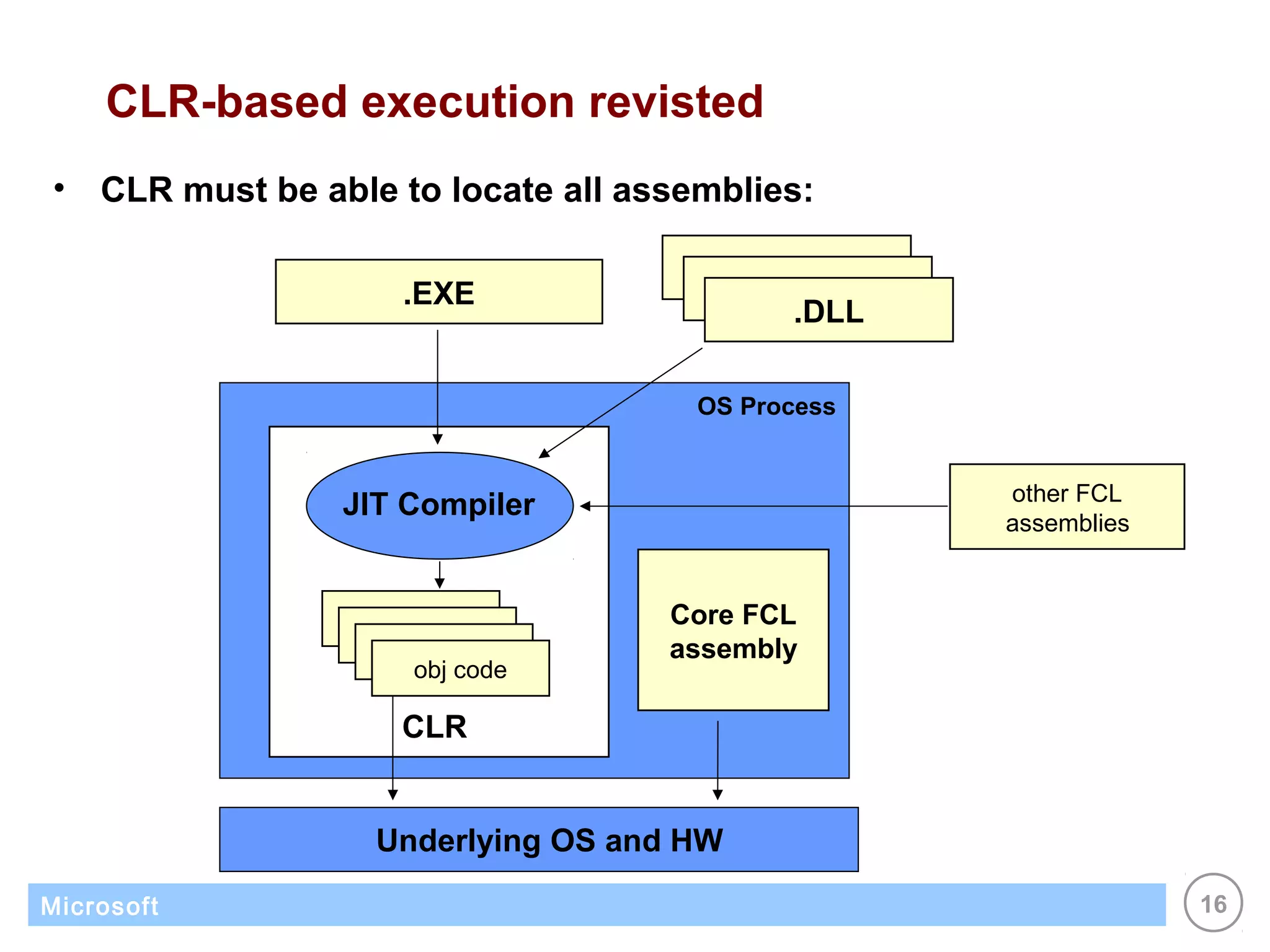
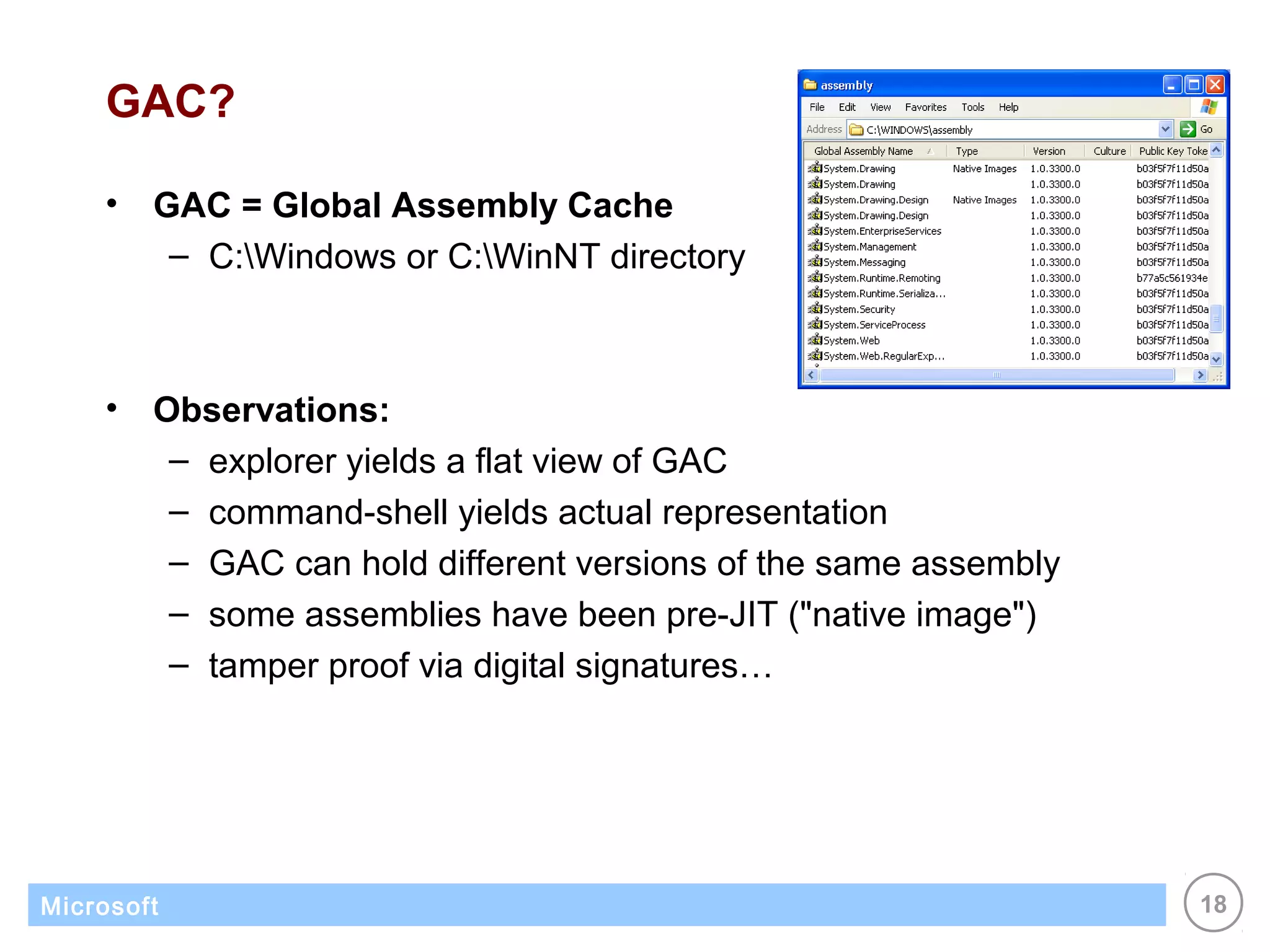
The .NET architecture consists of the Common Language Runtime (CLR) and Framework Class Library (FCL). The CLR defines a common programming model and standard type system for cross-platform, multi-language development. .NET supports multiple languages and compiles applications into assemblies that can run on any supported platform as long as the CLR and FCL are present. Component-based application designs with assemblies packaged into EXEs and DLLs are common.