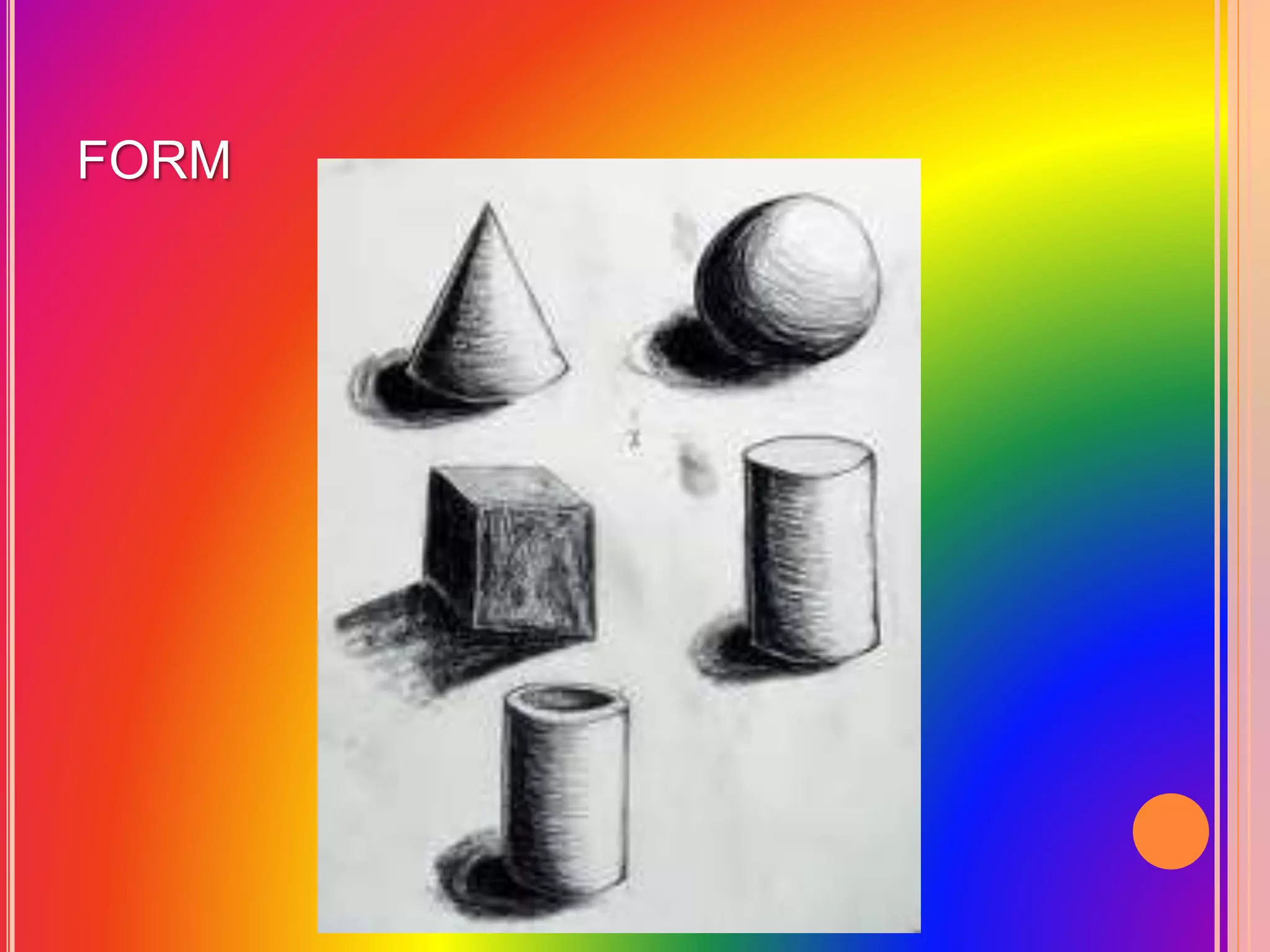
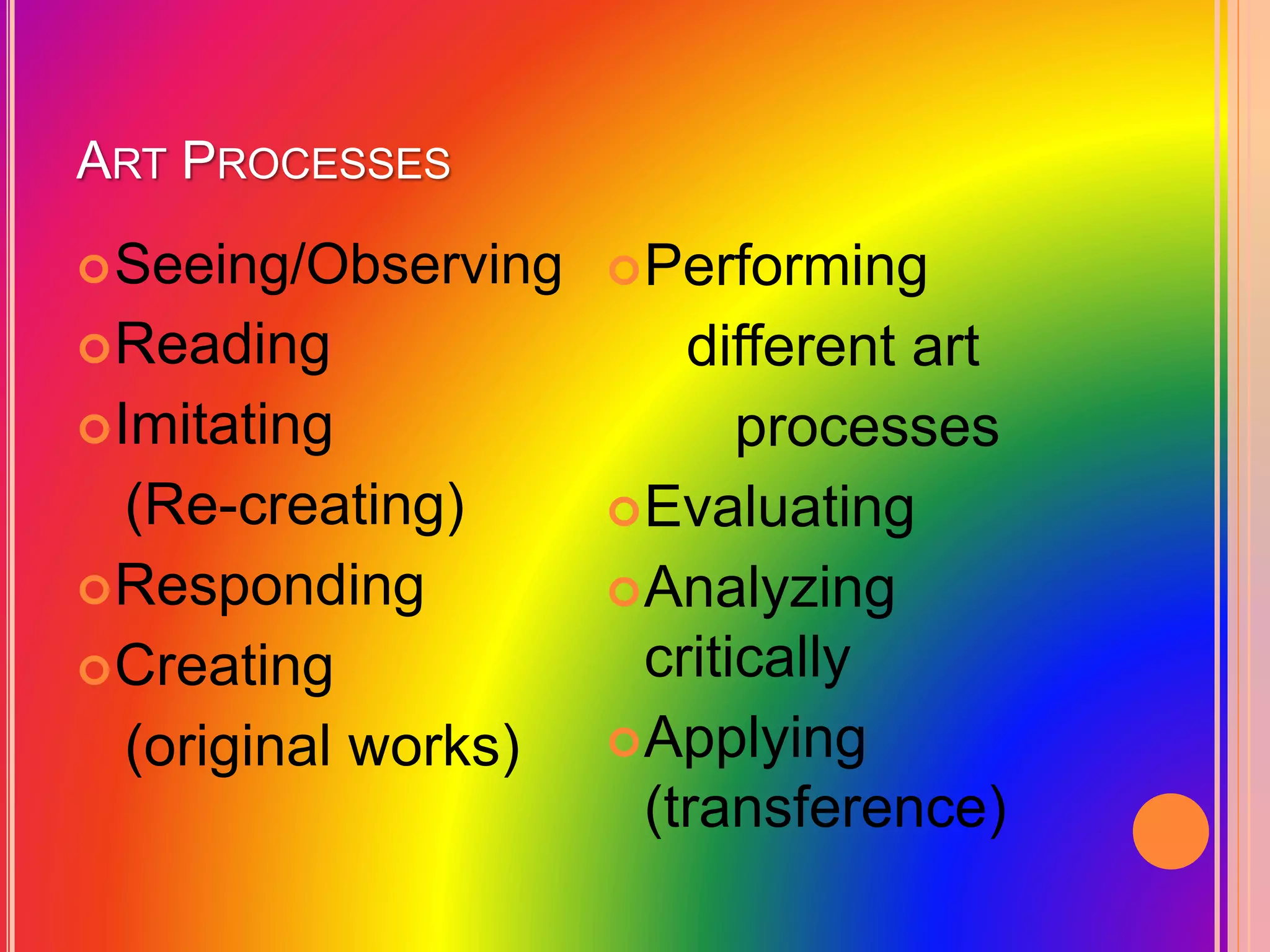
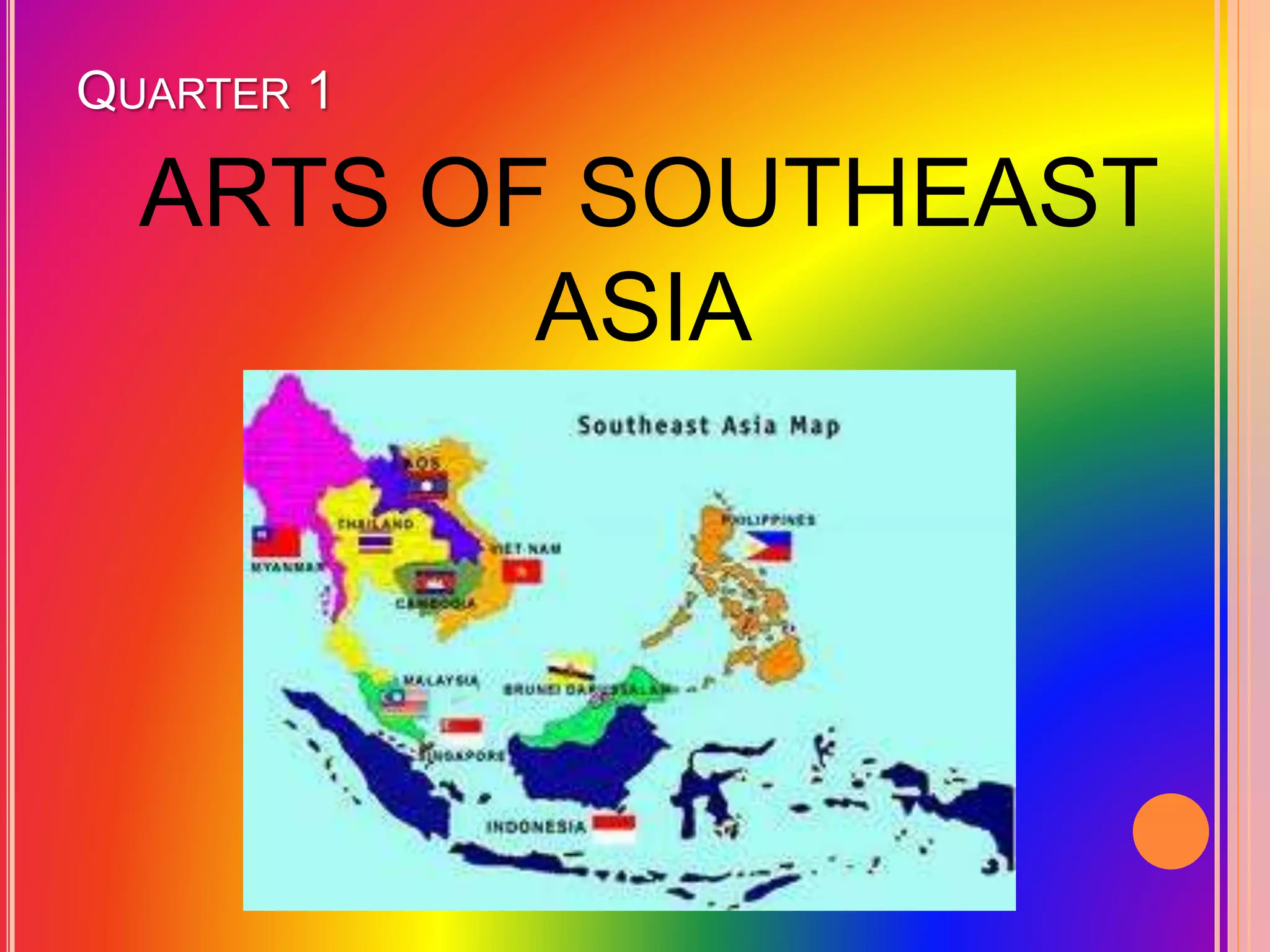
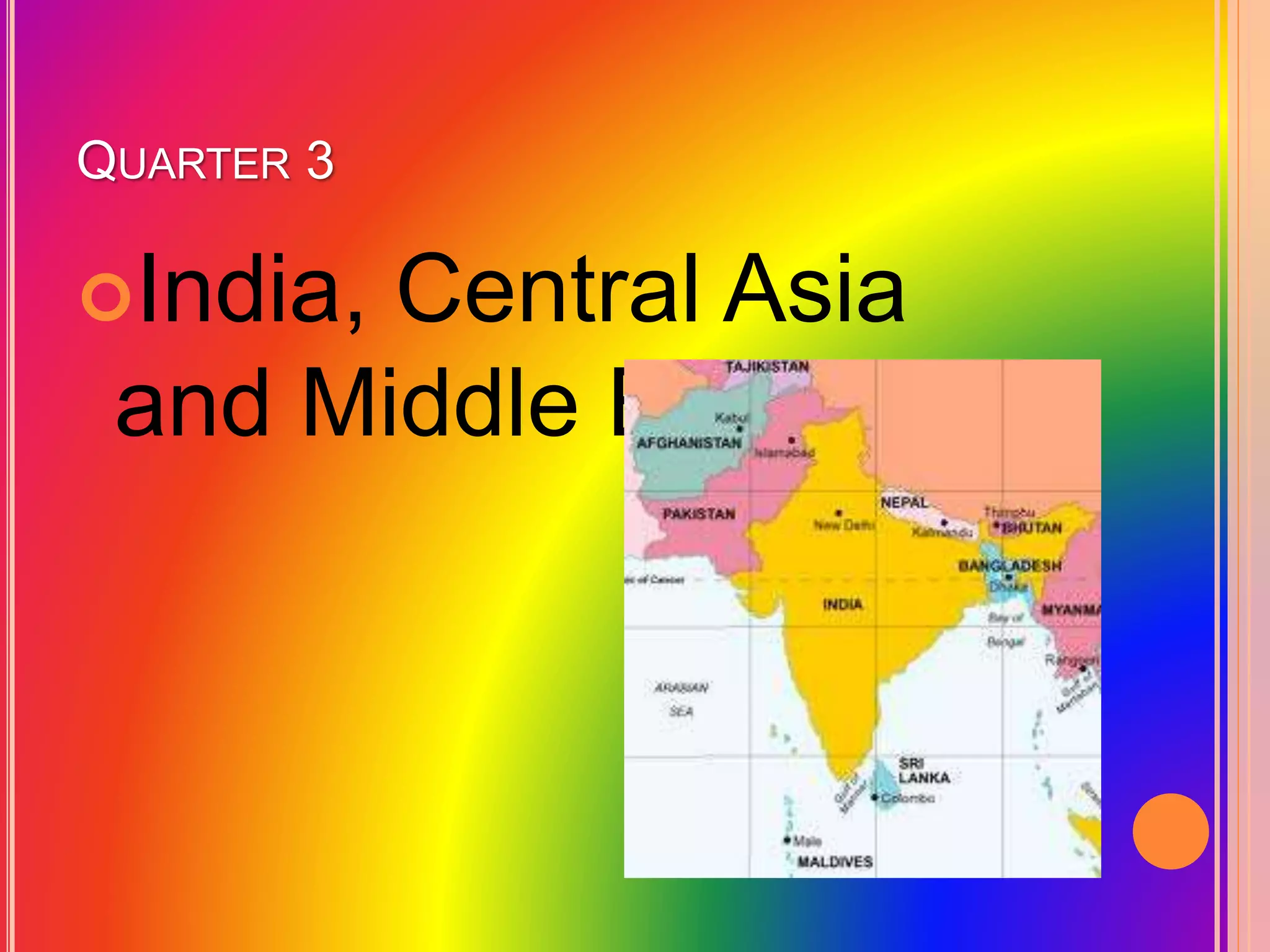
This document provides an overview of the Grade 8 Arts curriculum. It is divided into 4 quarters that cover different regions: Southeast Asia, East Asia, India/Central Asia/Middle East, and theater arts/festivals of China, Japan, Indonesia and Thailand. Each quarter includes sections on art forms and processes to learn about the relevant cultures. The art forms discussed include textiles, sculptures, paintings, performances, and festivals. The processes involve hands-on activities to recreate artworks from the regions.