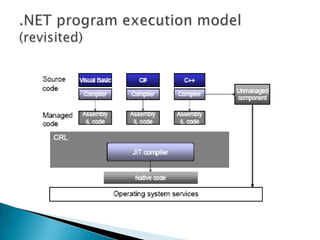
.Net Assemblies are the fundamental units of deployment and reuse in .Net applications. They consist of executable code (CIL/MSIL), type metadata, and resources. Assemblies provide a logical grouping of types and resources and record versioning and dependency information that allows side-by-side loading. Assemblies can be private and deployed with an application or shared and installed in the global assembly cache for use by all applications on a machine.