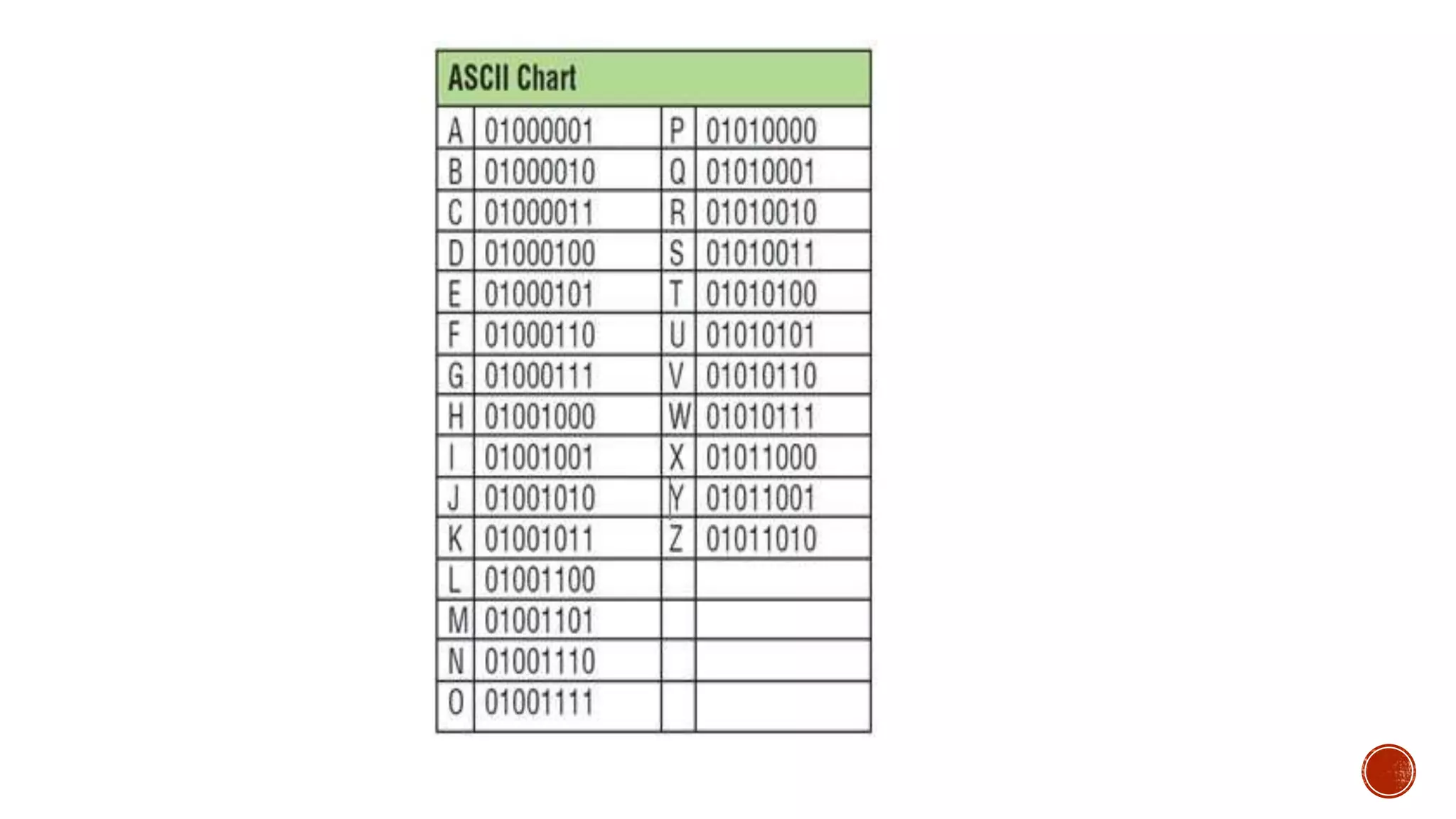
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a 7-bit character encoding scheme where each character is assigned a number from 0-127. It was developed in 1963 to provide a standard for coding characters like letters, numbers, and symbols. Computers use ASCII to represent text characters numerically so they can be stored and processed using binary numbers.