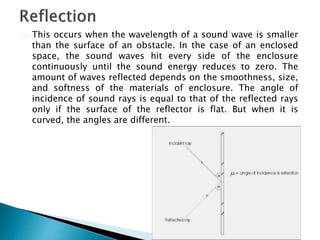
Sound is a disturbance that passes through a medium as longitudinal waves, causing the sensation of hearing. The speed of sound differs depending on the molecular composition of the medium. When sound waves encounter barriers in an enclosed space, they can be reflected, absorbed, refracted, diffused, diffracted, or transmitted. Reflection occurs when the wavelength is smaller than the surface, causing the waves to hit the enclosure continuously until the energy reduces to zero. Absorption occurs when some of the wave's energy is lost through transfer to barrier molecules. Refraction is the bending of sound waves when passing between different media. [END SUMMARY]