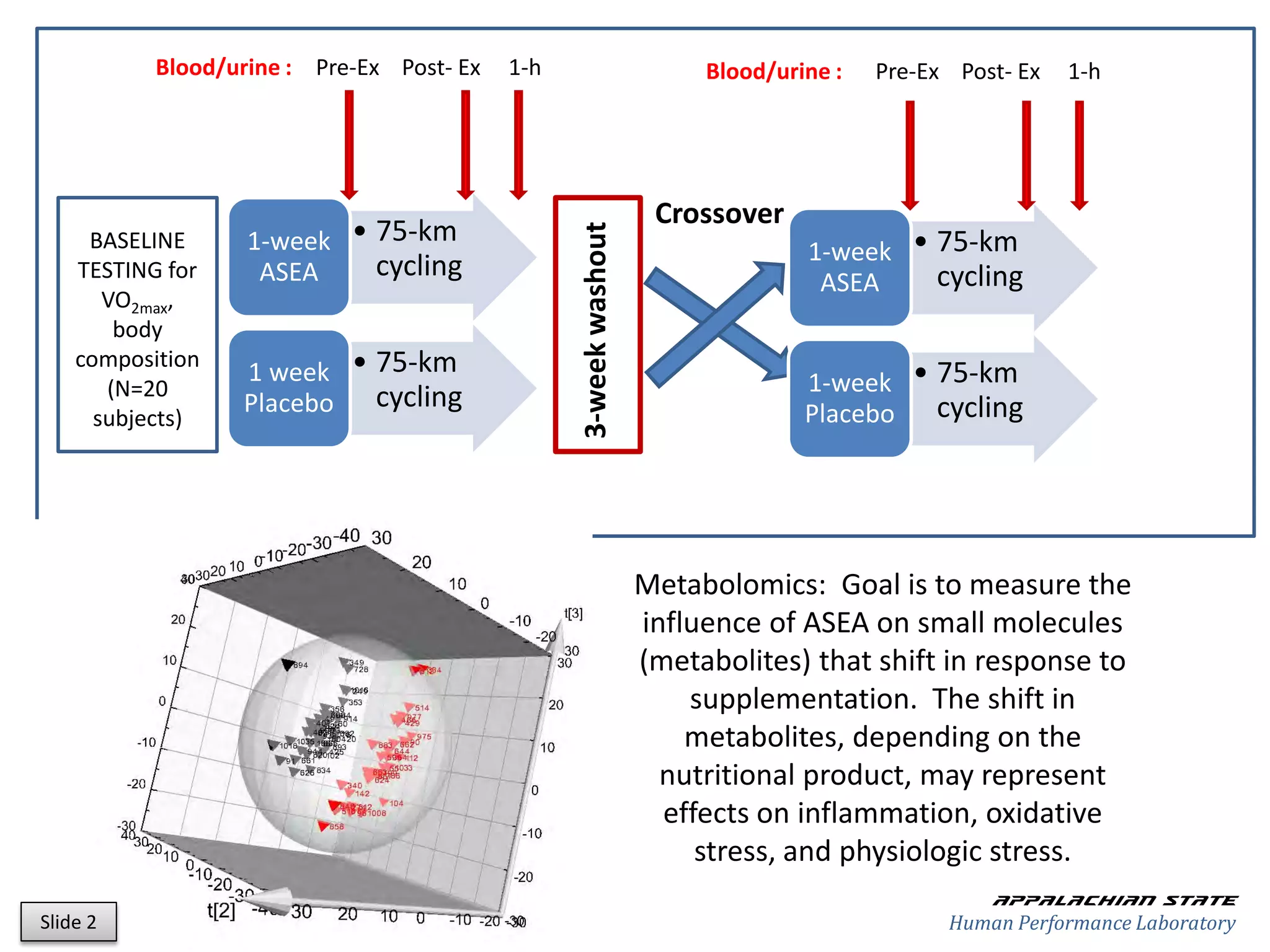
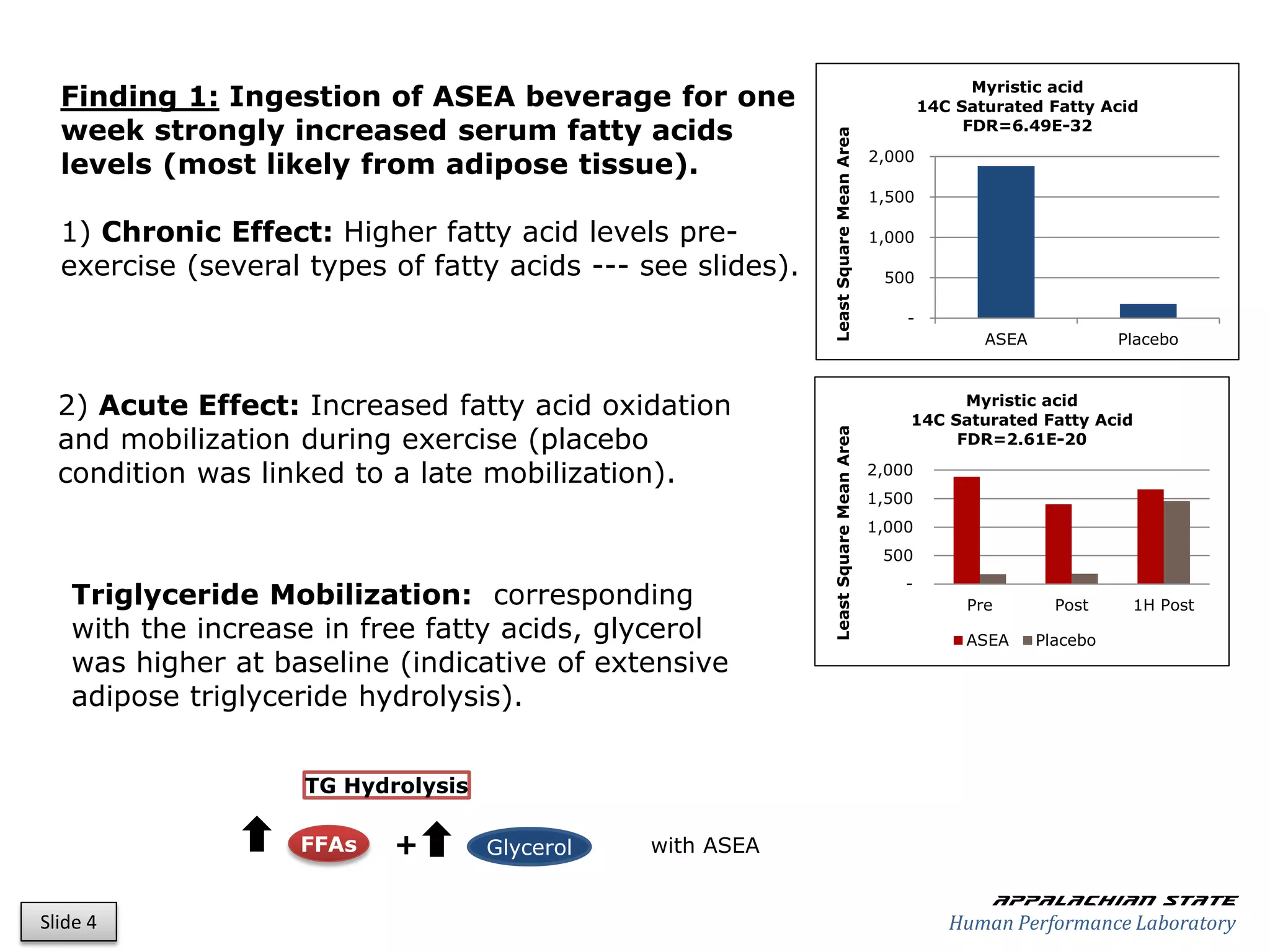
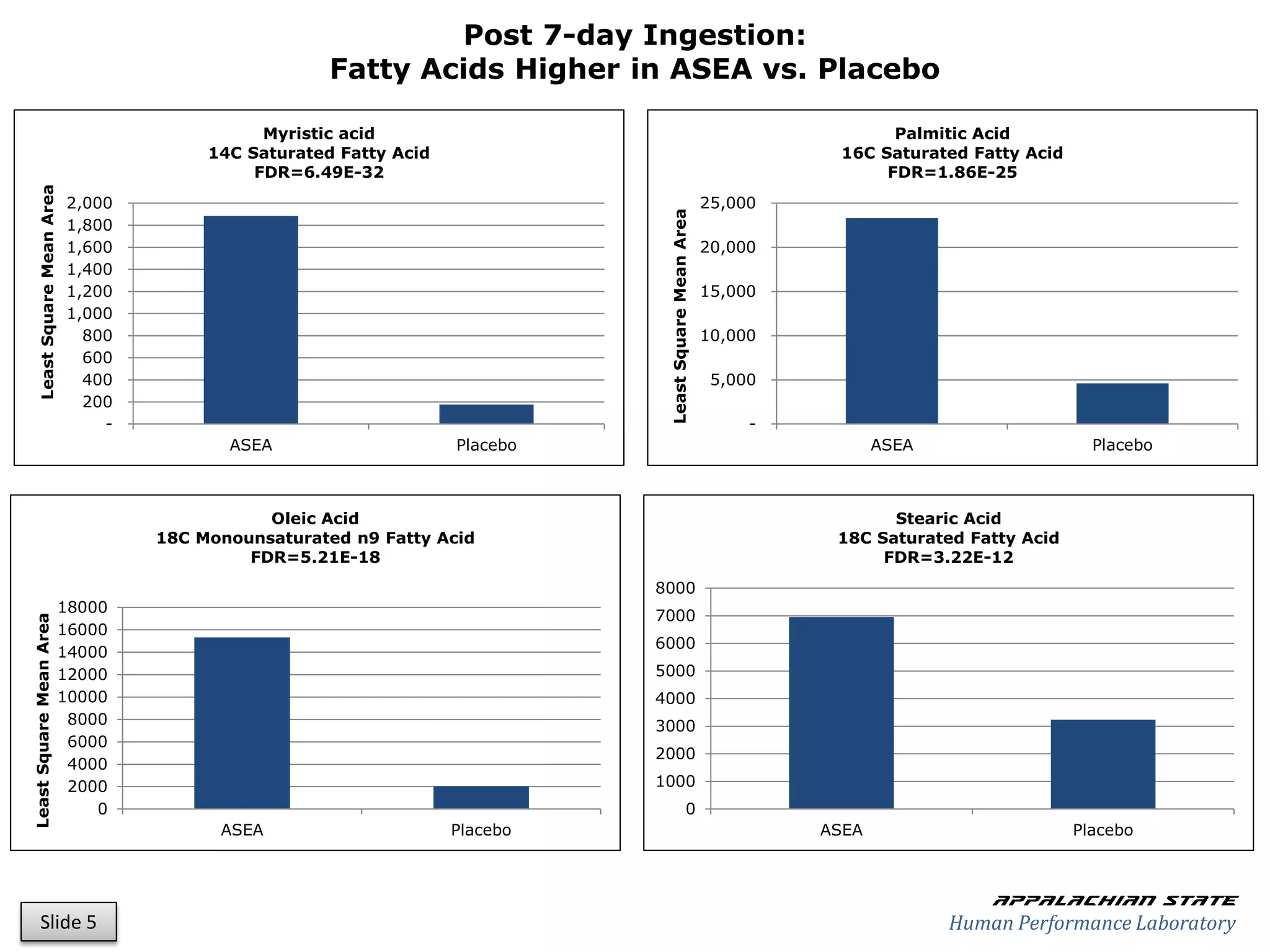
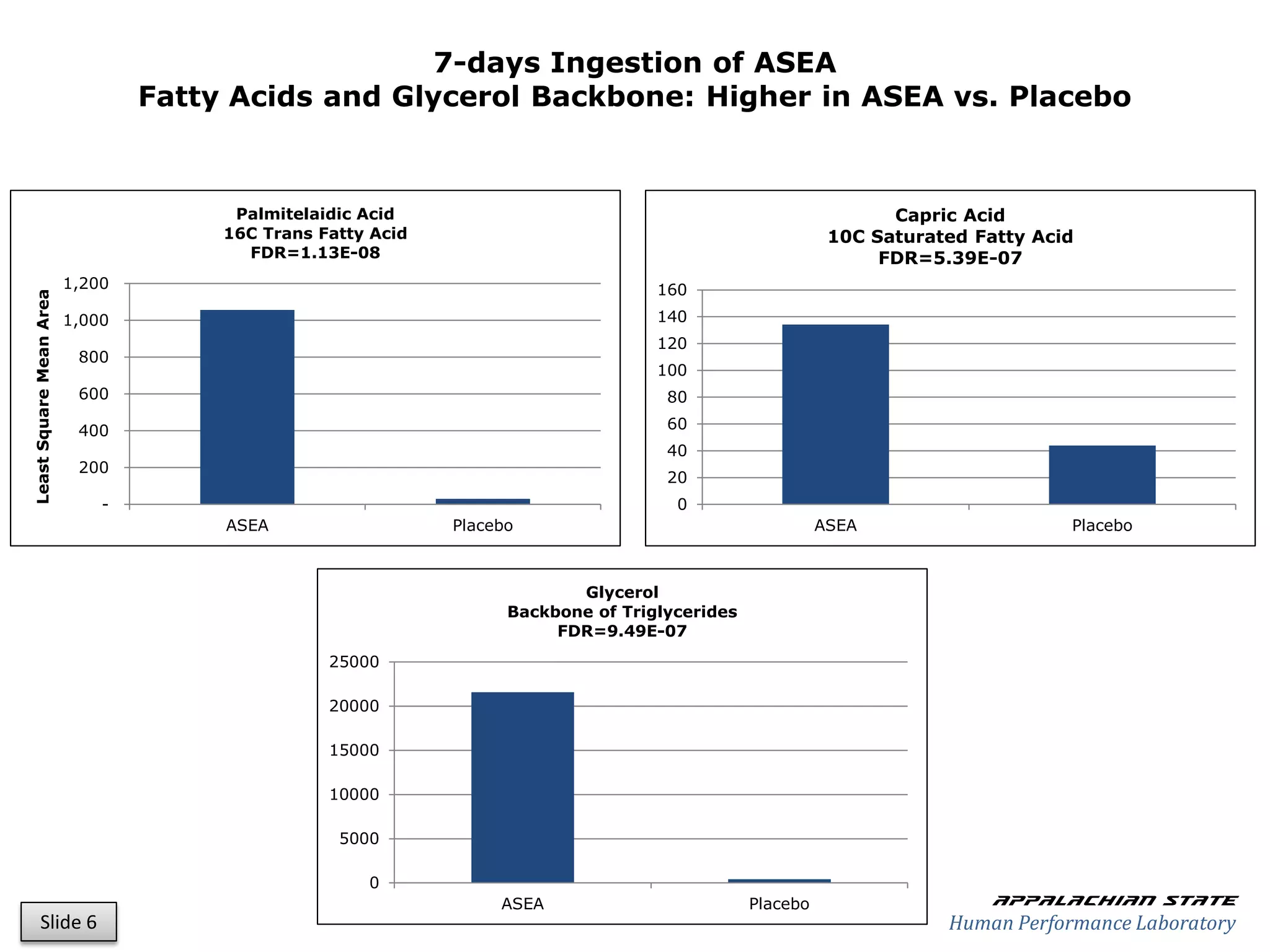
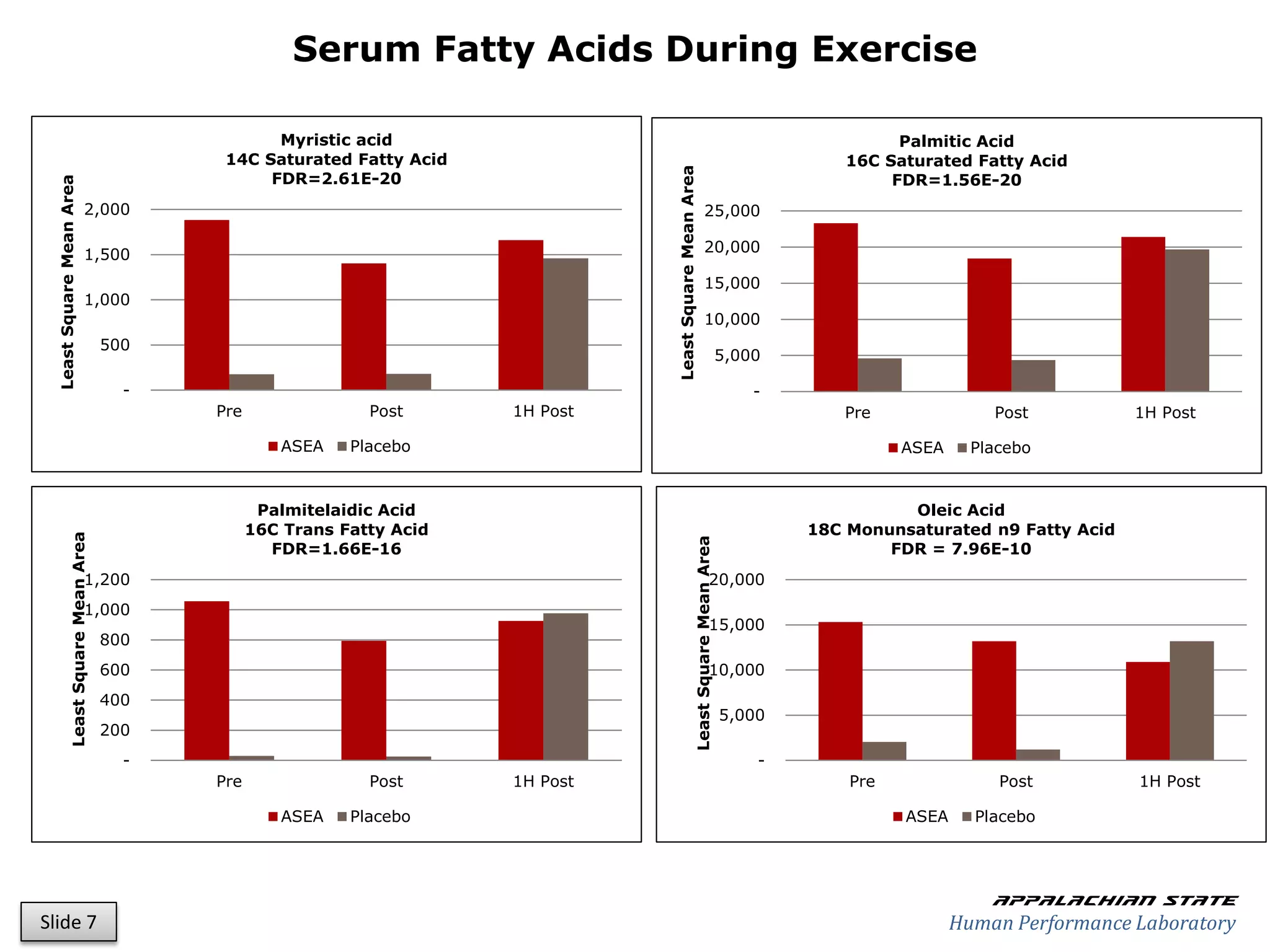
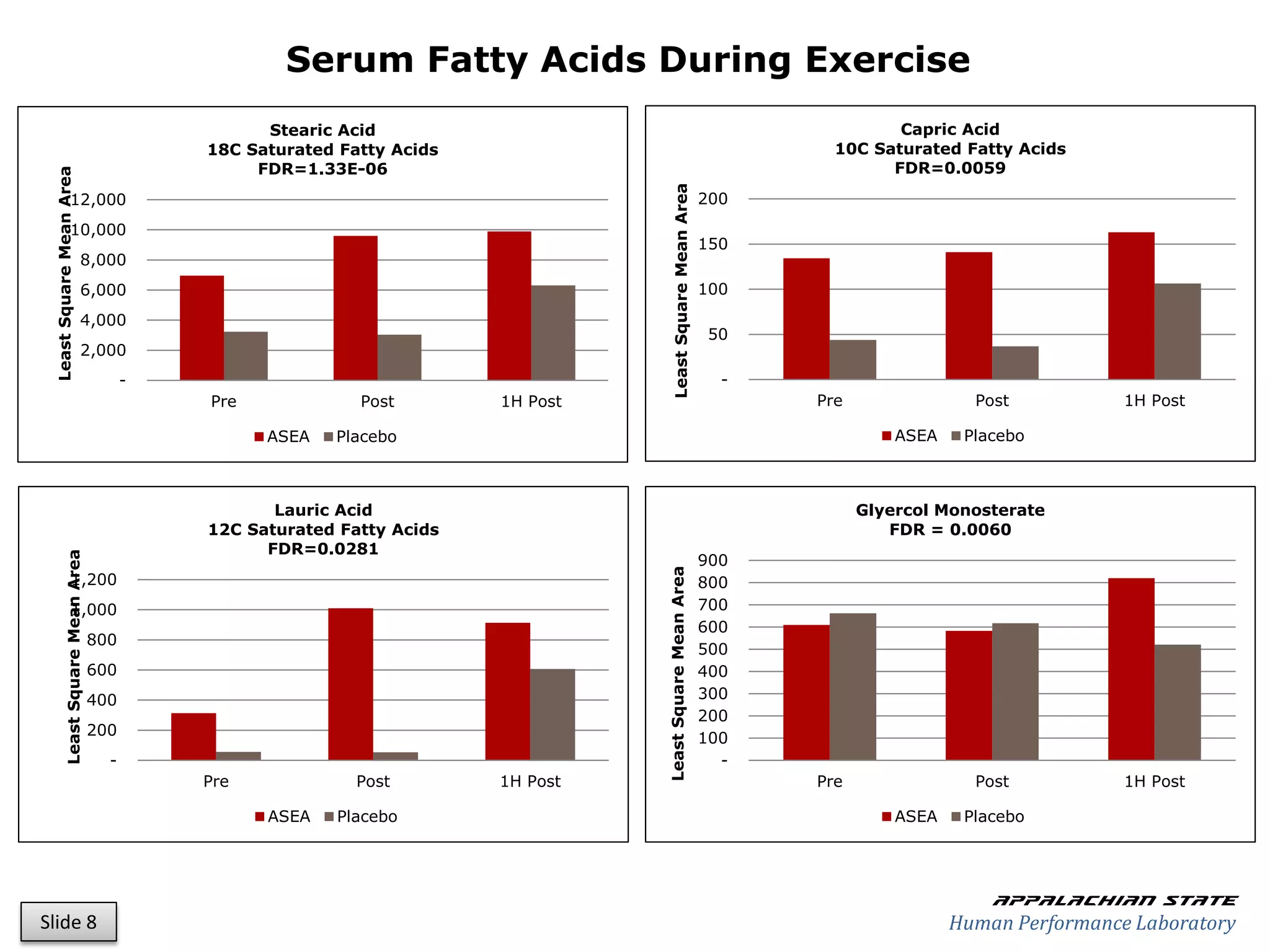
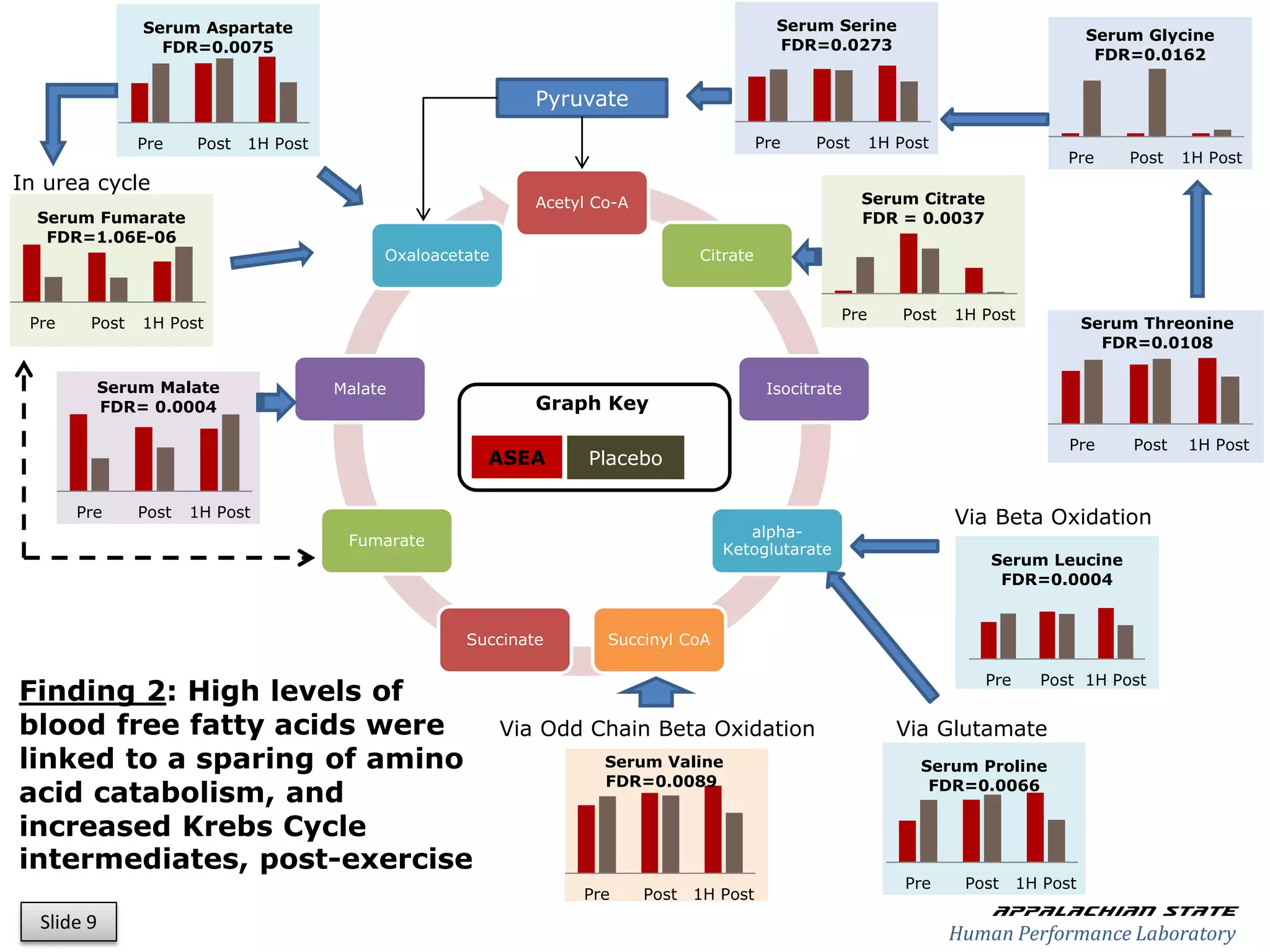
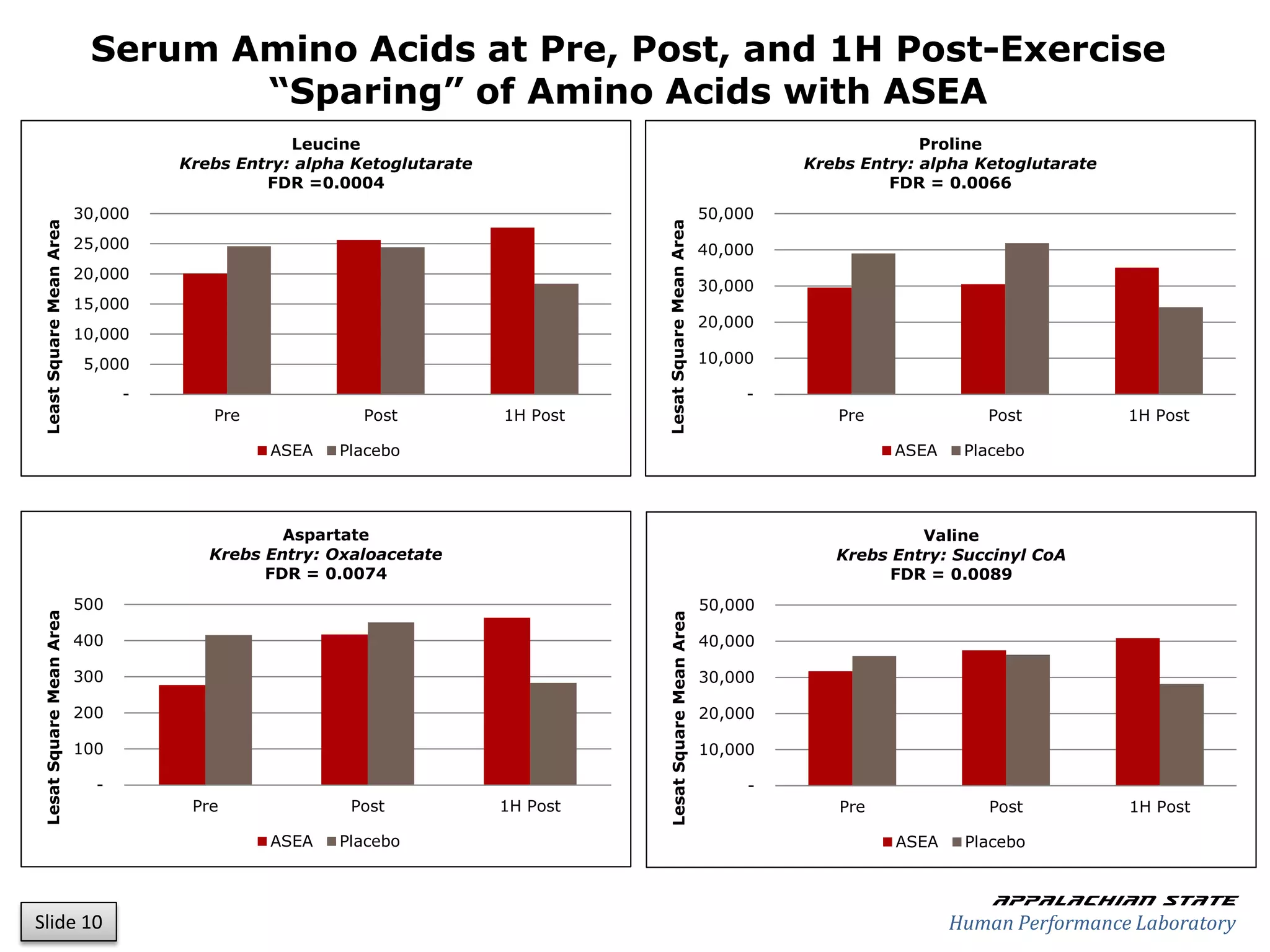
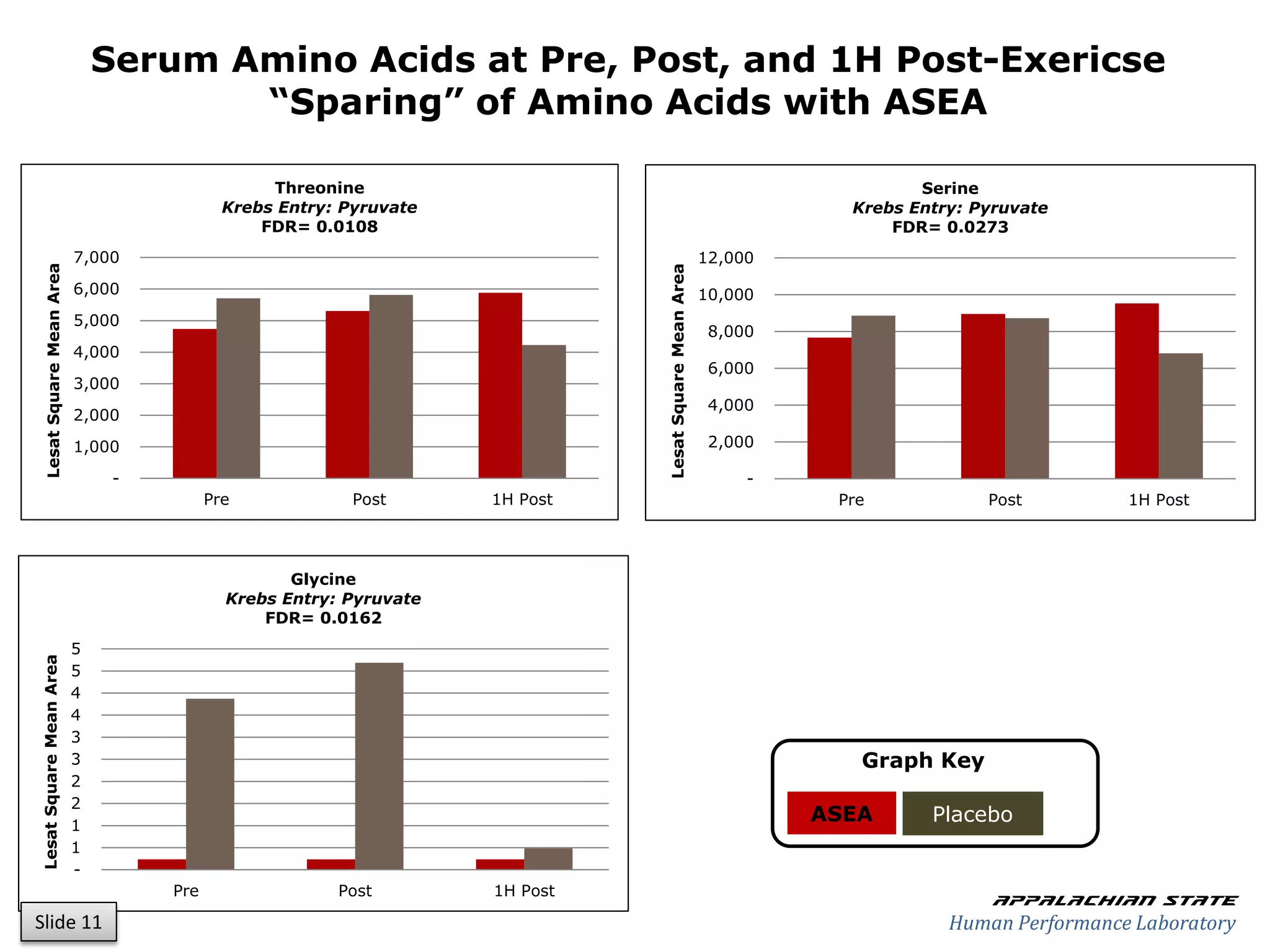
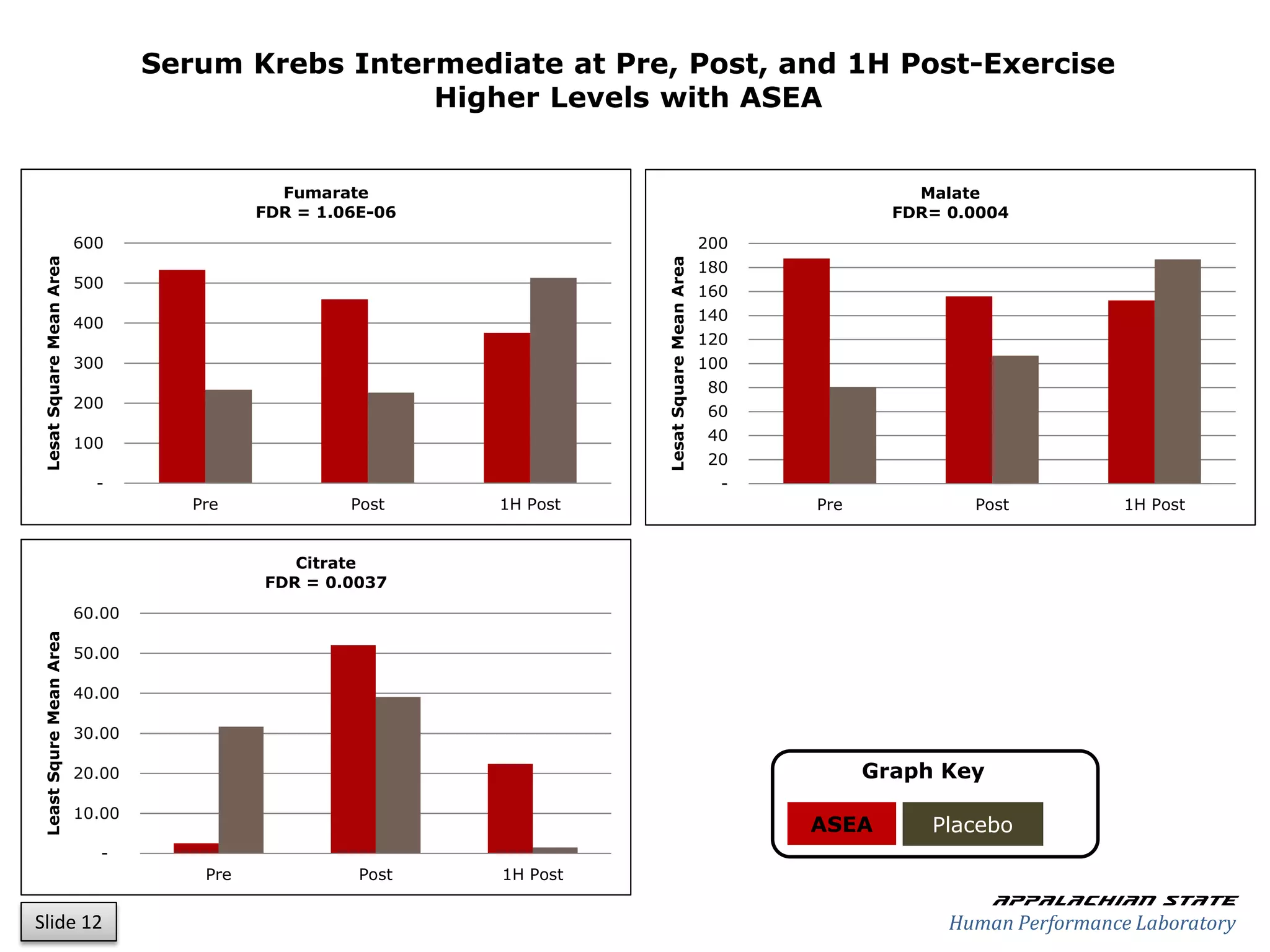
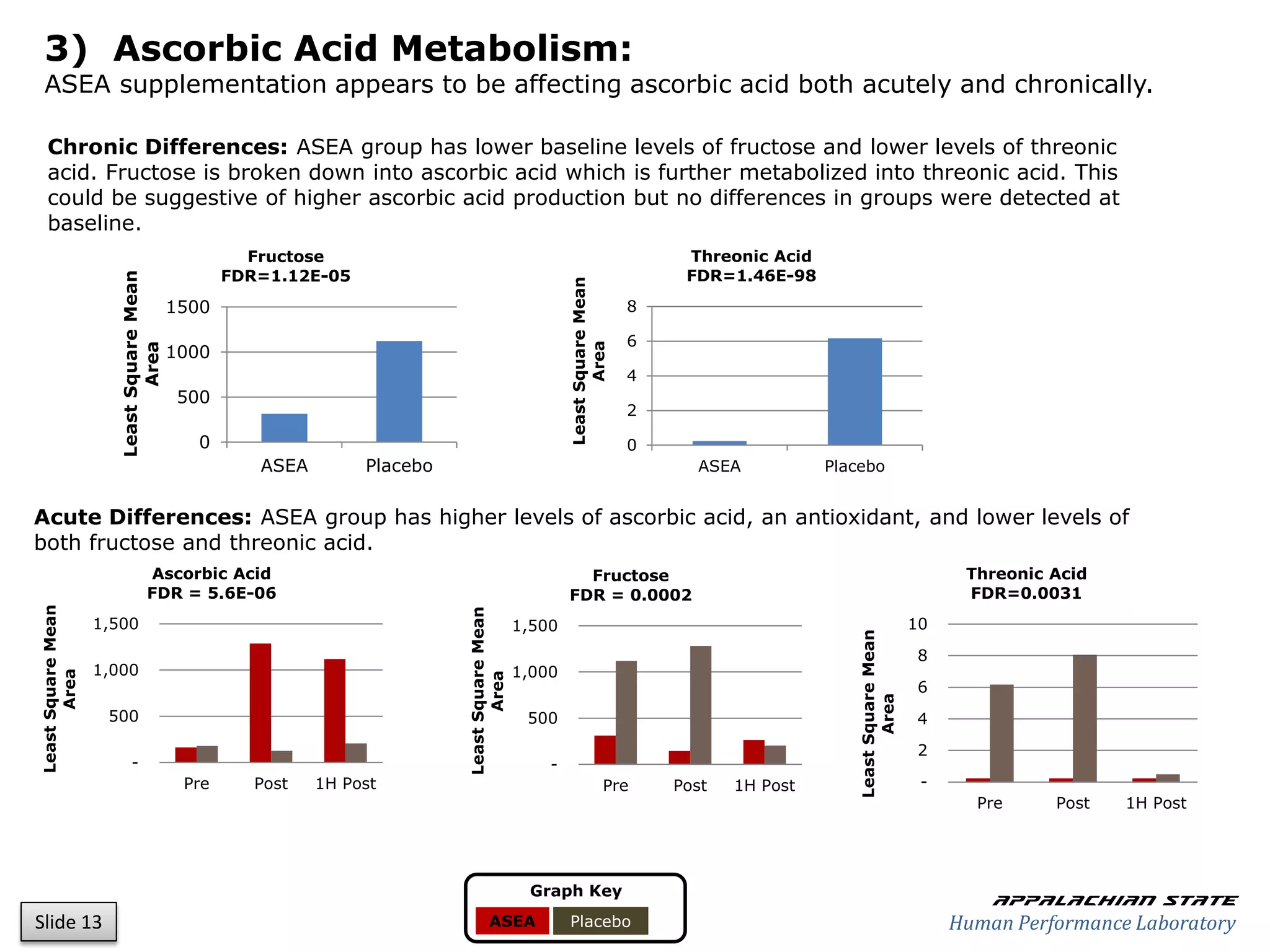
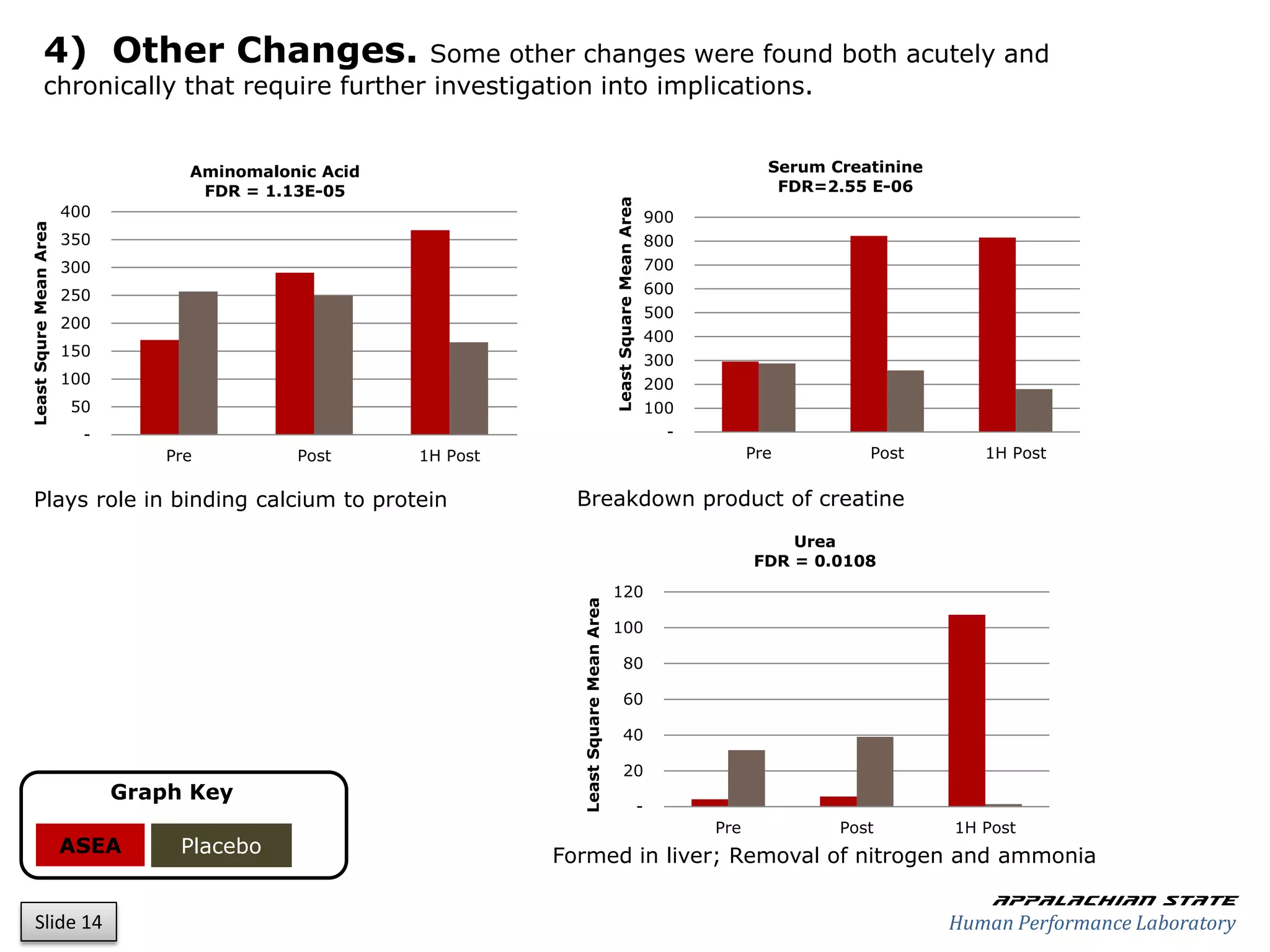
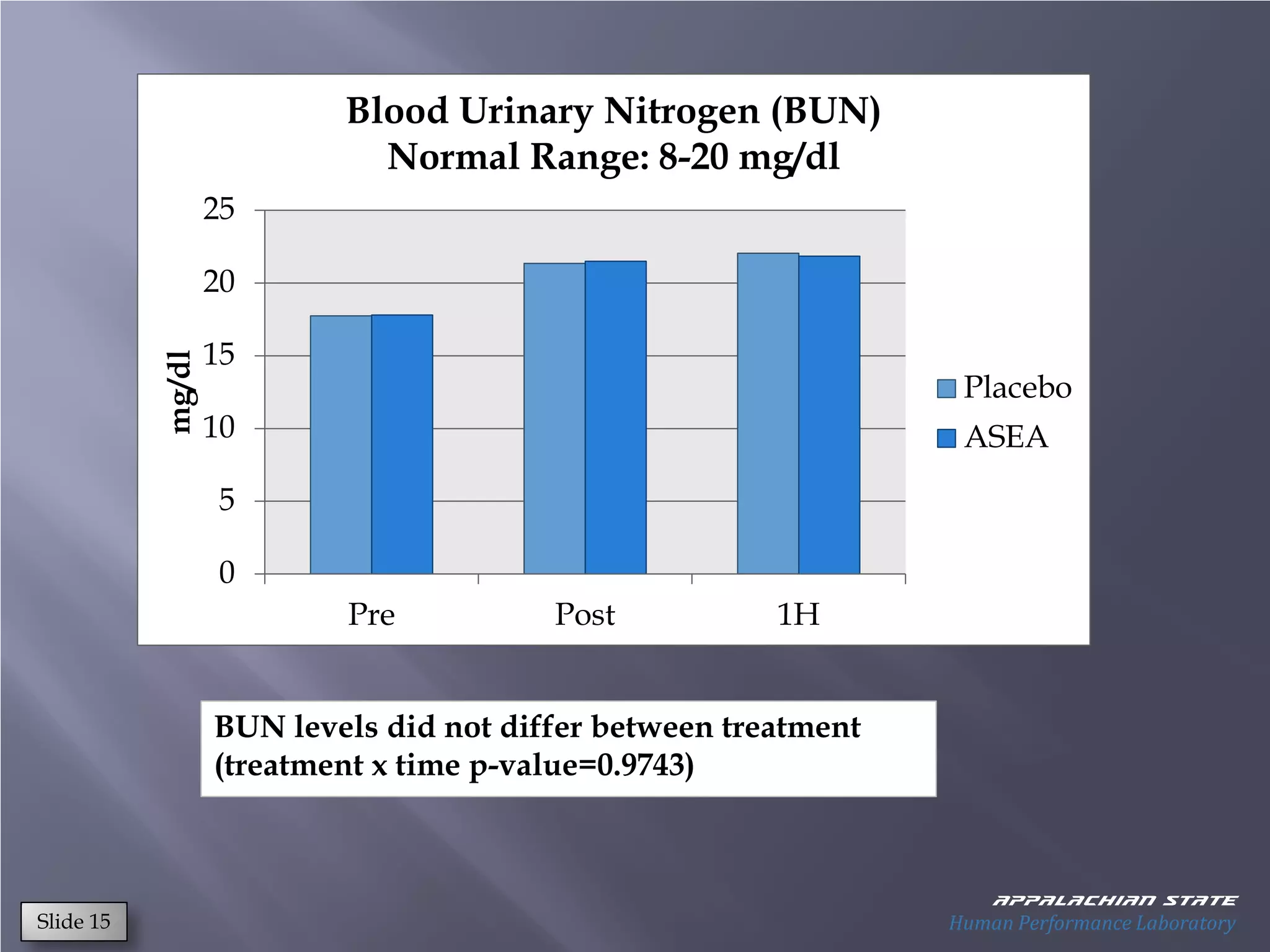
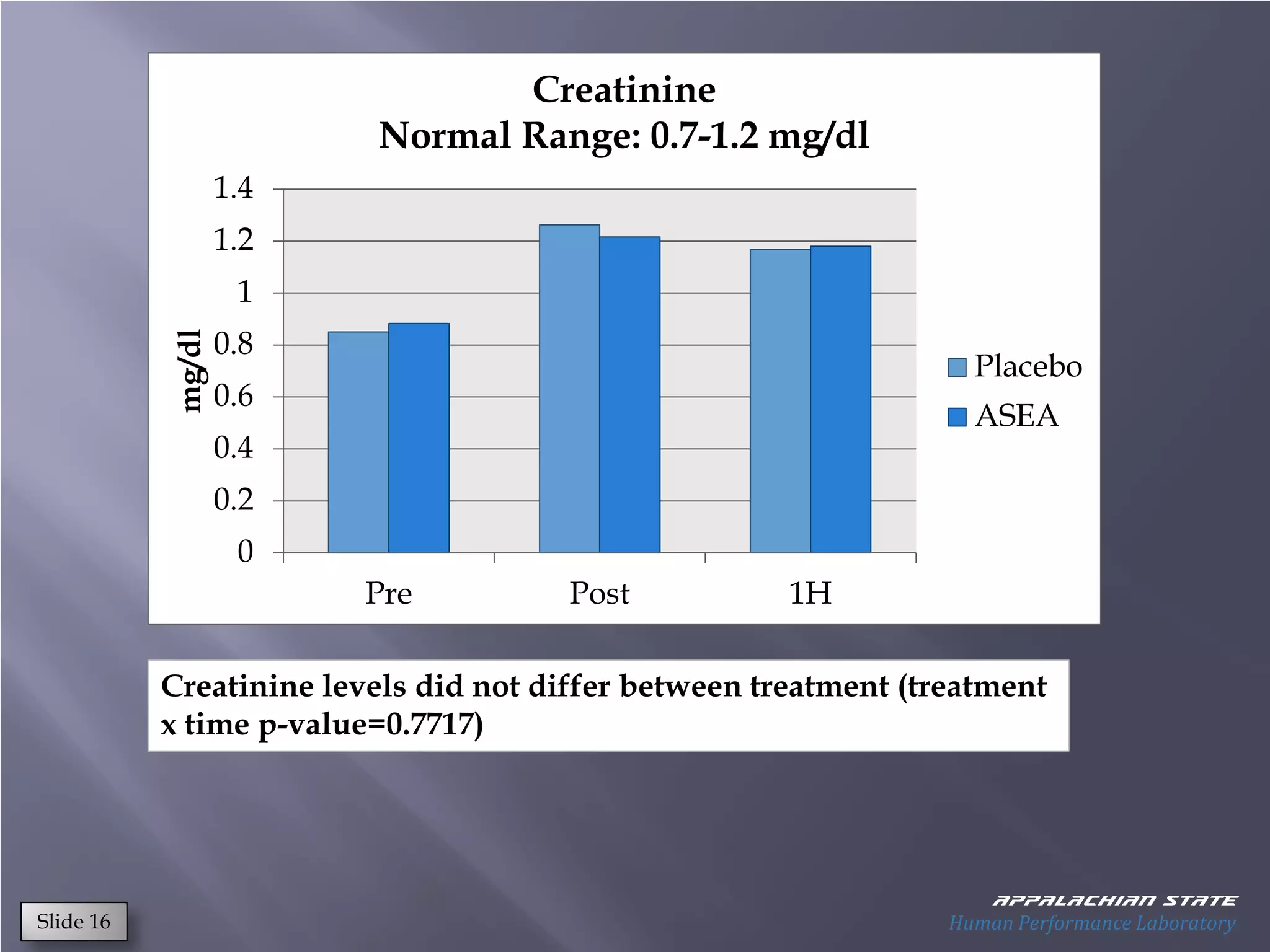
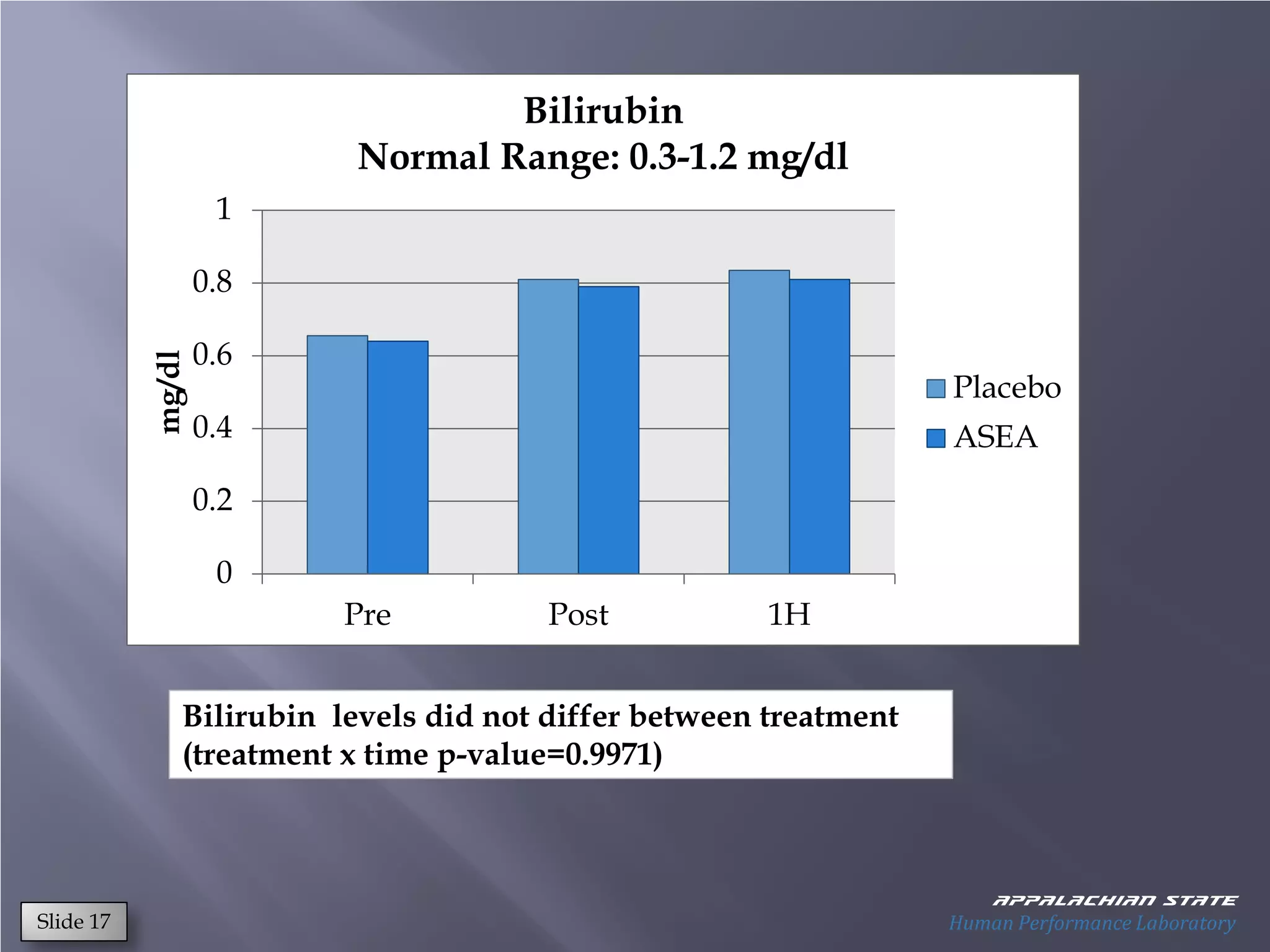
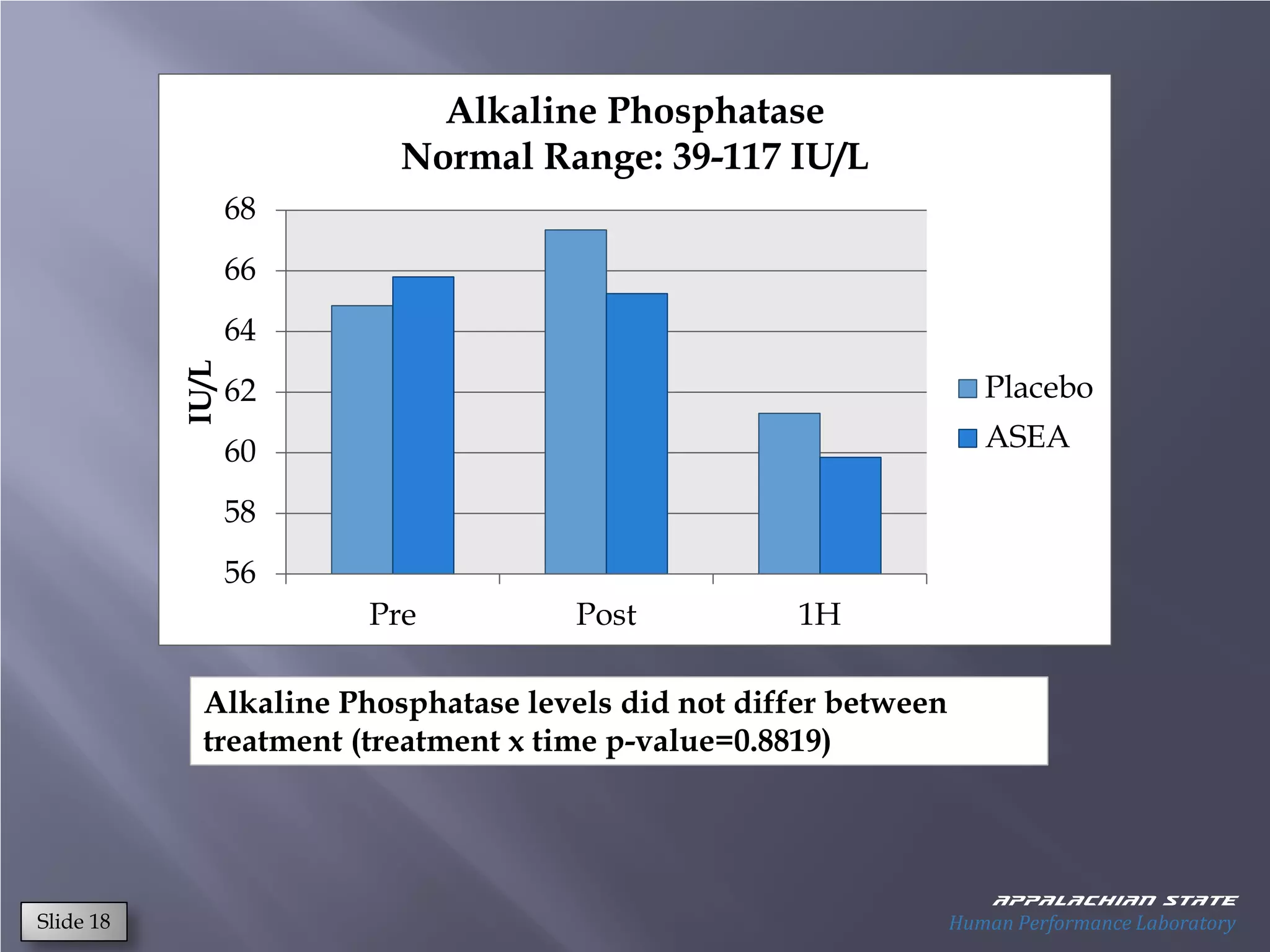
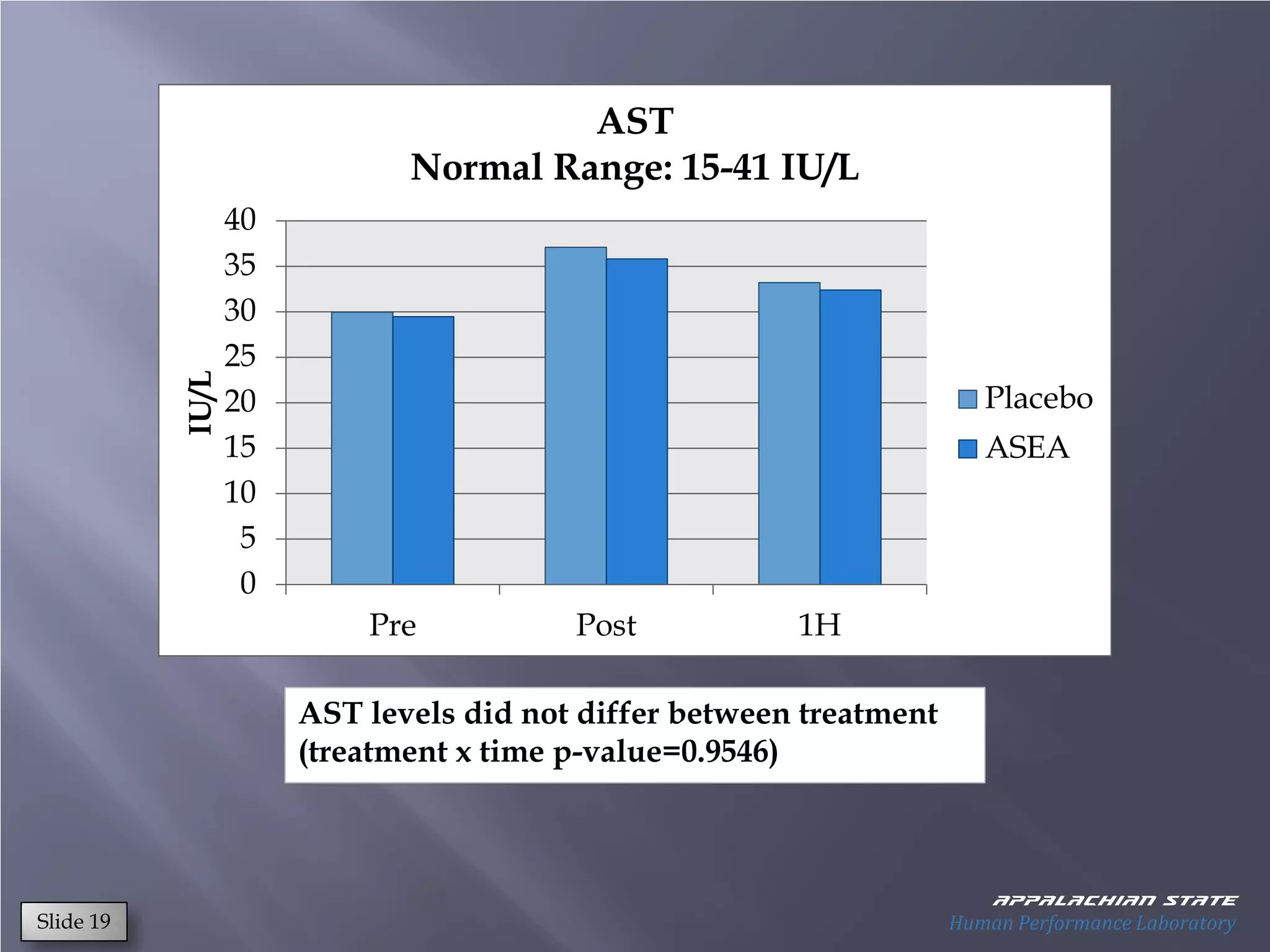
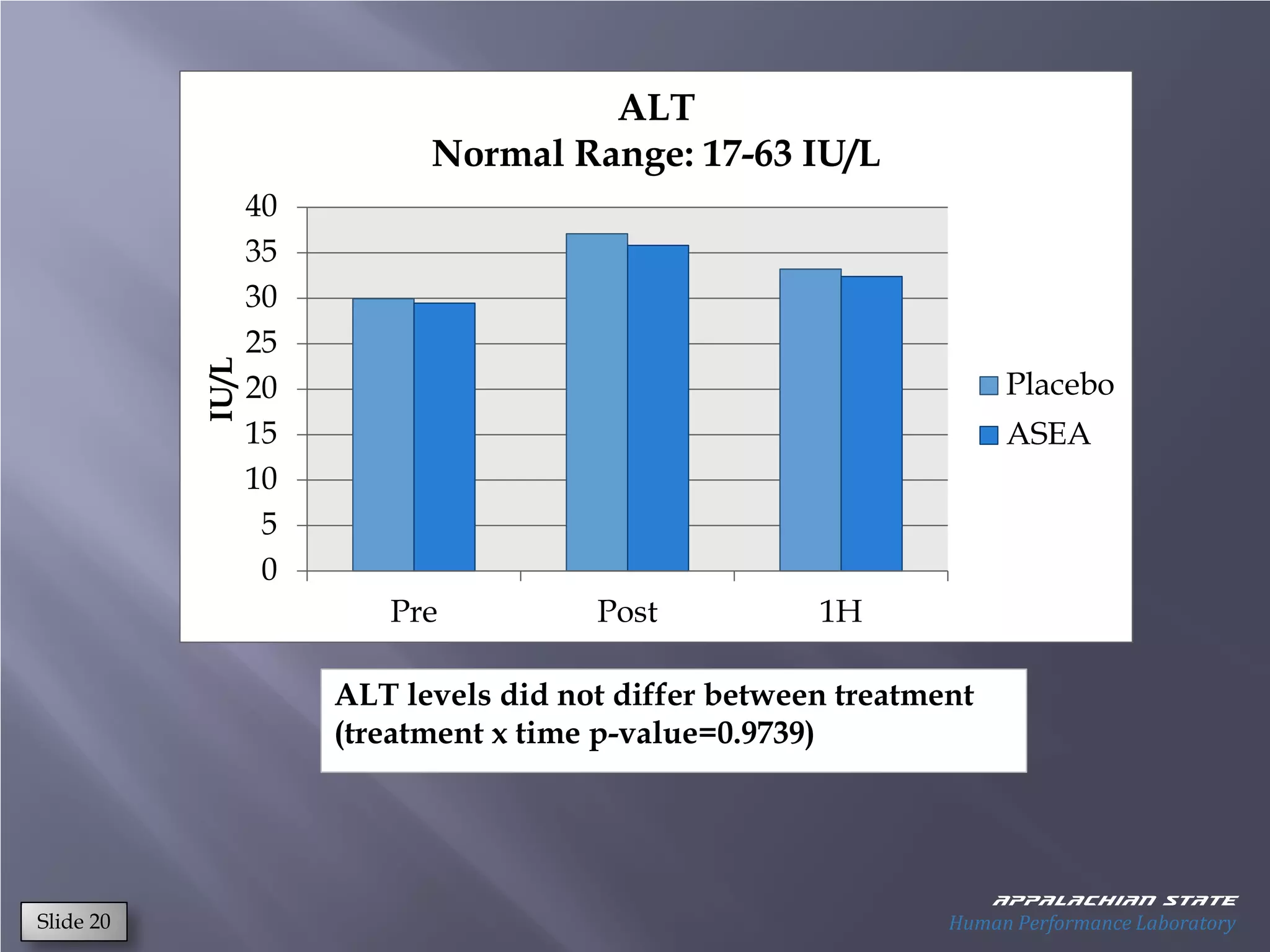
This document outlines the results of a metabolomics study on the effects of Asea supplementation in male cyclists, highlighting its impact on free fatty acids, fat oxidation, and amino acid sparing during exercise. The findings suggest significant increases in various serum metabolites, particularly in free fatty acids and ascorbic acid levels, after a week of Asea ingestion compared to a placebo. Additionally, changes in other metabolites related to energy metabolism and antioxidative stress were noted, indicating potential benefits of Asea supplementation for athletic performance.