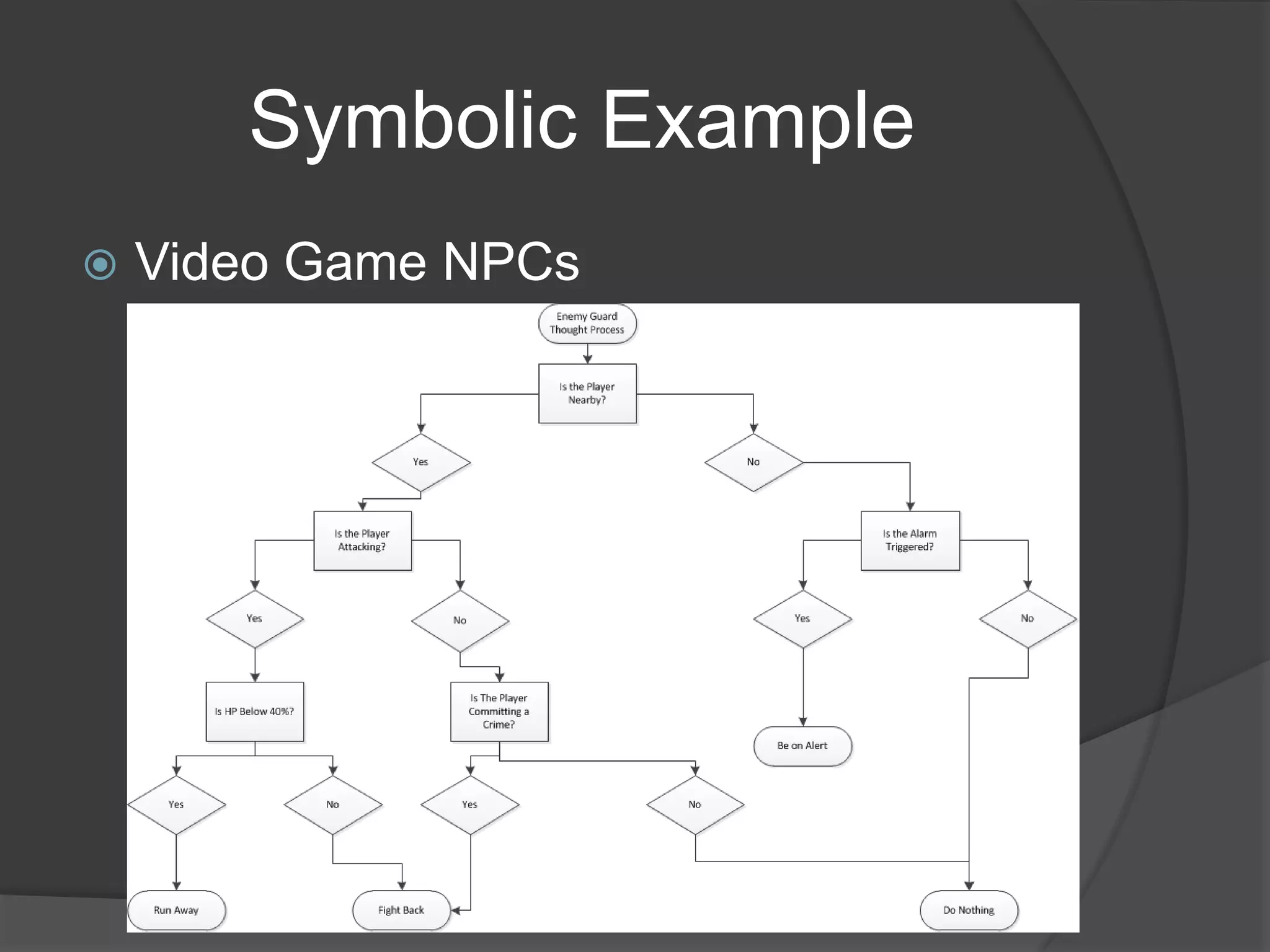
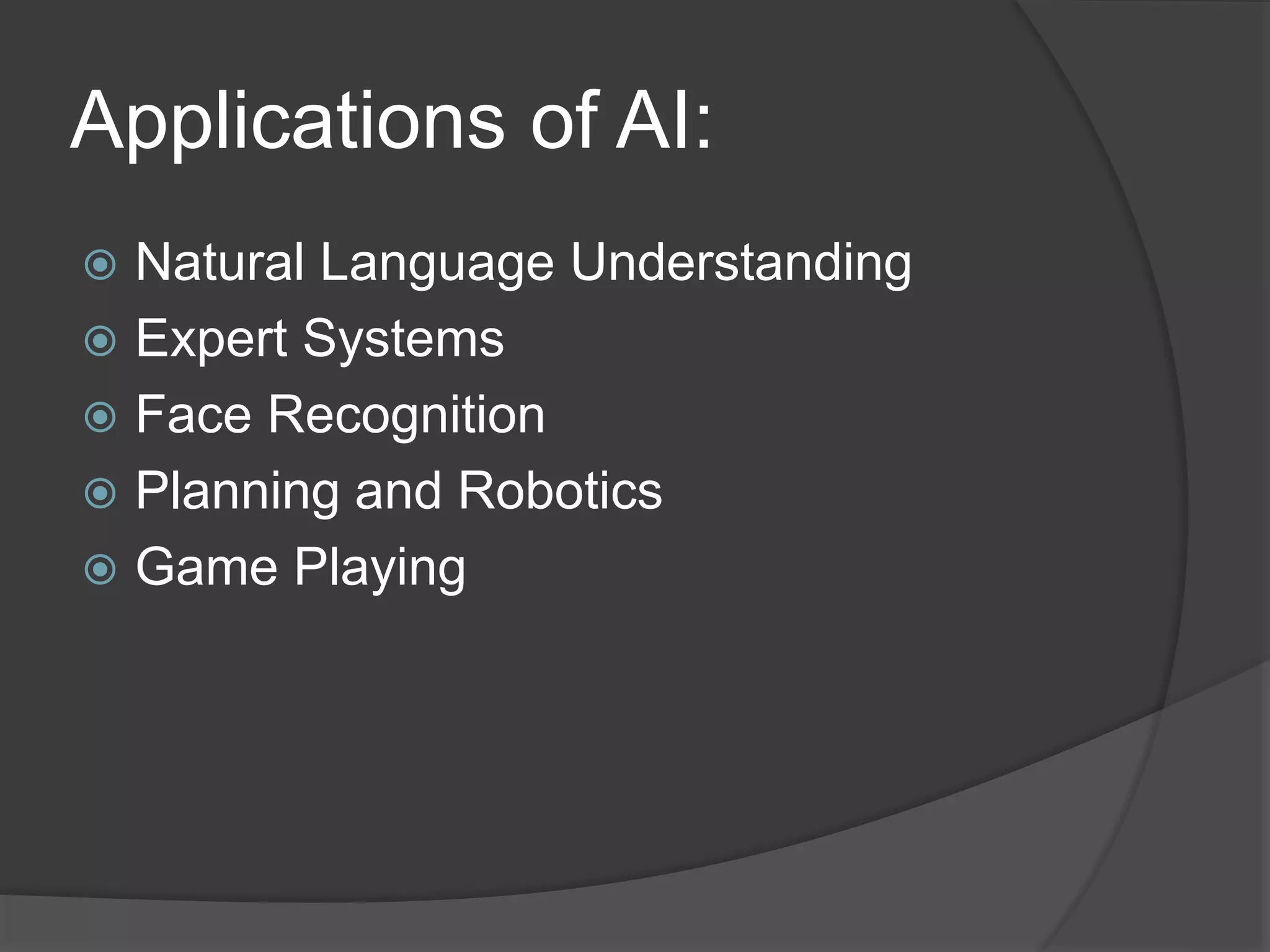
This document discusses different approaches to artificial intelligence including symbolic, sub-symbolic, and statistical approaches. It provides examples of applications of AI such as natural language processing, expert systems, face recognition, robotics, and game playing. While AI is present in many applications like Google and Siri, the document argues that current AI is still far from achieving human-level intelligence.


















![Work Cited
Jesus Suarez. “Intro to Neural Networks." Online video clip.
YouTube. YouTube, 14 Dec. 2009. Web. 14 Nov. 2013. http://youtu.be/DG5-UyRBQD4
GoogleTechTalks. “Google Faculty Summit 2009: Statistical Machine Translation.” Online video clip. Youtube. Youtube, 5 Oct. 2009.
Web. 14 Nov. 2013. http://youtu.be/y_PzPDRPwlA
PBS Idea Channel. “Is Developing Artificial Intelligence (AI) Ethical? | Idea Channel | PBS Digital Studios.” Online video clip. Youtube.
Youtube, 29 May, 2013. Web. 8 Nov. 2013. http://youtu.be/95KhuSbYJGE
PBSoffbook. “The Rise of Artificial Intelligence | Off Book | PBS Digital Studios.” Online video clip. Youtube. Youtube, 11 Jul. 2013. Web.
8 Nov. 2013. http://youtu.be/53K1dMyslJg
Computerphile. “How Intelligent is Artificial Intelligence? – Computerphile.” Online video clip. Youtube. Youtube, 27 Sept. 2013. Web. 8
Nov. 2013. http://youtu.be/hcoa7OMAmRk
Vojteek. “How to steal in Skyrim.” Online video clip. Youtube. Youtube, 10 Nov. 2011. Web. 8 Nov. 2013. http://youtu.be/rt5aUdijAN8
“Strong AI." Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. 21 Oct. 2013. Web. 8 Nov. 2013.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strong_AI
“Artificial Intelligence." Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. 11 Nov. 2013. Web. 8 Nov. 2013.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
“Artificial Intelligence (video games)." Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. 23 Oct. 2013. Web. 8 Nov. 2013.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence_%28video_games%29
“Intelligence." Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. 5 Nov.. 2013. Web. 8 Nov. 2013.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligence
“Artificiality." Wikipedia: The Free Encyclopedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. 9 Oct. 2013. Web. 8 Nov. 2013.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificiality
P.B. Khanale and S.D. Chitnis. “Handwritten Devanagari Character Recognition using Artificial Neural Network." Journal of Artificial
Intelligence, 4,1 (2011): 55-62. Print.
Vardi, Moshe Y. “Artificial Intelligence: Past and Future.“Communications of the ACM, 55,1 (2012): 5. Print.
Barbrook, Richard. “New York Prophecies: The Imaginary Future of Artificial Intelligence.." Science as Culture, 16,2 (2007): 151-167.
Print.
Clark, Liat. Google Brain Simulator Identifies Cats on Youtube. Wired.CO.UK, 26 Jun. 2012. Web. 8 Nov. 2013.
http://www.wired.co.uk/news/archive/2012-06/26/google-brain-recognises-cats
Jeff [Jeff Wofford]. “How Siri Works” Holy Ghost Stories. Holy Ghost Stories, 5 Oct. 2011. Web. 14 Nov. 2013.
http://www.jeffwofford.com/?p=817
GameTrailers. “The Science of Games – Artificial Intelligence.” Online video clip. Gametrailers. Gametrailers, 21 July. 2013. Web. 8 Nov.
2013. http://www.gametrailers.com/videos/fr3sos/science-of-games-artificial-intelligence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-160223182732/75/Artificial-inteligence-21-2048.jpg)