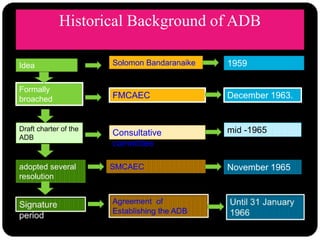
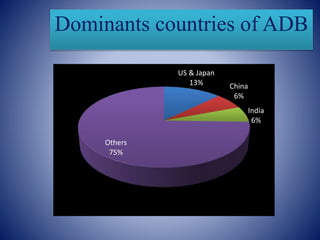
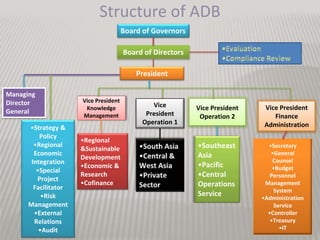
This presentation provides an overview of the Asian Development Bank (ADB). It discusses the ADB's historical background, objectives, structure, and functions. The key points are:
- The ADB was established in 1966 and is headquartered in Manila, Philippines. Its mission is to reduce poverty and improve living conditions in Asia and the Pacific.
- The ADB's main objectives are to foster economic growth, accelerate development, and eliminate poverty in Asia and the Pacific.
- The ADB provides loans, technical assistance, and promotes investment to support infrastructure, agriculture, social services, and other development projects across its 67 members.
- Governance and decision-making powers are held by the Board