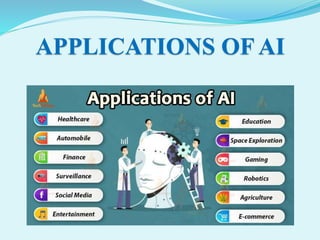
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) including its introduction, evolution, importance and applications. It begins with defining AI as helping machines function in human-like ways, such as recognizing faces and navigating streets. The document then discusses the history and development of AI since 1956. It explains the goals of AI to perform complex tasks like adapting to new situations. Several applications of AI are described including robotics, games, natural language processing, and pattern recognition for vision and sound. The document concludes by discussing the potential benefits and risks of increasingly advanced AI technologies.