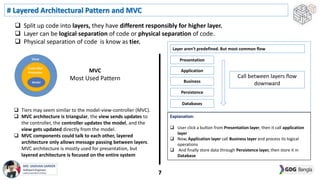
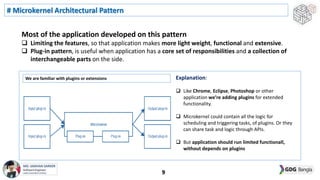
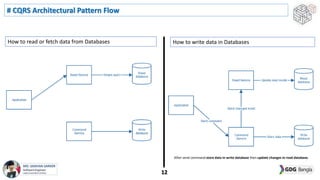
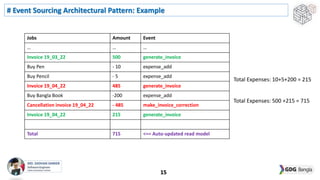
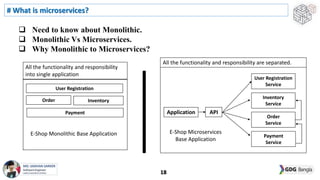
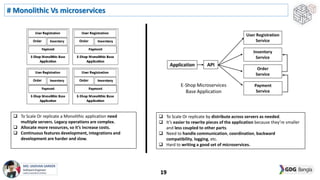
This document discusses software architecture patterns. It begins by defining software architecture patterns as reusable predefined solutions that provide instructions and guidelines. It then explains that software architecture patterns are used to provide solutions to commonly occurring problems by learning from past experiences. The document discusses some essential software architecture patterns like layered architecture, MVC, microkernel architecture, CQRS, event sourcing, and microservices. It provides examples and discusses the pros and cons of each pattern and when each would be most applicable.