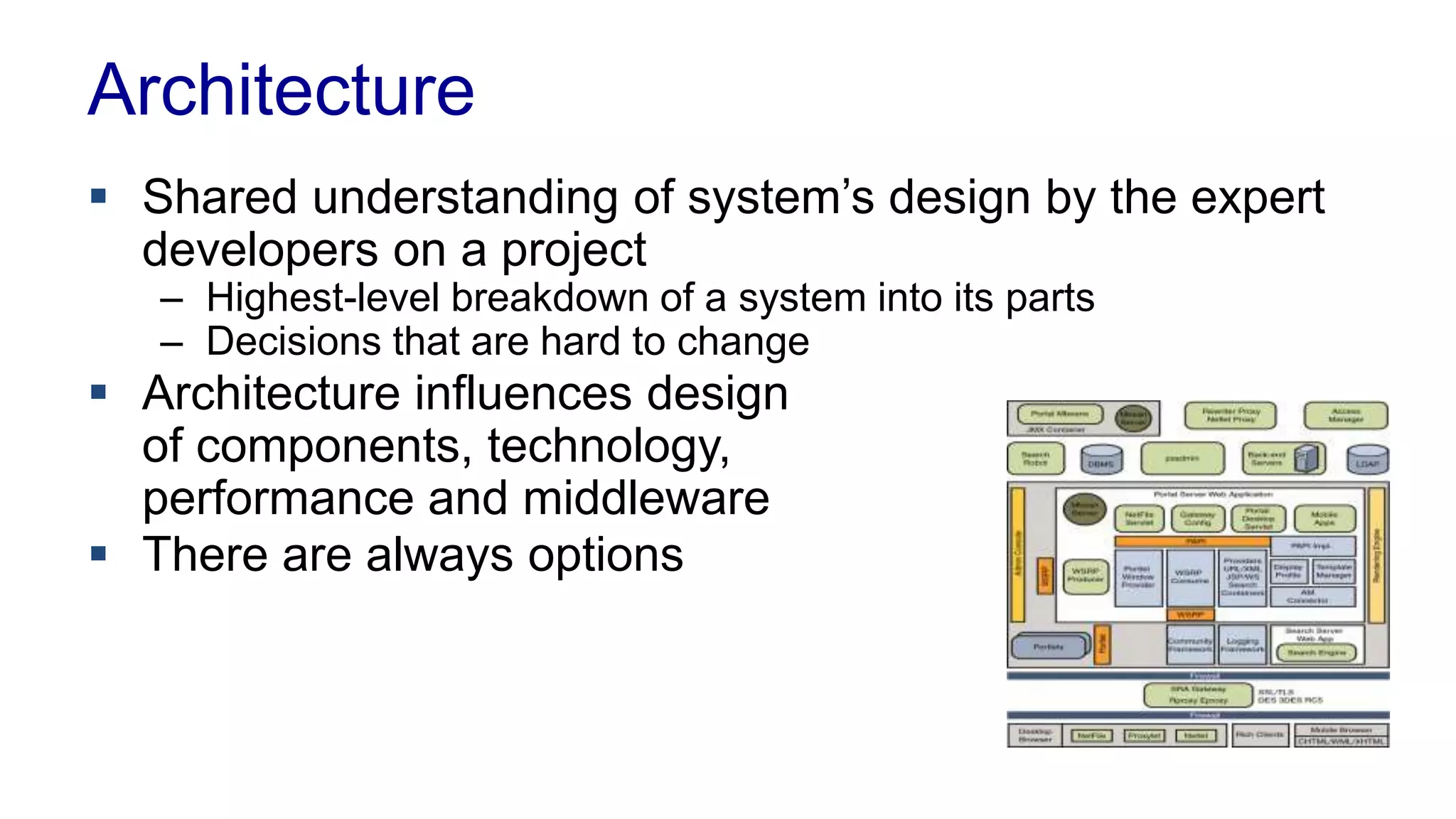
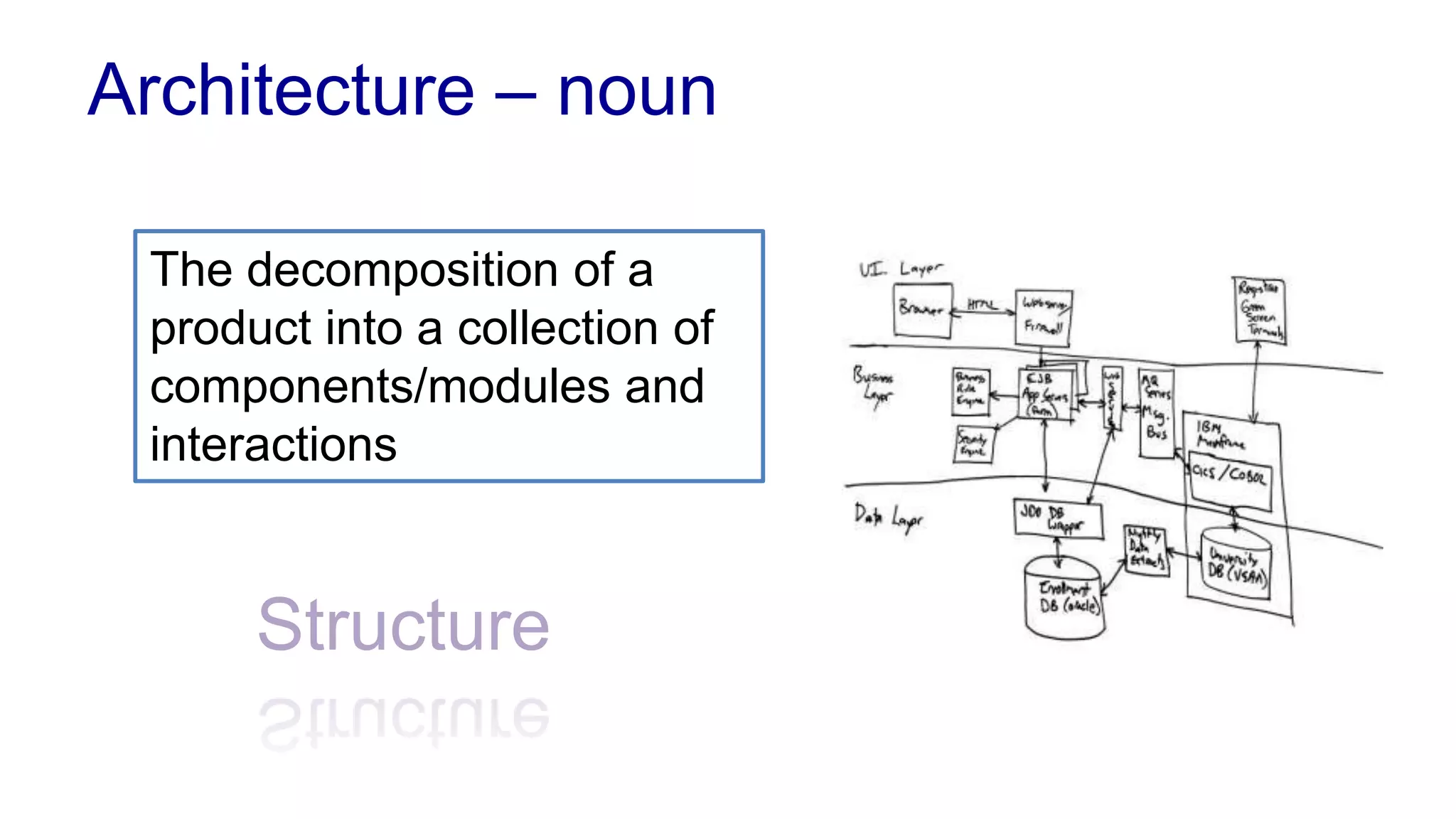
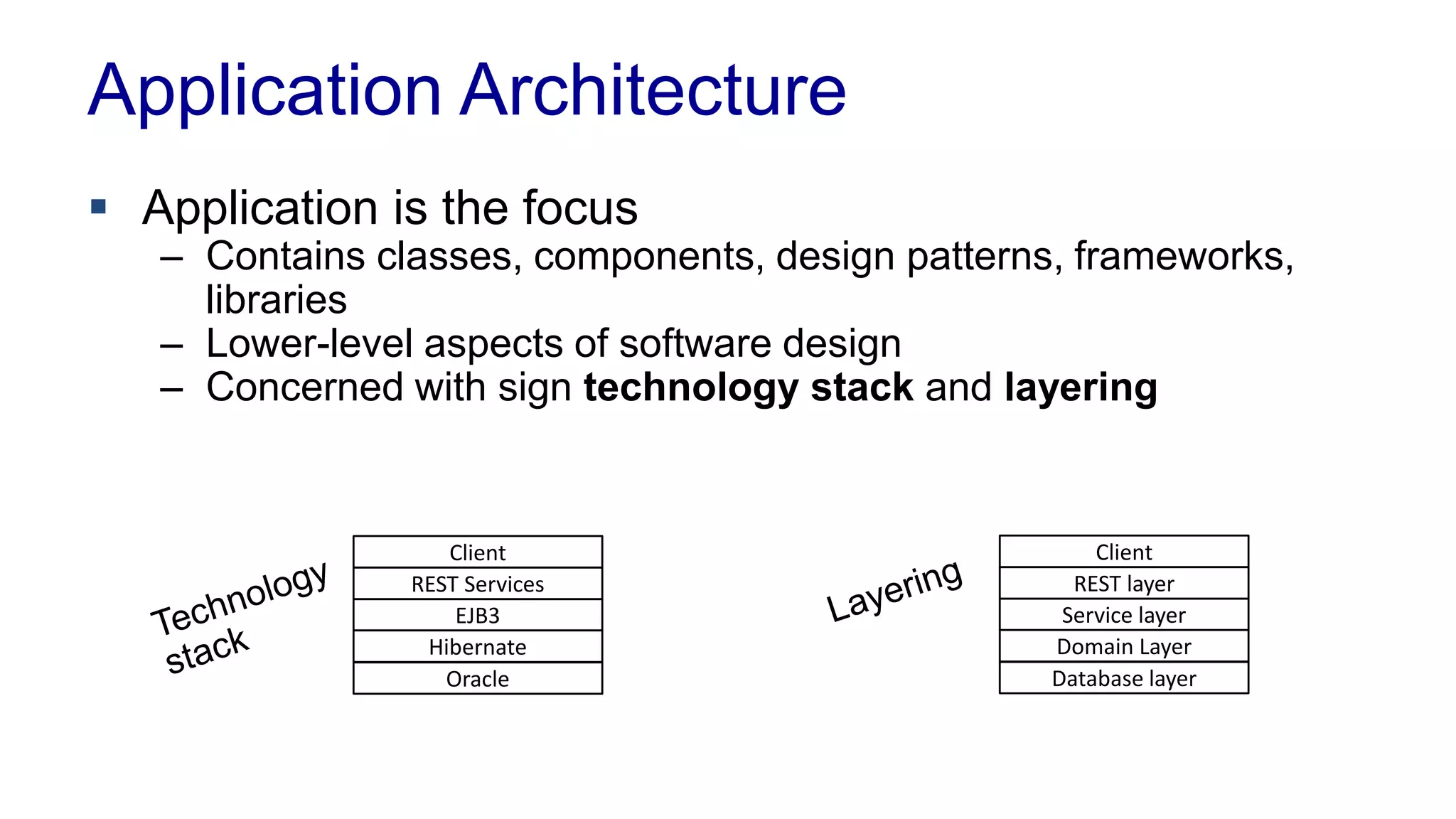
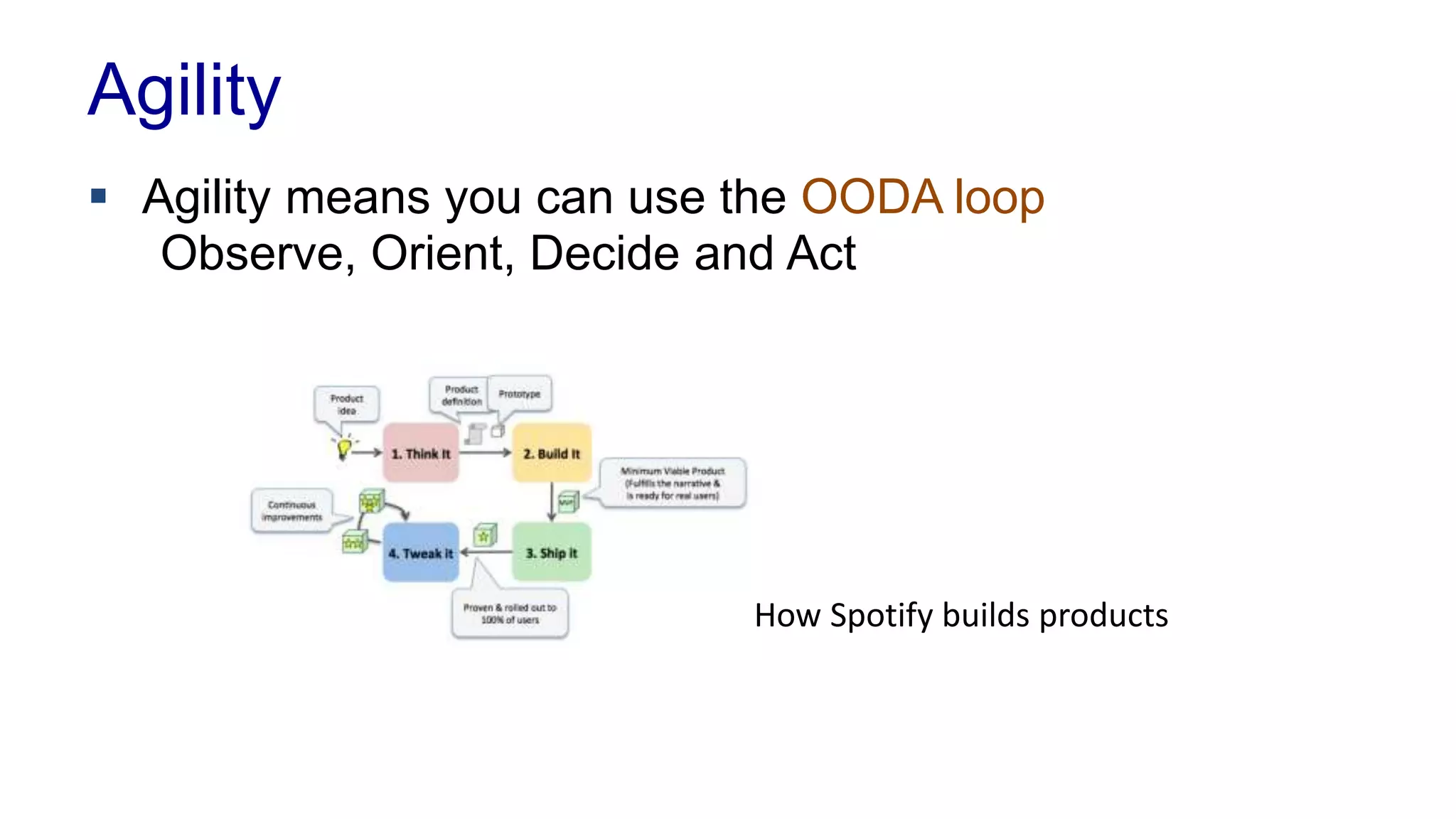
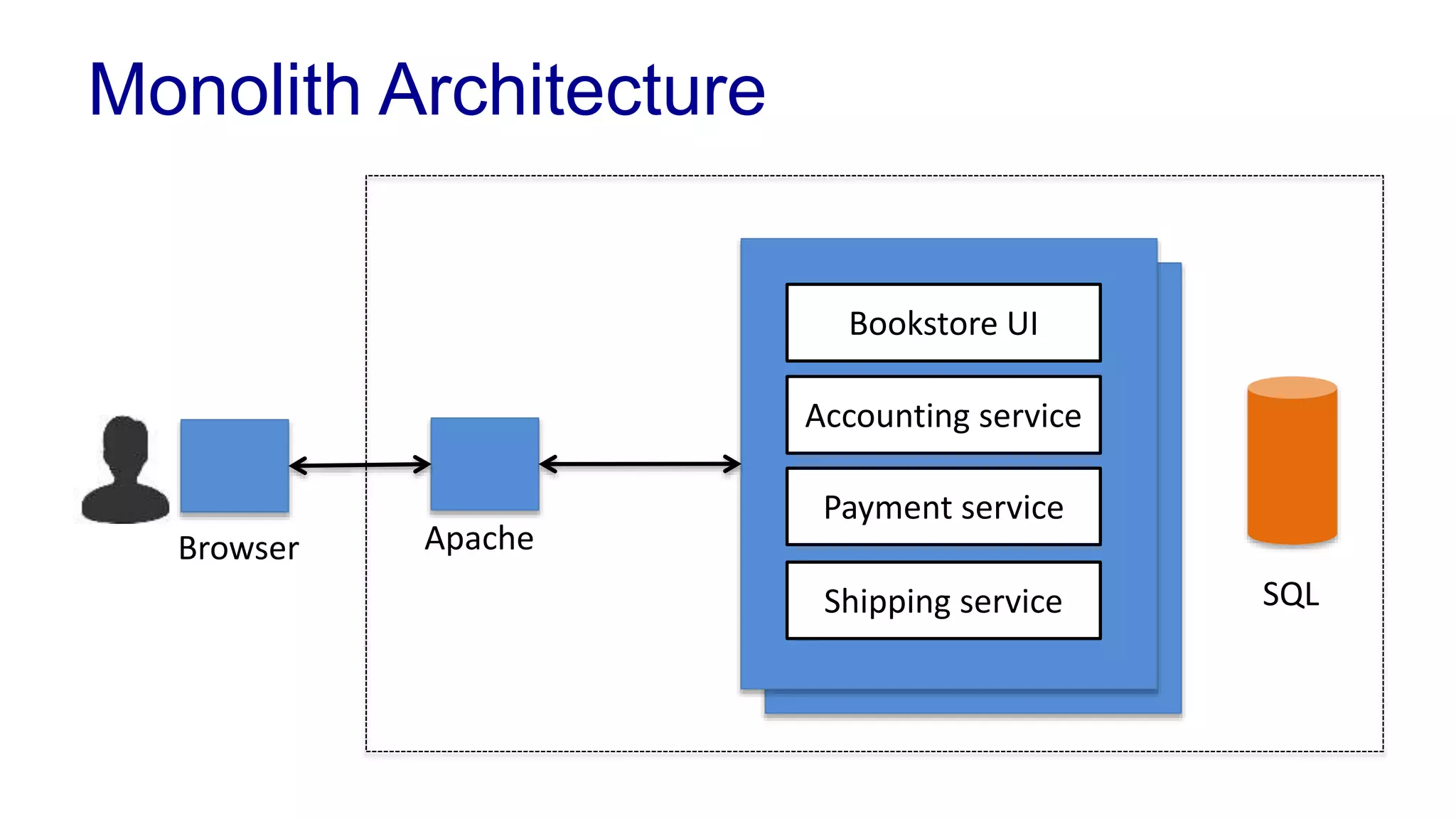
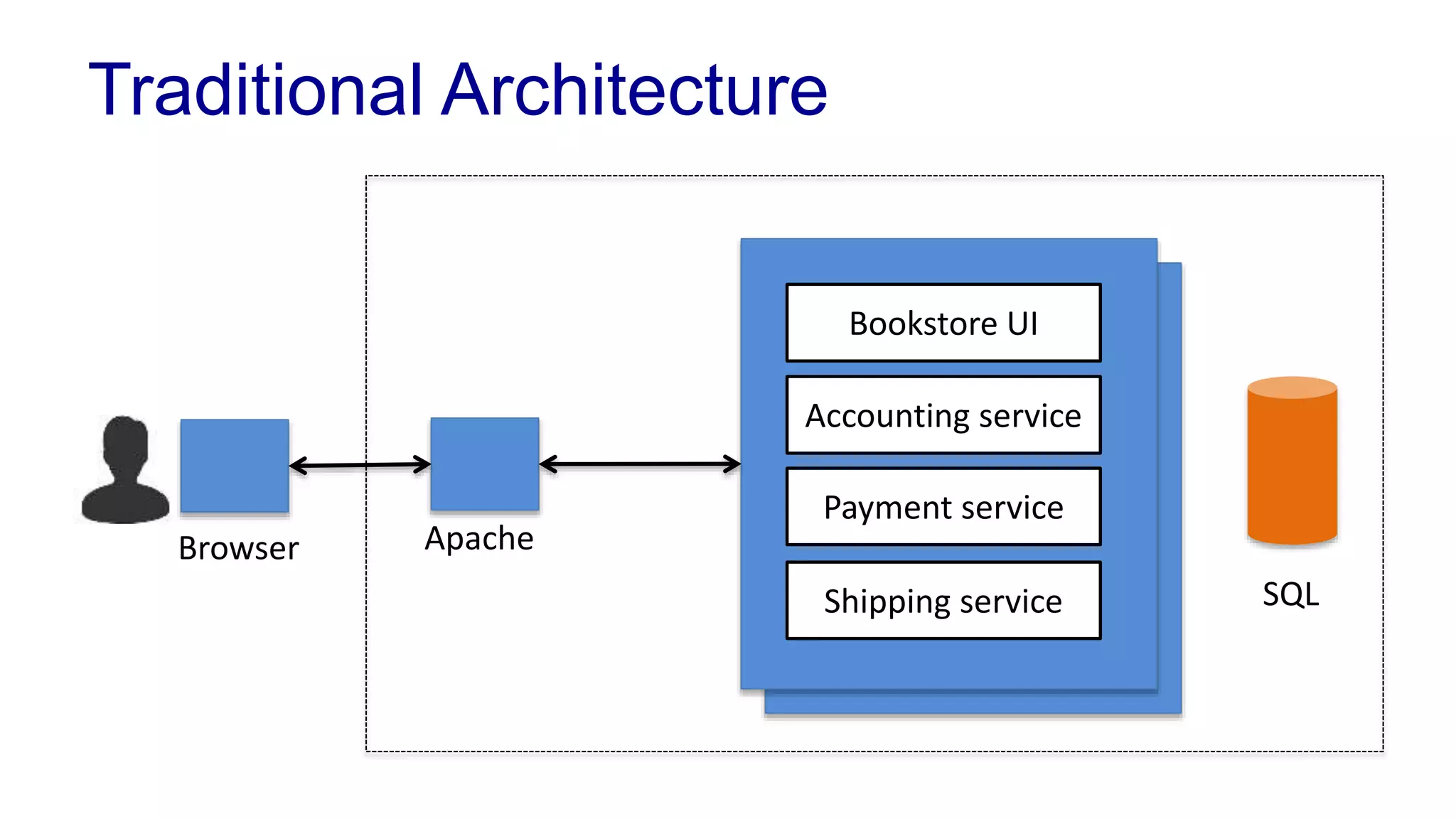
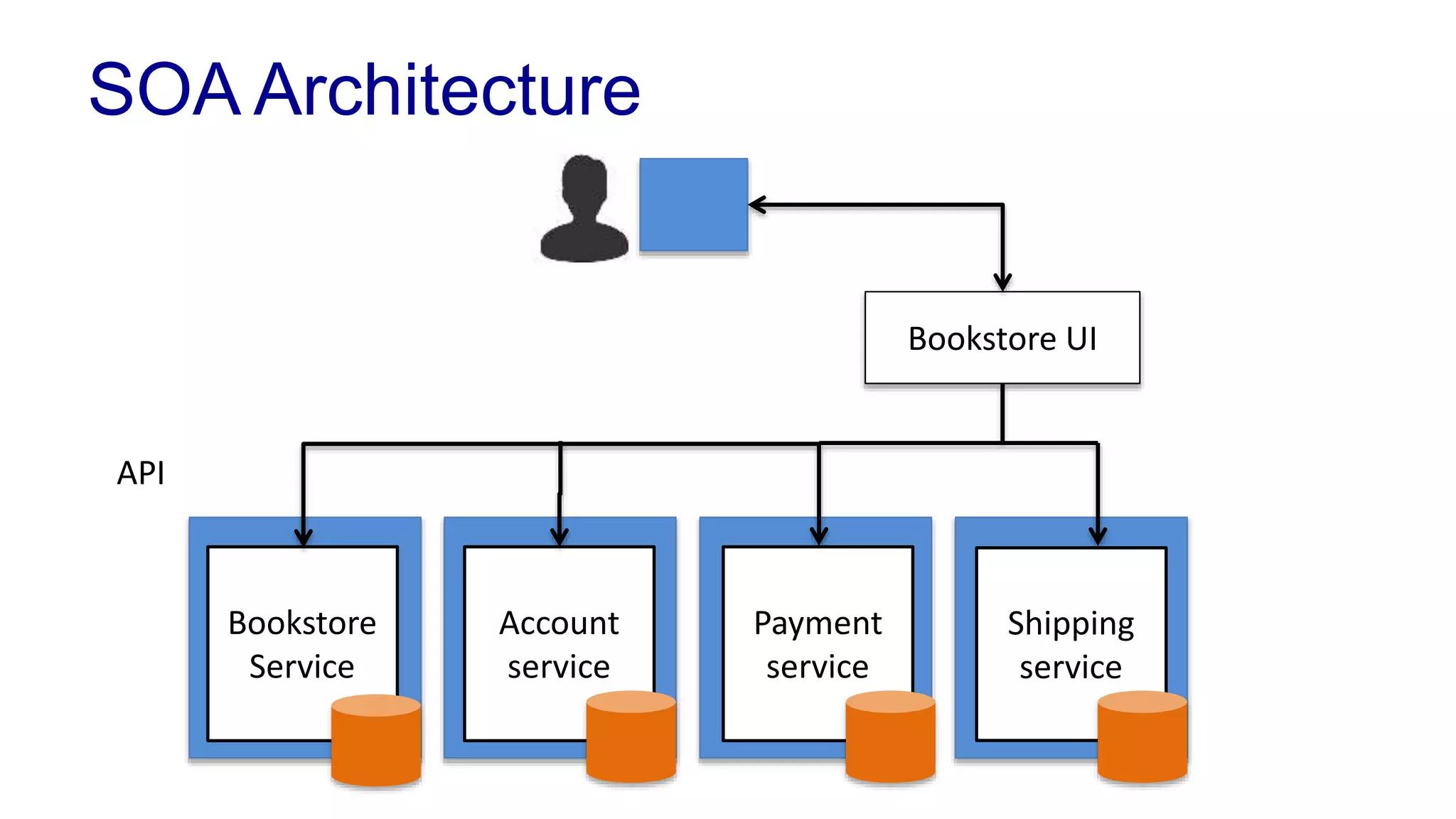
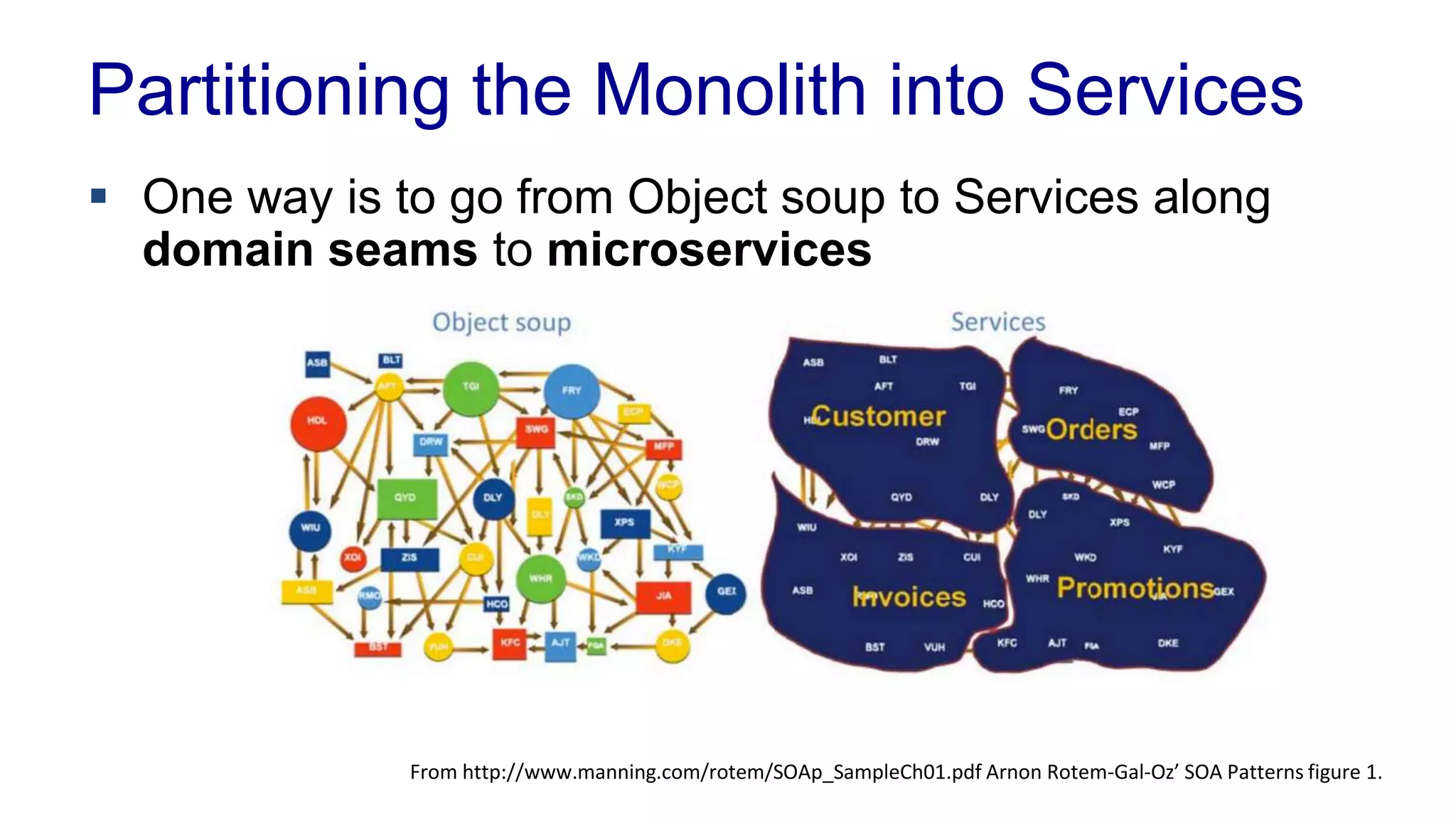
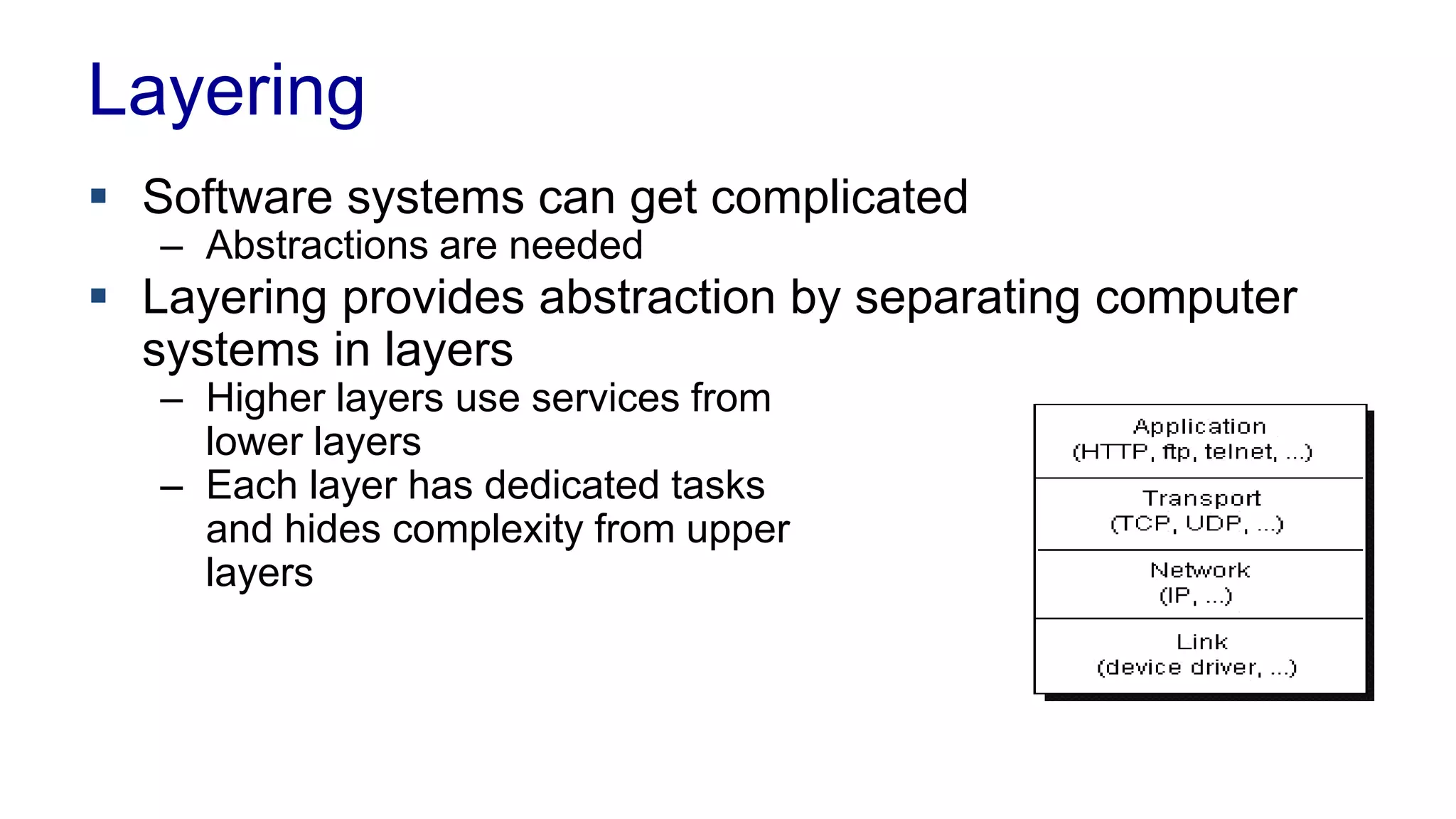
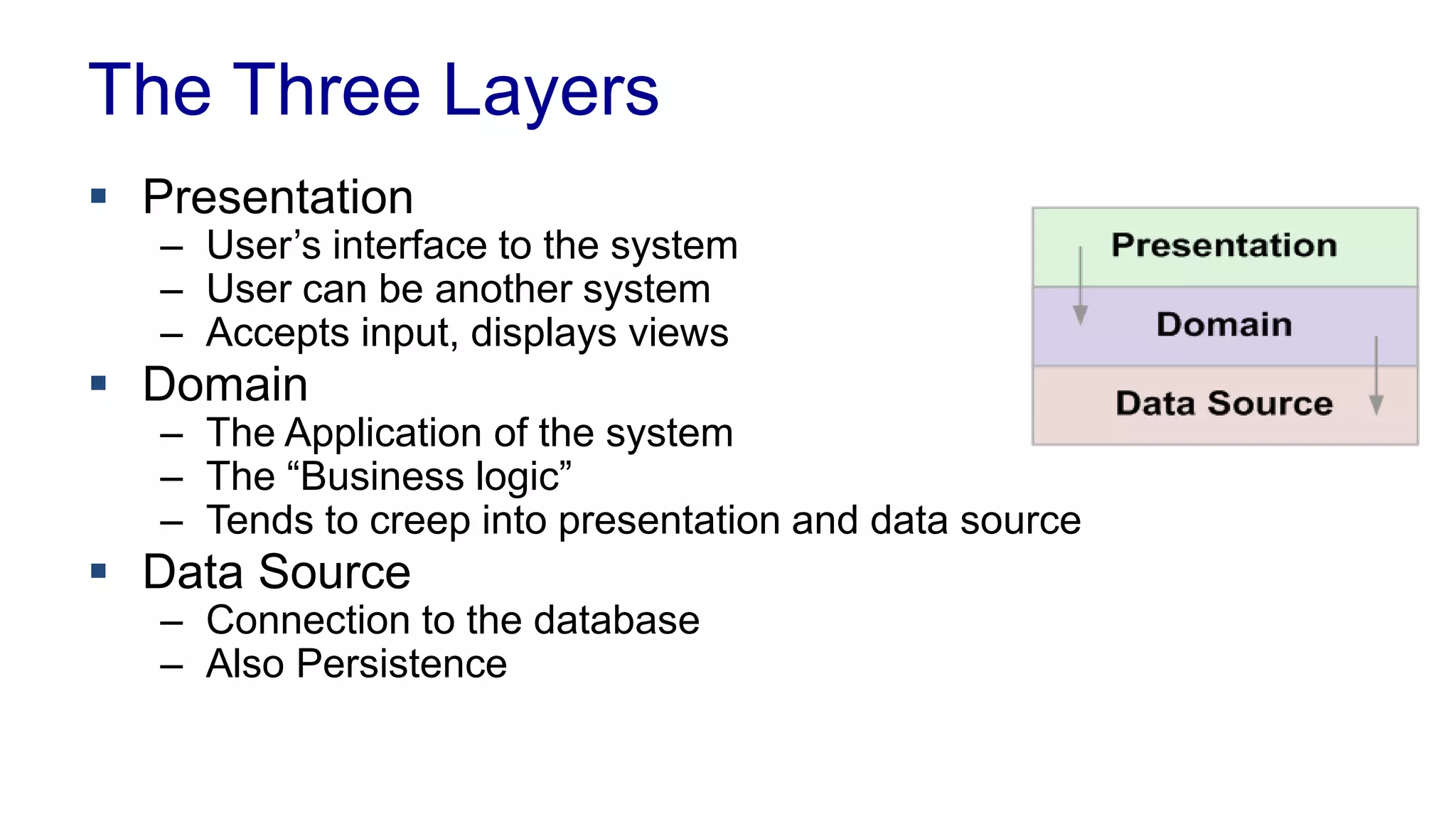
This document covers various architectural concepts in software development, including monolithic and service-oriented architecture, as well as the importance of design patterns and layering. It discusses the challenges and benefits associated with different architectures and emphasizes the need for a shared understanding of design among developers to facilitate scalability and performance. Additionally, the text touches on the evolution towards microservices and agile methodologies, highlighting the need for adaptability in modern software design.