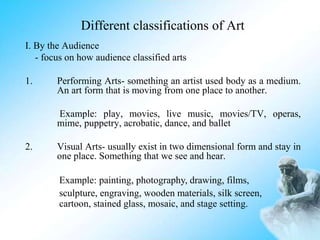
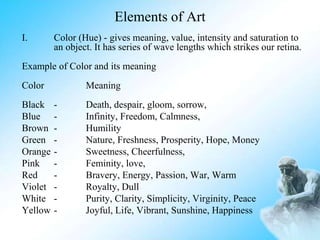
Art can be defined as a creative activity that involves skill in handling materials to express ideas, emotions, and feelings without words. There are various categories and elements of art. Categories include visual arts like painting and sculpture, performing arts like dance and theater, and literary arts. The elements of art that artists use include line, shape, color, texture, form, and space. Principles of art that guide composition include emphasis, balance, harmony, variety, movement, rhythm, proportion, and unity. Artworks can depict different subjects like nature, people, places, and events using techniques like realism, abstraction, and distortion. The artist's medium is the material they use and their technique is how they manipulate the medium to achieve